Language Proficiency Checklist (pdf)
Language Proficiency Checklist (pdf)
Language Proficiency Checklist (pdf)
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
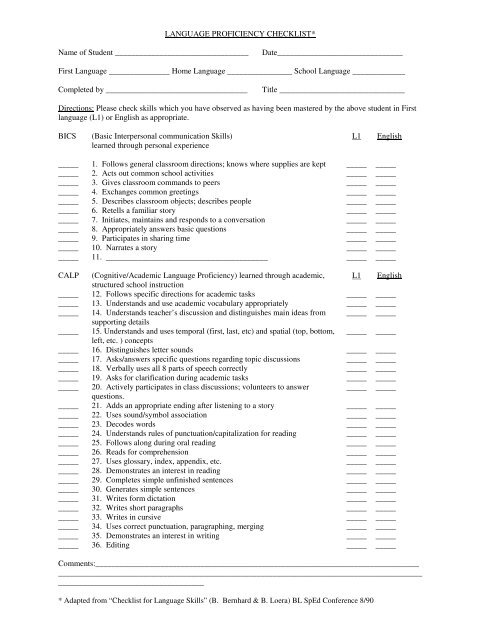
LANGUAGE PROFICIENCY CHECKLIST*Name of Student _________________________________Date_______________________________First <strong>Language</strong> _______________ Home <strong>Language</strong> ________________ School <strong>Language</strong> _____________Completed by ___________________________________Title _______________________________Directions: Please check skills which you have observed as having been mastered by the above student in Firstlanguage (L1) or English as appropriate.BICS(Basic Interpersonal communication Skills)learned through personal experienceL1English_____ 1. Follows general classroom directions; knows where supplies are kept _____ __________ 2. Acts out common school activities _____ __________ 3. Gives classroom commands to peers _____ __________ 4. Exchanges common greetings _____ __________ 5. Describes classroom objects; describes people _____ __________ 6. Retells a familiar story _____ __________ 7. Initiates, maintains and responds to a conversation _____ __________ 8. Appropriately answers basic questions _____ __________ 9. Participates in sharing time _____ __________ 10. Narrates a story _____ __________ 11. ________________________________________ _____ _____CALP (Cognitive/Academic <strong>Language</strong> <strong>Proficiency</strong>) learned through academic, L1 Englishstructured school instruction_____ 12. Follows specific directions for academic tasks _____ __________ 13. Understands and use academic vocabulary appropriately _____ __________ 14. Understands teacher’s discussion and distinguishes main ideas from _____ _____supporting details_____ 15. Understands and uses temporal (first, last, etc) and spatial (top, bottom, _____ _____left, etc. ) concepts_____ 16. Distinguishes letter sounds _____ __________ 17. Asks/answers specific questions regarding topic discussions _____ __________ 18. Verbally uses all 8 parts of speech correctly _____ __________ 19. Asks for clarification during academic tasks _____ __________ 20. Actively participates in class discussions; volunteers to answer _____ _____questions._____ 21. Adds an appropriate ending after listening to a story _____ __________ 22. Uses sound/symbol association _____ __________ 23. Decodes words _____ __________ 24. Understands rules of punctuation/capitalization for reading _____ __________ 25. Follows along during oral reading _____ __________ 26. Reads for comprehension _____ __________ 27. Uses glossary, index, appendix, etc. _____ __________ 28. Demonstrates an interest in reading _____ __________ 29. Completes simple unfinished sentences _____ __________ 30. Generates simple sentences _____ __________ 31. Writes form dictation _____ __________ 32. Writes short paragraphs _____ __________ 33. Writes in cursive _____ __________ 34. Uses correct punctuation, paragraphing, merging _____ __________ 35. Demonstrates an interest in writing _____ __________ 36. Editing _____ _____Comments:______________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________* Adapted from “<strong>Checklist</strong> for <strong>Language</strong> Skills” (B. Bernhard & B. Loera) BL SpEd Conference 8/90
CLASSROOM BEHAVIOR:Classroom Behaviors Possibly Associated with Learning Disabilitiesand Second <strong>Language</strong> Acquisition (ELL Student)Learning Disabled StudentMay be quiet or withdrawnMay move about constantlyIs often tardy or absentMay have difficulty with peer relationshipsIs disorganizedIs easily distractedDisplays inconsistencies in behaviorSeems to misunderstand oral directionsVERBAL: FIRST LANGUAGE:May hesitate often when speaking (revisions andfalse starts due to processing problems)Has poor verbal expression for ageELL StudentMay be quiet or withdrawn during initial time in 2 ndlanguage class.May show a lot of movement when becomesfrustratedNot as much importance put on regular schoolattendance in many casesLittle difficulty with dominant language friendsDegree of organization depends on the child, not onthe languageMay appear distracted, but may be due to lack ofunderstandingMay display inconsistency in behavior when doesnot understand“Misunderstands” due to lack of experience with 2 ndlanguageVERBAL: