100 Underwriting Management - The Malaysian Insurance Institute
100 Underwriting Management - The Malaysian Insurance Institute
100 Underwriting Management - The Malaysian Insurance Institute
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
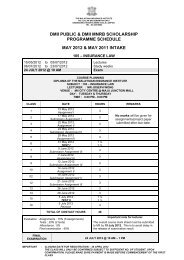
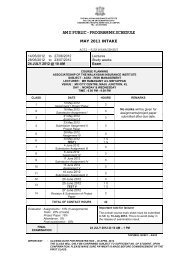
<strong>The</strong> <strong>Malaysian</strong> <strong>Insurance</strong> <strong>Institute</strong>(35445-H)<strong>100</strong> <strong>Underwriting</strong> <strong>Management</strong>Objectives:To provide an understanding of and the ability to apply the requirements for managing a general insuranceunderwriting account through selection of class of business and design of products; Setting the underwriting policyfor those products; establishing the price; management of exposures; the implementation of operational controls;budgeting and monitoring results.Learning Outcomes:At the end of the course, student should be able to:1. Understand the fundamentals of underwriting in insurance.2. Explain the development of risk premium.3. Apply statistical modeling techniques in underwriting.4. Discuss how quoted premium is developed.5. Discuss the underwriting operations in insurance companies.6. Explain the importance of budgeting and monitoring in underwriting performance.Notes:<strong>The</strong> syllabus will be based on <strong>Malaysian</strong> law & practice. Reference is made to UK law & practice where applicable.Syllabus:1. SELECTION OF CLASS OF BUSINESS AND DESIGN OF PRODUCTS1.1 Impact of corporate objectives on business selection, financial targets and ethical stance.1.2 Resource capability with respect to expertise, systems and capital.1.3 Importance of entry and exit costs.1.4 Other factors influencing the selection of classes of business and types of cover to be provided.1.5 Solvency and capital base,1.6 Voluntary and statutory constrains on underwriting practice in Malaysia.1.7 Authorization by Central Bank of Malaysia1.8 Requirements associated with compulsory covers.1.9 Contribution of market research to determining:• Target customers;• Cover to be provided;• Demand for a product;• Competitive positioning.1.10 Characteristics and operation of various distribution channels including bancassurance practices in Malaysia.1.11 Implications of market structure and competitiveness for entry to the international market.1.12 Authorization of international business. Special requirements of global insurance programmes.
1.13 Availability and cost of reinsurance.1.14 Relationship between reinsurance equalization reserves and capital requirements.2. SETTING THE UNDERWRITING POLICY FOR THOSE PRODUCTS2.1 Establishment of criteria for:• policy terms;• use of excesses, deductibles, loadings and incentives (eg. long-term agreement no-claim discount profitcommission);• first loss;• scheme underwriting;2.2 Internal and external constrains on:• what is covered;• limits to cover;• market position;• new business growth.2.3 Liaison with the claims management function.2.4 Establishment and significant of:• classification and categorization of risk;• acceptance and renewal underwriting criteria;• risk improvement and survey criteria.2.5 Identifying exposure to single risks and single events.2.6 Effect of prevailing market conditions.2.7 Significance of EML to setting underwriting policy.2.8 Use of binding authorities and line slips.3. ESTABLISHING THE PRICE3.1 Rating• Sources, availability and types of data essential to the underwriting process.• Interpretation of the results of statistical modeling.• Treatment of reinsurance costs.• Burning cost and the treatment of large claims and their effect on individual rating.• Principles and use of retrospective rating.• Predicting the effect of changes in law, and changes in economic, political and environmental conditions.3.2 Statistical methods• Interpretation and significance of claims information.• Homogeneity, claim frequency and the nature of risk.• Suitability and use of statistics and statistical modeling.• Distinction between underwriting year, policy year, accounting year and calendar year.3.3 Pricing factors• Risk premium;• Expenses, return on capital, investment income, tax and intermediary remuneration;• Competitor analysis.
4. MANAGEMENT OF EXPOSURES4.1 Measuring exposure to single risks and single events.4.2 Significance of seasonal and cyclical influence and establishing maxima for assessing exposure.4.3 Aggregation of exposures from single risks or single events.4.4 Aggregation of losses in any one year.4.5 Financial stability, stabilisation of claims ratio/or profit balance between classes of business and the desirability ofspreading risk with reference to:• use of layered covers and deductibles;• gross and net acceptance limits;• reinsurance.5. IMPLEMENTATION OF OPERATIONAL CONTROLS5.1 Constraints on authorities and authority levels, including Chief Executive sign-off.5.2 Auditing underwriting policy.5.3 Methods of dealing with back-logs.5.4 Information technology and is application to account management.6. BUDGETING AND MONITORING RESULTS6.1 Fluctuations in claims costs.6.2 Effect on premium of changes in rating and exposures.6.3 Reasons for monitoring and what is to be monitored.6.4 Techniques for monitoring underwriting results.6.5 Use of information derived from monitoring.6.6 Allowance for:• pipeline premiums;• IBNR claims.Primary Texts1. Coursebook 815 : <strong>Underwriting</strong> <strong>Management</strong>. London <strong>The</strong> CII.2. Pre-Contract Examination for <strong>Insurance</strong> Agents - MIIPeriodicals1. <strong>Insurance</strong> Annual Report, Bank Negara Malaysia2. Asia <strong>Insurance</strong> Review.3. <strong>The</strong> Journal, <strong>The</strong> CII.4. Post Magazine.5. <strong>The</strong> Edge Daily.6. BNM Annual Report.7. BNM Takaful Annual Report.