B-Alert Published Studies: Citations - Biopac
B-Alert Published Studies: Citations - Biopac
B-Alert Published Studies: Citations - Biopac
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
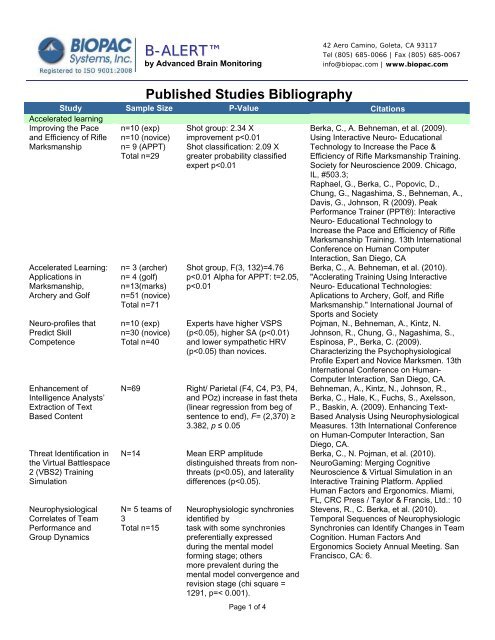
B-ALERTby Advanced Brain Monitoring42 Aero Camino, Goleta, CA 93117Tel (805) 685-0066 | Fax (805) 685-0067info@biopac.com | www.biopac.com<strong>Published</strong> <strong>Studies</strong> BibliographyStudy Sample Size P-Value <strong>Citations</strong>Accelerated learningImproving the Paceand Efficiency of RifleMarksmanshipAccelerated Learning:Applications inMarksmanship,Archery and GolfNeuro-profiles thatPredict SkillCompetenceEnhancement ofIntelligence Analysts’Extraction of TextBased ContentThreat Identification inthe Virtual Battlespace2 (VBS2) TrainingSimulationNeurophysiologicalCorrelates of TeamPerformance andGroup Dynamicsn=10 (exp)n=10 (novice)n= 9 (APPT)Total n=29n= 3 (archer)n= 4 (golf)n=13(marks)n=51 (novice)Total n=71n=10 (exp)n=30 (novice)Total n=40Shot group: 2.34 Ximprovement p
PsychophysiologicalCharacterization ofLearning and SkillAcquisitionB-<strong>Alert</strong> by Advanced Brain Monitoring — <strong>Published</strong> <strong>Studies</strong> BibliographyStudy Sample Size P-Value <strong>Citations</strong>N=18 There were no significantdifferences in E whether or notthe problem was solved but WLwas significantly lower whenthe solution to the problem wasmissed twice (0.59 ± 0.02 vs. 0.64 ± 0.02, p = .002)Interfacing Humans & ComputersImpact of SimulatorFidelity on Behaviorand NeurophysiologyN=12 Late P300 component confirmsprevious reports (Kok, 1985) ofdegraded stimuli elicitingreduced amplitude P300EEG-basedQuantification of<strong>Alert</strong>ness, Cognitionand Memory with aWireless SensorHeadsetImpact of Visio-HapticFeedback on EEG<strong>Alert</strong>nessEEG-based detectionof WorkloadManaging FatigueN=45 EEG-WL effectively trackedtask difficulty (3 levels) inWarship commander task (F =7.369, p < 0.005) in novices, aswell as tracked improvement asexperience was obtained, F =3.118, p < 0.01. These datawere replicated in a basicneurocognitive task with threelevels (F = 21.962, p < 0.001).N=5 90% of events in a videogaming environment that weretagged for the user with hapticfeedback were associated withpeaks in EEG measures of highengagement/attention. Thisfeedback was most effective infirst person shooting types ofgames, and very effective forracing and sports types as well.N=80 Development (n=13) andvalidation (n=67) of the EEG-WL model. The developedmodel tracked task difficultyacross 5 tasks with increasingcognitive difficulty over timewithin the task. WL was foundto be elevated during thelearning portion of multiplelearning and memory tasks(F(1,49)=34.79, p
Identification ofIndividuals Susceptibleto Sleep DeprivationB-<strong>Alert</strong> by Advanced Brain Monitoring — <strong>Published</strong> <strong>Studies</strong> BibliographyStudy Sample Size P-Value <strong>Citations</strong>N=24 Thresholds were applied acrosstime-points to the PVT, PALand MWT measures in an effortto stratify individuals into threegroups (good, fair, poorperformers) based onvulnerability to sleepdeprivation [2,3]. A 3(group) X10(time-points) repeatedmeasures ANOVA revealedsignificant effects betweengroups during the PVT for B-<strong>Alert</strong> %Sleepy (p
B-<strong>Alert</strong> by Advanced Brain Monitoring — <strong>Published</strong> <strong>Studies</strong> BibliographyStudy Sample Size P-Value <strong>Citations</strong>to the recognition (“testing”)period (EEG-engagementt=2.59, p