Nuclear and Particle Physics SubAtomic Physics
Nuclear and Particle Physics SubAtomic Physics
Nuclear and Particle Physics SubAtomic Physics
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
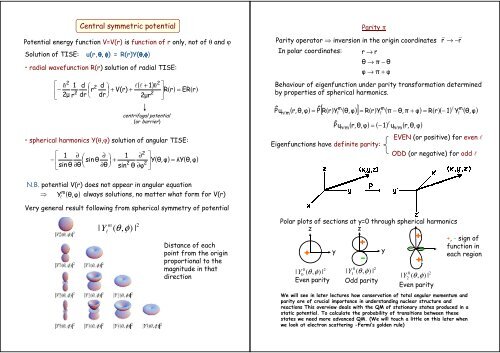
Central symmetric potentialPotential energy function V=V(r) is function of r only, not of θ <strong>and</strong> ϕSolution of TISE:• radial wavefunction R(r) solution of radial TISE:2( l 1)⎡ h 1 d ⎛ 2 d ⎞ l + h⎢−r + V(r) +2µ2⎜ ⎟r dr dr2⎣ ⎝ ⎠ 2µr2centrifugal potential(or barrier)⎤⎥R( r) = ER( r)⎦• spherical harmonics Y(θ,ϕ) solution of angular TISE:⎡− ⎢⎣1sin θu(r,θ, φ) = R(r)Y(θ,φθ,φ)∂ ⎛ ∂ 1sin θ⎞⎜ ⎟ +∂θ⎝ ∂θ⎠ sin2∂2θ ∂φ2⎤⎥Y θ,φ⎦( ) = λY( θ,φ)Parity πParity operator ⇒ inversion in the origin coordinatesPˆ uIn polar coordinates:nlmm( r, θ, φ) = Pˆ R( r) Y ( θ,φ)r → rθ → π − θφ → π + φr r→ −Behaviour of eigenfunction under parity transformation determinedby properties of spherical harmonics.ml m[ ] = R( r) Y ( π − θ, π + φ) = R( r)( − 1) Y ( θ,φ)lPˆunlmEigenfunctions have definite parity:ll( r, θ,φ) = ( − 1) u ( r, θ,φ)nlmEVEN (or positive) for even lODD (or negative) for odd llN.B. potential V(r) does not appear in angular equation⇒always solutions, no matter what form for V(r)Ylm ( θ,φ)Very general result following from spherical symmetry of potentialm| ( θ,φ)Y l2|Distance of eachpoint from the originproportional to themagnitude in thatdirectionPolar plots of sections at y=0 through spherical harmonicszz+0 2| Y0 ( θ , φ)|Even parityy+-0 2| Y1 ( θ,φ)|Odd parityWe will see in later lectures how conservation of total angular momentum <strong>and</strong>parity are of crucial importance in underst<strong>and</strong>ing nuclear structure <strong>and</strong>reactions This overview deals with the QM of stationary states produced in astatic potential. To calculate the probability of transitions between thesestates we need more advanced QM. (We will touch a little on this later whenwe look at electron scattering -Fermi’s golden rule)y+-+ -0 2| Y2 ( θ,φ)|Even parity+, - sign offunction ineach region