The physics of 2-state systems
The physics of 2-state systems
The physics of 2-state systems
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
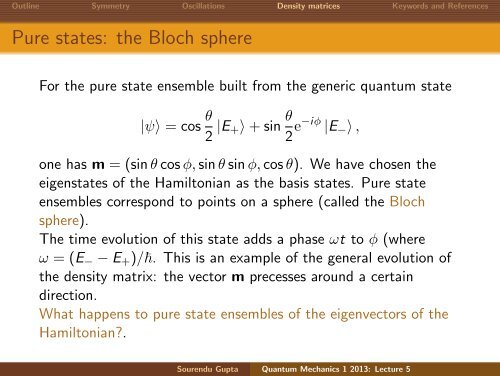
Outline Symmetry Oscillations Density matrices Keywords and ReferencesPure <strong>state</strong>s: the Bloch sphereFor the pure <strong>state</strong> ensemble built from the generic quantum <strong>state</strong>|ψ〉 = cos θ 2 |E +〉+sin θ 2 e−iφ |E − 〉,one has m = (sinθcosφ,sinθsinφ,cosθ). We have chosen theeigen<strong>state</strong>s <strong>of</strong> the Hamiltonian as the basis <strong>state</strong>s. Pure <strong>state</strong>ensembles correspond to points on a sphere (called the Blochsphere).<strong>The</strong> time evolution <strong>of</strong> this <strong>state</strong> adds a phase ωt to φ (whereω = (E − −E + )/. This is an example <strong>of</strong> the general evolution <strong>of</strong>the density matrix: the vector m precesses around a certaindirection.What happens to pure <strong>state</strong> ensembles <strong>of</strong> the eigenvectors <strong>of</strong> theHamiltonian?.Sourendu Gupta Quantum Mechanics 1 2013: Lecture 5