Adaptation of water resources management to climate change
Adaptation of water resources management to climate change
Adaptation of water resources management to climate change
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
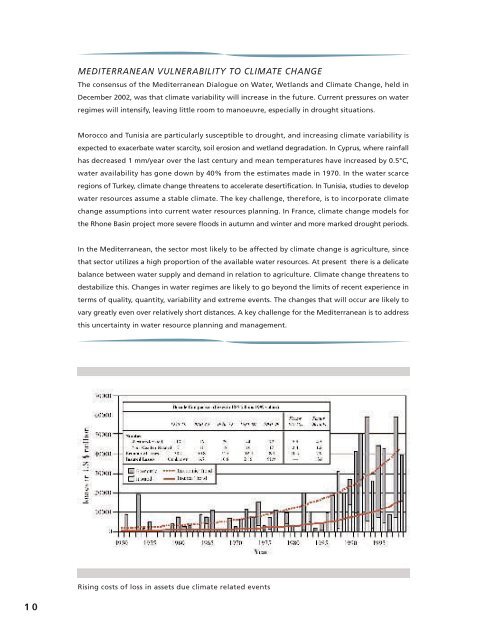
MEDITERRANEAN VULNERABILITY TO CLIMATE CHANGEThe consensus <strong>of</strong> the Mediterranean Dialogue on Water, Wetlands and Climate Change, held inDecember 2002, was that <strong>climate</strong> variability will increase in the future. Current pressures on <strong>water</strong>regimes will intensify, leaving little room <strong>to</strong> manoeuvre, especially in drought situations.Morocco and Tunisia are particularly susceptible <strong>to</strong> drought, and increasing <strong>climate</strong> variability isexpected <strong>to</strong> exacerbate <strong>water</strong> scarcity, soil erosion and wetland degradation. In Cyprus, where rainfallhas decreased 1 mm/year over the last century and mean temperatures have increased by 0.5°C,<strong>water</strong> availability has gone down by 40% from the estimates made in 1970. In the <strong>water</strong> scarceregions <strong>of</strong> Turkey, <strong>climate</strong> <strong>change</strong> threatens <strong>to</strong> accelerate desertification. In Tunisia, studies <strong>to</strong> develop<strong>water</strong> <strong>resources</strong> assume a stable <strong>climate</strong>. The key challenge, therefore, is <strong>to</strong> incorporate <strong>climate</strong><strong>change</strong> assumptions in<strong>to</strong> current <strong>water</strong> <strong>resources</strong> planning. In France, <strong>climate</strong> <strong>change</strong> models forthe Rhone Basin project more severe floods in autumn and winter and more marked drought periods.In the Mediterranean, the sec<strong>to</strong>r most likely <strong>to</strong> be affected by <strong>climate</strong> <strong>change</strong> is agriculture, sincethat sec<strong>to</strong>r utilizes a high proportion <strong>of</strong> the available <strong>water</strong> <strong>resources</strong>. At present there is a delicatebalance between <strong>water</strong> supply and demand in relation <strong>to</strong> agriculture. Climate <strong>change</strong> threatens <strong>to</strong>destabilize this. Changes in <strong>water</strong> regimes are likely <strong>to</strong> go beyond the limits <strong>of</strong> recent experience interms <strong>of</strong> quality, quantity, variability and extreme events. The <strong>change</strong>s that will occur are likely <strong>to</strong>vary greatly even over relatively short distances. A key challenge for the Mediterranean is <strong>to</strong> addressthis uncertainty in <strong>water</strong> resource planning and <strong>management</strong>.Rising costs <strong>of</strong> loss in assets due <strong>climate</strong> related events10










![View full document [PDF 988.55 KB] - PreventionWeb](https://img.yumpu.com/47733942/1/184x260/view-full-document-pdf-98855-kb-preventionweb.jpg?quality=85)
![View full document (in French) [PDF 4.96 MB] - PreventionWeb](https://img.yumpu.com/47223870/1/184x260/view-full-document-in-french-pdf-496-mb-preventionweb.jpg?quality=85)


![View full document [PDF 25.02 MB] - PreventionWeb](https://img.yumpu.com/44204570/1/190x234/view-full-document-pdf-2502-mb-preventionweb.jpg?quality=85)
