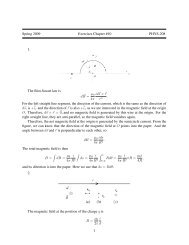
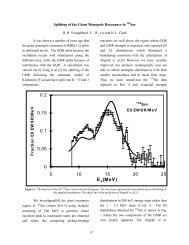
Prolate-oblate oscillation between the ground states of even-even ...
Prolate-oblate oscillation between the ground states of even-even ...
Prolate-oblate oscillation between the ground states of even-even ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Groud state deformationsThe e-e SHEs form three regions:1) a prolate-deformed (for N < 172),2) spherical (N>180),3) <strong>the</strong> transitional region (<strong>between</strong> <strong>the</strong> former two).
Geometric sizes
sphericalGeometric collective model (GCM) - A. Bohr (1952)V(,) = A 2 + B 3 cos 3 + C 4 ,(C>0)B0A = A 1 = 0: spinodal point<strong>oblate</strong>(=/3)critical-s<strong>of</strong>tprolateA 1spinodal0(=0)phase coexistanceA 2A = A c = B 2 /(4C): critical pointVA0 A c( = /3) ( = 0)A = A 2 = 9B 2 /(32C): antisinodal pointA = A c (B 0) and A < 0 (B = 0): first-order phase transition linesA = B = 0: second-order phase transition point (triple-point)
Interacting boson approximation (IBA-1) – Arima, IachelloU (6) U (5) O(5) O(3) O(2)U (6) SU (3) O(3) O(2)U (6) SU (3) O(3) O(2)U (6) O(6) O(5) O(3) O(2)U (6) O(6) O(5) O(3) O(2)Dynamical symmetries:U (5)SU (3), SU (3)O(6), O(3)(vibrational)(rotational)(-s<strong>of</strong>t)Critical-point solutions:2 3 4V ( , ) A B cos3 CV ( , ) V ( ) V( )1 2X (5) V V V c c 0)2:1 well( ),2( o) , (E(5 ) : V V ( ),V 01 well2(Fig. Casten)
sphericalExtended triangle <strong>of</strong> IBA-1 – Casten060 ospherevibrator0 oU(5)060 ocriticalX(5)0 o<strong>oblate</strong>SU(3)O(6)060 o-s<strong>of</strong>t00 o60 orotor<strong>oblate</strong>0 oprolate0X(5)60 ocritical0 oSU(3)060 orotorprolate0 o
<strong>Prolate</strong>-<strong>oblate</strong> <strong>oscillation</strong>
<strong>Prolate</strong>-<strong>oblate</strong> <strong>oscillation</strong>
<strong>Prolate</strong>-<strong>oblate</strong> <strong>oscillation</strong>
<strong>Prolate</strong>-<strong>oblate</strong> <strong>oscillation</strong>
<strong>Prolate</strong>-<strong>oblate</strong> <strong>oscillation</strong>
<strong>Prolate</strong>-<strong>oblate</strong> <strong>oscillation</strong>
<strong>Prolate</strong>-<strong>oblate</strong> <strong>oscillation</strong>
<strong>Prolate</strong>-<strong>oblate</strong> <strong>oscillation</strong>E(5)
<strong>Prolate</strong>-<strong>oblate</strong> <strong>oscillation</strong>
<strong>Prolate</strong>-<strong>oblate</strong> <strong>oscillation</strong>
<strong>Prolate</strong>-<strong>oblate</strong> <strong>oscillation</strong>
<strong>Prolate</strong>-<strong>oblate</strong> <strong>oscillation</strong>
<strong>Prolate</strong>-<strong>oblate</strong> <strong>oscillation</strong>
<strong>Prolate</strong>-<strong>oblate</strong> <strong>oscillation</strong>
<strong>Prolate</strong>-<strong>oblate</strong> <strong>oscillation</strong>
<strong>Prolate</strong>-<strong>oblate</strong> <strong>oscillation</strong>
<strong>Prolate</strong>-<strong>oblate</strong> <strong>oscillation</strong>
<strong>Prolate</strong>-<strong>oblate</strong> <strong>oscillation</strong>
<strong>Prolate</strong>-<strong>oblate</strong> <strong>oscillation</strong>E(5)
<strong>Prolate</strong>-<strong>oblate</strong> <strong>oscillation</strong>
<strong>Prolate</strong>-<strong>oblate</strong> <strong>oscillation</strong>
<strong>Prolate</strong>-<strong>oblate</strong> <strong>oscillation</strong>
<strong>Prolate</strong>-<strong>oblate</strong> <strong>oscillation</strong>
Superdeformed <strong>oblate</strong> (SDO) SHE??
Superdeformed <strong>oblate</strong> (SDO ) SHE! Jachimowicz et al., Phys. Rev. C 83, 054302 (2011)
Superdeformed <strong>oblate</strong> (SDO) SHE!
First & second minima
First & second minima
First & second minima
En. difference <strong>between</strong> prolate and <strong>oblate</strong> minima
ConclusionsSU(3)prolate rotorSU(3)<strong>oblate</strong> rotorSDOE(5)triple pointU(5)vibratorO(6)-s<strong>of</strong>t
Conclusions The e-e SHEs form three regions: <strong>the</strong> prolate-deformed SU(3) (for N < 172), sphericalU(5) (for N>180), and transitional region (-s<strong>of</strong>t) O(6) <strong>between</strong> <strong>the</strong> former two. On <strong>the</strong> border <strong>between</strong> <strong>the</strong> O(6) and U(5) regions (for N = 180) nuclei exhibit a ra<strong>the</strong>rflat potential bottom and acquire <strong>the</strong> triple-point solutions called E(5). The existence <strong>of</strong> superdeformed <strong>oblate</strong> (SDO) nuclei - SU(3) for N 166 and Z 120was validated. Theoretical indications <strong>of</strong> a prolate-<strong>oblate</strong> <strong>oscillation</strong> <strong>between</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>ground</strong> <strong>states</strong> <strong>of</strong> SHEsin <strong>the</strong> transitional region O(6) were found. The heaviest <strong>even</strong>-<strong>even</strong> nuclei produced by 48 Ca induced reactions on actinide targetsfall into <strong>the</strong> class <strong>of</strong> O(6) -s<strong>of</strong>t nuclei.Jachimowicz et al., Phys. Rev. C 83, 054302 (2011).
Thank you!
Ehrenfest classification, 1933:The phase transition is <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> k-th order if <strong>the</strong> k-thderivative <strong>of</strong> <strong>the</strong> <strong>the</strong>rmodynamic free energy withrespect to some <strong>the</strong>rmodynamic variable changesdiscontinuously at <strong>the</strong> critical point.
Alpha emission
First & second minima