hx1nech25.pdf
hx1nech25.pdf
hx1nech25.pdf
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
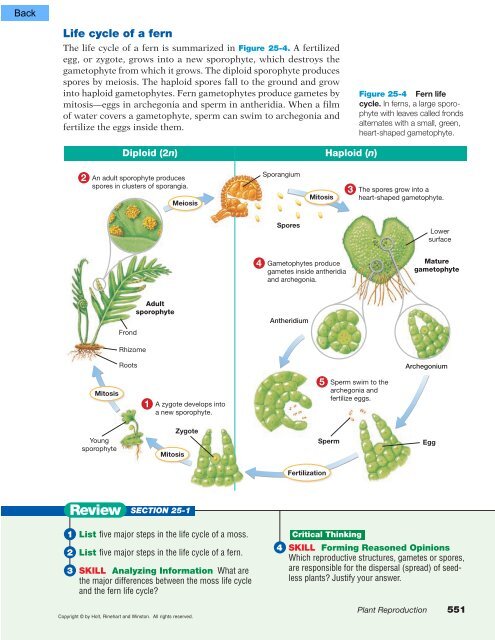
Life cycle of a fernThe life cycle of a fern is summarized in Figure 25-4. A fertilizedegg, or zygote, grows into a new sporophyte, which destroys thegametophyte from which it grows. The diploid sporophyte producesspores by meiosis. The haploid spores fall to the ground and growinto haploid gametophytes. Fern gametophytes produce gametes bymitosis—eggs in archegonia and sperm in antheridia. When a filmof water covers a gametophyte, sperm can swim to archegonia andfertilize the eggs inside them.Figure 25-4 Fern lifecycle. In ferns, a large sporophytewith leaves called frondsalternates with a small, green,heart-shaped gametophyte.Diploid (2n)Haploid (n)2An adult sporophyte producesspores in clusters of sporangia.MeiosisSporangiumMitosis3 The spores grow into aheart-shaped gametophyte.SporesLowersurface4 Gametophytes producegametes inside antheridiaand archegonia.MaturegametophyteFrondAdultsporophyteAntheridiumRhizomeRootsArchegoniumMitosis1 A zygote develops intoa new sporophyte.5 Sperm swim to thearchegonia andfertilize eggs.YoungsporophyteMitosisZygoteSpermEggFertilizationReviewSECTION 25-11 List five major steps in the life cycle of a moss.2 List five major steps in the life cycle of a fern.3 SKILL Analyzing Information What arethe major differences between the moss life cycleand the fern life cycle?Copyright © by Holt, Rinehart and Winston. All rights reserved.Critical Thinking4 SKILL Forming Reasoned OpinionsWhich reproductive structures, gametes or spores,are responsible for the dispersal (spread) of seedlessplants? Justify your answer.Plant Reproduction 551






![alumni e-mail addresses by classes - word[3]](https://img.yumpu.com/13381322/1/190x245/alumni-e-mail-addresses-by-classes-word3.jpg?quality=85)








