Learning Objectives - McMaster Pediatrics Residency Program
Learning Objectives - McMaster Pediatrics Residency Program
Learning Objectives - McMaster Pediatrics Residency Program
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
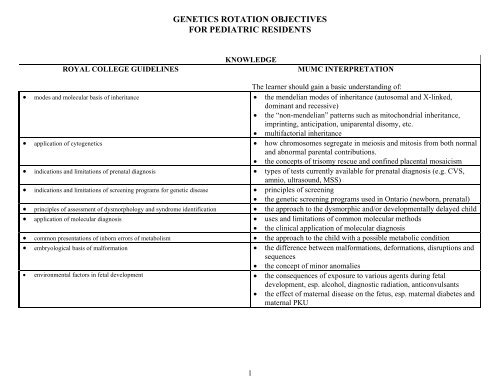
GENETICS ROTATION OBJECTIVESFOR PEDIATRIC RESIDENTSKNOWLEDGEROYAL COLLEGE GUIDELINES MUMC INTERPRETATIONThe learner should gain a basic understanding of:• modes and molecular basis of inheritance • the mendelian modes of inheritance (autosomal and X-linked,dominant and recessive)• the “non-mendelian” patterns such as mitochondrial inheritance,imprinting, anticipation, uniparental disomy, etc.• multifactorial inheritance• application of cytogenetics • how chromosomes segregate in meiosis and mitosis from both normaland abnormal parental contributions.• the concepts of trisomy rescue and confined placental mosaicism• indications and limitations of prenatal diagnosis • types of tests currently available for prenatal diagnosis (e.g. CVS,amnio, ultrasound, MSS)• indications and limitations of screening programs for genetic disease • principles of screening• the genetic screening programs used in Ontario (newborn, prenatal)• principles of assessment of dysmorphology and syndrome identification • the approach to the dysmorphic and/or developmentally delayed child• application of molecular diagnosis • uses and limitations of common molecular methods• the clinical application of molecular diagnosis• common presentations of inborn errors of metabolism • the approach to the child with a possible metabolic condition• embryological basis of malformation • the difference between malformations, deformations, disruptions andsequences• the concept of minor anomalies• environmental factors in fetal development • the consequences of exposure to various agents during fetaldevelopment, esp. alcohol, diagnostic radiation, anticonvulsants• the effect of maternal disease on the fetus, esp. maternal diabetes andmaternal PKU1
SKILLSROYAL COLLEGE GUIDELINES MUMC INTERPRETATIONThe learner should be able to:construction and interpretation of a pedigree • elicit an appropriate genetic family history using standardisednotation, with an awareness of time constraints• elicit a pertinent pregnancy, developmental, medical and socialhistory• apply the family history information to the clinical situation (e.g.interpretation, risk assessment and calculation)ability to provide genetic counselling to a family / individual with aknown genetic or inherited disorder, or referral to appropriate source• convey genetic, medical and technical information in a clear way tofamilies• appreciate the psychosocial impact of genetic conditions on families• outline the principles of genetic counselling pertinent to a given case• understand the issues surrounding genetic testing of adolescents andchildren• access genetics resource materials and understand their use in clinicalsituations• access lay materials written for patients, as well as support groupinformationClinical assessment and judgment • recognize a dysmorphic child and appreciate how minor congenitalanomalies contribute to the whole picture• differentiate between malformations, deformations, disruptions, andsequencesInvestigations • assess which type of testing is appropriate to order in theinvestigation of genetics patients (e.g. metabolic, chromosome orDNA tests)• assess which type of prenatal testing could be offered in a particularclinical situation••• comprehend basic cytogenetic and molecular lab reports2
PROBLEMSROYAL COLLEGE GUIDELINES MUMC INTERPRETATION• the dysmorphic child• exposure to a possible teratogen• approaches to and initial investigations of suspected inherited metabolic diseases• common genetic syndromes (e.g. Down syndrome, Turner syndrome, Fragile-XThe following opportunities will be provided in order to assist the learnerin obtaining the desired knowledge and skills:The resident will be exposed to multiple pediatric genetic diagnosticsituations and will encounter patients will both rare and common geneticconditions. These encounters will be under the supervision of the clinicalor metabolic geneticist and will include both inpatients and outpatientsEach resident will be exposed to a counselling session for at least onecase of each of the following types of inheritance if possible:• autosomal recessive• autosomal dominant• X-linked recessive• multifactorial• cytogenetic• DNA-based diagnostics• predictive testing• mitochondrialMost of these encounters will be under the supervision of one of the 4genetic counsellors.We have developed a package of reading materials which will assist thelearner in attaining his/her knowledge objectives and this will be givenout at the start of the rotation.Updated July 20113