SECOND LANGUAGE:May hesitate often when speaking in English(revisions and false starts due to lack of vocabulary)May have poor verbal expression in EnglishREADING: 2nd Grade or AboveFrequent substitutions for wordsLoses place, repeats wordsDoes not read fluentlyConfuses similar words and lettersUses fingers to follow alongDoes not usually read willinglyConfused by words with multiple meaningsFrequent substitutions for wordsMay lose place, repeat wordsDoes not read fluentlyConfuses similar words and lettersMay use fingers to follow alongMay not read willinglyConfused by words with multiple meaningsSource: Bilingual Handbook, Chula Vista Elementary School District
SPELLING: 2 nd grade or aboveLearned spelling words are not used correctly inspontaneous writingMay use incorrect order of letters in wordsELL StudentLearned spelling words are not used spontaneouswriting. Spells with Spanish phonetic system.May use incorrect order of letters in wordsHas difficulty copying from board or other sourceMay reverse letters and words (mirror image)WRITING: 2 nd grade or aboveCannot stay on lineHas difficulty copying from board or other sourceUses poor written expression for ageIs slow in completing written workFrequently writing is laboriousFrequently does not integrate learned grammar skillsinto spontaneous writing activitiesUses Spanish phonetic system in English writtenexpressionIs slow in completing written work in EnglishFrequently writing is laborious and slow in EnglishFrequently does not integrate learned grammar skillsinto skills into spontaneous writing activitiesMATHEMATICS:Has difficulty associating number with symbolCannot remember math factsConfuses columns, spacing and math process signsHas difficulty with story problemsFails to comprehend math conceptsLimited English vocabulary causes difficulty withstory problemsLimited English vocabulary causes difficulty with newor abstract math conceptsMOTOR:Displays poor coordination for ageMay have problems of balanceMay confuse right and left, even after age 7May have poor muscle strength for ageLacks rhythm in movements, loses sequenceSource: Bilingual Handbook, Chula Vista Elementary School District
DEVELOPMENT OF PRIMARY LANGUAGEDEVELOPMENT OF SECOND LANGUAGESilent Period: Child does not speak for firstyear of life but participates in countlesslistening activities.Early Responses: These occur in a physicalmode as child responds to commands, i. e.,“Pick up teddy bear,” etc. speech is notexpected yet.This developmental sequence beginsregardless of age or grade at which astudent engages in second languageinstruction.Pre-Kindergarten Enter SchoolOral Responses: First speech is usually singlewords, such as nouns. Production is reinforcedwith praise and excitement.Error Correction: Minimal. Syntax errors aredevelopmental. Parent negotiates for meaning,i.e., “Do you mean chocolate milk?”<strong>Language</strong> Experiences: Embedded in context,where meaning is clear. Conversations relate toconcrete, here and now objects or experiences.Concept Development: An Integral part oflanguage at this stage. The student is able tocommunicate fully. Vocabulary is expanded.Reading: Readiness skills lead to beginningreading with ease in most instances.Writing: The student begins to handle themechanics of writing.Continues to expand all areas of academicskills.Silent Period: Student learning a second languageneeds time to listen and understand rather than beingpushed into production. (approximately six months)Physical Response: Activities are an excellentmethod of assuming understanding of languagewithout pressure to produce.Oral Response: Student will answer with one word,and/or yes/no responses. Comprehension is moreadvanced than production.Error Correction: Student will benefit more fromteacher modeling correct responses than fromnegative correction techniques.<strong>Language</strong> Acquisition: Can be encouraged throughvaried activities which provide comprehensibleinput.Concepts: Those learned in primary language arelabeled and transferred into the second language.New concepts are developed in second language.Reading: Literacy in second language is achievedwith ease if above steps have been followed.Whenever students enter 2nd language school environmentWriting: Mechanics of written language aredeveloped.Source: Bilingual Handbook, Chula Vista Elementary School District