Removal of pharmaceuticals during river bank filtration - LEESU
Removal of pharmaceuticals during river bank filtration - LEESU
Removal of pharmaceuticals during river bank filtration - LEESU
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
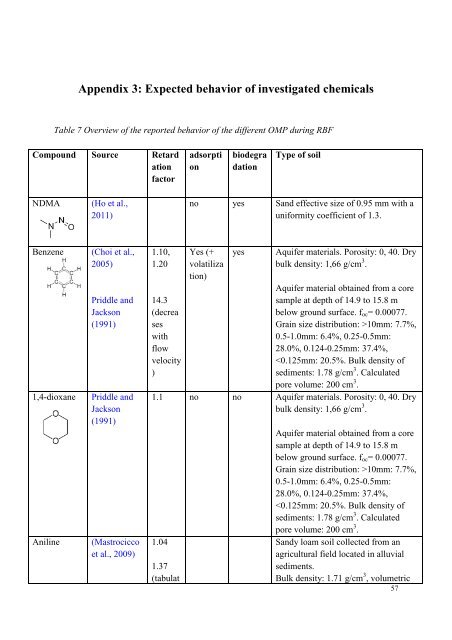
Appendix 3: Expected behavior <strong>of</strong> investigated chemicalsTable 7 Overview <strong>of</strong> the reported behavior <strong>of</strong> the different OMP <strong>during</strong> RBFCompound Source RetardationfactoradsorptionbiodegradationType <strong>of</strong> soilNDMA(Ho et al.,2011)no yes Sand effective size <strong>of</strong> 0.95 mm with auniformity coefficient <strong>of</strong> 1.3.Benzene1,4-dioxaneAniline(Choi et al.,2005)Priddle andJackson(1991)Priddle andJackson(1991)(Mastrociccoet al., 2009)1.10,1.2014.3(decreaseswithflowvelocity)Yes (+volatilization)yesAquifer materials. Porosity: 0, 40. Drybulk density: 1,66 g/cm 3 .Aquifer material obtained from a coresample at depth <strong>of</strong> 14.9 to 15.8 mbelow ground surface. f oc = 0.00077.Grain size distribution: >10mm: 7.7%,0.5-1.0mm: 6.4%, 0.25-0.5mm:28.0%, 0.124-0.25mm: 37.4%,10mm: 7.7%,0.5-1.0mm: 6.4%, 0.25-0.5mm:28.0%, 0.124-0.25mm: 37.4%,



![[pastel-00730831, v1] Incidence des pratiques d'entretien ... - LEESU](https://img.yumpu.com/50938896/1/184x260/pastel-00730831-v1-incidence-des-pratiques-dentretien-leesu.jpg?quality=85)











