Groundwater Use in Earthquake Emergency: A Case Study ... - IWRA
Groundwater Use in Earthquake Emergency: A Case Study ... - IWRA
Groundwater Use in Earthquake Emergency: A Case Study ... - IWRA
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
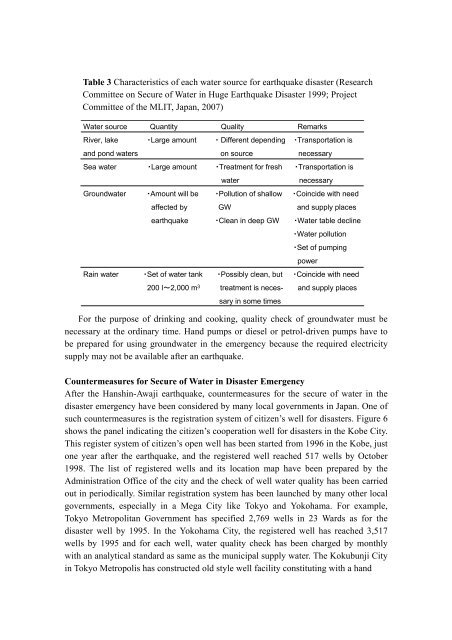
Table 3 Characteristics of each water source for earthquake disaster (ResearchCommittee on Secure of Water <strong>in</strong> Huge <strong>Earthquake</strong> Disaster 1999; ProjectCommittee of the MLIT, Japan, 2007)Water source Quantity Quality RemarksRiver, lake ・Large amount ・ Different depend<strong>in</strong>g ・Transportation isand pond waters on source necessarySea water ・Large amount ・Treatment for fresh ・Transportation iswaternecessary<strong>Groundwater</strong> ・Amount will be ・Pollution of shallow ・Co<strong>in</strong>cide with needaffected by GW and supply placesearthquake ・Clean <strong>in</strong> deep GW ・Water table decl<strong>in</strong>e・Water pollution・Set of pump<strong>in</strong>gpowerRa<strong>in</strong> water ・Set of water tank ・Possibly clean, but ・Co<strong>in</strong>cide with need200 l~2,000 m 3 treatment is neces- and supply placessary <strong>in</strong> some timesFor the purpose of dr<strong>in</strong>k<strong>in</strong>g and cook<strong>in</strong>g, quality check of groundwater must benecessary at the ord<strong>in</strong>ary time. Hand pumps or diesel or petrol-driven pumps have tobe prepared for us<strong>in</strong>g groundwater <strong>in</strong> the emergency because the required electricitysupply may not be available after an earthquake.Countermeasures for Secure of Water <strong>in</strong> Disaster <strong>Emergency</strong>After the Hansh<strong>in</strong>-Awaji earthquake, countermeasures for the secure of water <strong>in</strong> thedisaster emergency have been considered by many local governments <strong>in</strong> Japan. One ofsuch countermeasures is the registration system of citizen’s well for disasters. Figure 6shows the panel <strong>in</strong>dicat<strong>in</strong>g the citizen’s cooperation well for disasters <strong>in</strong> the Kobe City.This register system of citizen’s open well has been started from 1996 <strong>in</strong> the Kobe, justone year after the earthquake, and the registered well reached 517 wells by October1998. The list of registered wells and its location map have been prepared by theAdm<strong>in</strong>istration Office of the city and the check of well water quality has been carriedout <strong>in</strong> periodically. Similar registration system has been launched by many other localgovernments, especially <strong>in</strong> a Mega City like Tokyo and Yokohama. For example,Tokyo Metropolitan Government has specified 2,769 wells <strong>in</strong> 23 Wards as for thedisaster well by 1995. In the Yokohama City, the registered well has reached 3,517wells by 1995 and for each well, water quality check has been charged by monthlywith an analytical standard as same as the municipal supply water. The Kokubunji City<strong>in</strong> Tokyo Metropolis has constructed old style well facility constitut<strong>in</strong>g with a hand