Vegetated Geogrids
Vegetated Geogrids
Vegetated Geogrids
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
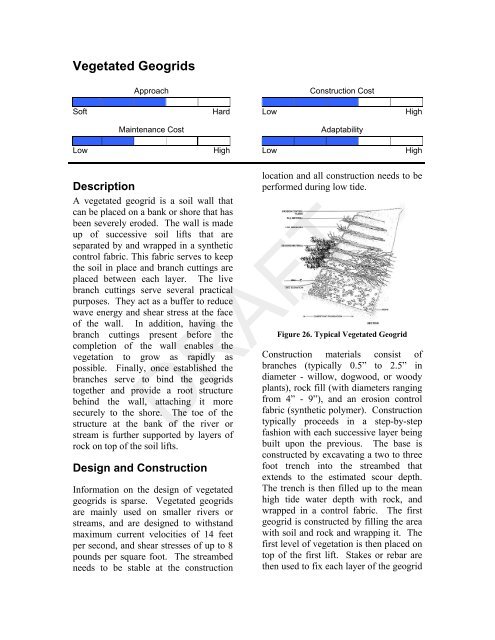
<strong>Vegetated</strong> <strong>Geogrids</strong>ApproachConstruction CostSoft Hard Low HighMaintenance CostAdaptabilityLow High Low HighDescriptionA vegetated geogrid is a soil wall thatcan be placed on a bank or shore that hasbeen severely eroded. The wall is madeup of successive soil lifts that areseparated by and wrapped in a syntheticcontrol fabric. This fabric serves to keepthe soil in place and branch cuttings areplaced between each layer. The livebranch cuttings serve several practicalpurposes. They act as a buffer to reducewave energy and shear stress at the faceof the wall. In addition, having thebranch cuttings present before thecompletion of the wall enables thevegetation to grow as rapidly aspossible. Finally, once established thebranches serve to bind the geogridstogether and provide a root structurebehind the wall, attaching it moresecurely to the shore. The toe of thestructure at the bank of the river orstream is further supported by layers ofrock on top of the soil lifts.Design and ConstructionInformation on the design of vegetatedgeogrids is sparse. <strong>Vegetated</strong> geogridsare mainly used on smaller rivers orstreams, and are designed to withstandmaximum current velocities of 14 feetper second, and shear stresses of up to 8pounds per square foot. The streambedneeds to be stable at the constructionlocation and all construction needs to beperformed during low tide.Figure 26. Typical <strong>Vegetated</strong> GeogridConstruction materials consist ofbranches (typically 0.5” to 2.5” indiameter - willow, dogwood, or woodyplants), rock fill (with diameters rangingfrom 4” - 9”), and an erosion controlfabric (synthetic polymer). Constructiontypically proceeds in a step-by-stepfashion with each successive layer beingbuilt upon the previous. The base isconstructed by excavating a two to threefoot trench into the streambed thatextends to the estimated scour depth.The trench is then filled up to the meanhigh tide water depth with rock, andwrapped in a control fabric. The firstgeogrid is constructed by filling the areawith soil and rock and wrapping it. Thefirst level of vegetation is then placed ontop of the first lift. Stakes or rebar arethen used to fix each layer of the geogridDRAFT