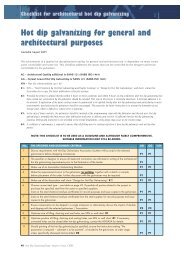
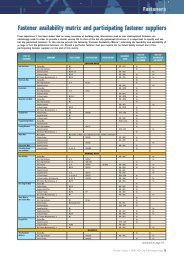
Fasteners - hdgasa
Fasteners - hdgasa
Fasteners - hdgasa
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Fasteners</strong>Typical corrosion evident around the majorityof the stainless steel screws and aluminiumrubber bonded carbon steel washers.State of the corrosive attack on the hot dip galvanized painted lip channel with remains of thealuminium washers and the relatively “unaffected” stainless steel fasteners.stainless steel topspeed roof screw, it willform the anode and corrode in preferenceto the stainless steel, being the cathode.In addition, the aluminium roof sheeting,in contact with the stainless steel screwwill also corrode increasing the size ofthe hole and allowing the roof sheetingto pull past the fixing screw and corrodedwasher. It is for this reason that thestainless steel fasteners have remained,the washers have corroded away and theattachment of the aluminium sheetinghas been compromised. Further evidenceof this process is the resultant corrosionproducts, probably aluminium oxide,evident around all the attachment points.Turning to the question of the corrosiveattack on the hot dip galvanized andpainted “C” type lip channels, we have afailure of the top paint coating. Once the“barrier protection” of the paint coatinghas been compromised the underlyingzinc coating will start corroding forming awhite patina, which has the tendency tospull off the surrounding paint. Furtherevidence of the white patina can befound on the hot dip galvanizedperimeter fencing, where no top paintcoating has been applied. This patina isthe result of the zinc reaction with thechlorides contained in the sea spray, andconsists of zinc chlorides, zinc hydroxidesand zinc oxides. These products ofcorrosion are evidence of the slowlycorroding barrier protection provided bythe hot dip galvanized coating.Examination of these purlin sectionsindicates a lack of adhesion of the paintcoating to that of the hot dip galvanizedsurface. No primer has been employedand the paint coating was found to be fartoo thin, providing minimal additionalcorrosion protective properties. Wherepaint is to be used in conjunction withhot dip galvanizing, surface preparationis of paramount importance, followed bya paint system that is compatible withthat of zinc. This is generally referred toas a Duplex coating system and quality iscontrolled by the use of laid downspecifications. What is evident on thissite does not conform or meet therequirements of a Duplex coating system.The hot dip galvanized purlin sectionswill provide corrosion protection to thecarbon steel structural elements, but willremain aesthetically unacceptable.ConclusionThe corrosion evidence found on the roofand the supporting structure is the resultof differential metals being used in thedesign. In addition, an inadequate paintspecification and/or application of thehot dip galvanized lip channels havebeen employed.RecommendationsRectification will require two areas ofattention.ELECTRO-POSITIVEELECTRO-NEGATIVEGoldSilverStainless SteelNickelAluminum BronzeCopperBrassTinLeadCast Iron Low alloyedSteel Low alloyedCarbon SteelCadmiumAluminiumZincMagnesiumMore nobleLess nobleSelected number of metals from the Galvanic Series (not all).Corrosion products evident around every fastening location.8 Hot Dip Galvanizing Today Volume 8 Issue 1 2011