chapter v cropping pattern, crop diversification and value addition
chapter v cropping pattern, crop diversification and value addition
chapter v cropping pattern, crop diversification and value addition
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
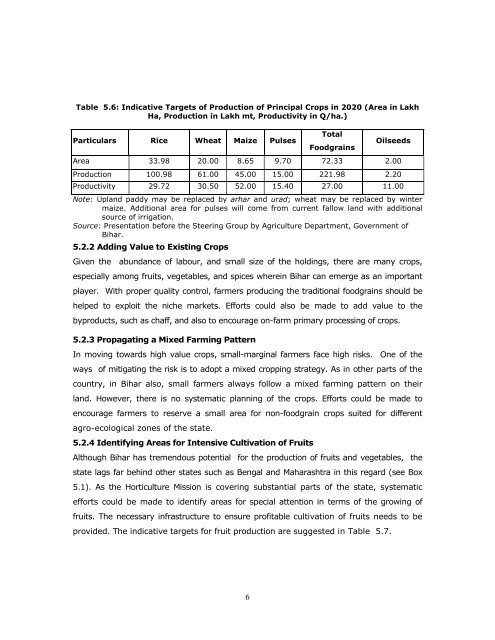
Table 5.6: Indicative Targets of Production of Principal Crops in 2020 (Area in LakhHa, Production in Lakh mt, Productivity in Q/ha.)Particulars Rice Wheat Maize PulsesTotalFoodgrainsOilseedsArea 33.98 20.00 8.65 9.70 72.33 2.00Production 100.98 61.00 45.00 15.00 221.98 2.20Productivity 29.72 30.50 52.00 15.40 27.00 11.00Note: Upl<strong>and</strong> paddy may be replaced by arhar <strong>and</strong> urad; wheat may be replaced by wintermaize. Additional area for pulses will come from current fallow l<strong>and</strong> with <strong>addition</strong>alsource of irrigation.Source: Presentation before the Steering Group by Agriculture Department, Government ofBihar.5.2.2 Adding Value to Existing CropsGiven the abundance of labour, <strong>and</strong> small size of the holdings, there are many <strong>crop</strong>s,especially among fruits, vegetables, <strong>and</strong> spices wherein Bihar can emerge as an importantplayer. With proper quality control, farmers producing the traditional foodgrains should behelped to exploit the niche markets. Efforts could also be made to add <strong>value</strong> to thebyproducts, such as chaff, <strong>and</strong> also to encourage on-farm primary processing of <strong>crop</strong>s.5.2.3 Propagating a Mixed Farming PatternIn moving towards high <strong>value</strong> <strong>crop</strong>s, small-marginal farmers face high risks. One of theways of mitigating the risk is to adopt a mixed <strong><strong>crop</strong>ping</strong> strategy. As in other parts of thecountry, in Bihar also, small farmers always follow a mixed farming <strong>pattern</strong> on theirl<strong>and</strong>. However, there is no systematic planning of the <strong>crop</strong>s. Efforts could be made toencourage farmers to reserve a small area for non-foodgrain <strong>crop</strong>s suited for differentagro-ecological zones of the state.5.2.4 Identifying Areas for Intensive Cultivation of FruitsAlthough Bihar has tremendous potential for the production of fruits <strong>and</strong> vegetables, thestate lags far behind other states such as Bengal <strong>and</strong> Maharashtra in this regard (see Box5.1). As the Horticulture Mission is covering substantial parts of the state, systematicefforts could be made to identify areas for special attention in terms of the growing offruits. The necessary infrastructure to ensure profitable cultivation of fruits needs to beprovided. The indicative targets for fruit production are suggested in Table 5.7.6