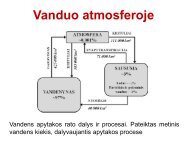
- Page 2 and 3:
Abstractshttp://www.isce2012.lt2
- Page 4 and 5:
Meeting Overview4
- Page 6 and 7:
Program
- Page 8 and 9:
Monday 23rd July8:30-9:00Welcome-Re
- Page 10 and 11:
Monday 23rd July16.30-16.4516.45-17
- Page 12 and 13:
Tuesday 24th July14:00-14:1514:15-1
- Page 14 and 15:
Wednesday 25th July8:30-9:00Welcome
- Page 16 and 17:
Thursday 26th July14:00-14:1514:15-
- Page 18 and 19:
Abstracts
- Page 20 and 21:
Sunday 22nd July, 17:30 - 18:30 hSI
- Page 22 and 23:
Thursday 26th July, 9:00 - 10:00 hS
- Page 24 and 25:
Monday 23rd July, 9:00 - 10:00 hThe
- Page 26 and 27:
Tuesday 24th July, 9:00 - 10:00 hA
- Page 28 and 29:
Wednesday 25th July, 9:00 - 10:00 h
- Page 30 and 31: Symposium 1. Plant - Animal - Anima
- Page 32 and 33: Monday 23rd July, 11:00 - 11:15 hLo
- Page 34 and 35: Monday 23rd July, 11:30 - 11:45 hAs
- Page 36 and 37: Monday 23rd July, 14:00 - 14:30 hKE
- Page 38 and 39: Monday 23rd July, 14:45 - 15:00 hWh
- Page 40 and 41: Monday 23rd July, 15:15 - 15:30 hDi
- Page 42 and 43: Monday 23rd July, 15:45 - 16:00 hCa
- Page 44 and 45: Monday 23rd July, 16:45 - 17:00 hCh
- Page 46 and 47: Monday 23rd July, 17:15 - 17:30 hPh
- Page 49 and 50: Monday 23rd July, 11:00 - 11:15 hA
- Page 51 and 52: Monday 23rd July, 11:30 - 11:45 hAc
- Page 53 and 54: Monday 23rd July, 14:00 - 14:15 hSp
- Page 55 and 56: Monday 23rd July, 14:30 - 14:45 hTh
- Page 57 and 58: Monday 23rd July, 15:00 - 15:15 hSo
- Page 59 and 60: Monday 23rd July, 15:30 - 15:45 hEv
- Page 61 and 62: Monday 23rd July, 16:30 - 16:45 hMo
- Page 63: Monday 23rd July, 17:00 - 17:15 hDe
- Page 66 and 67: Thursday 26th July, 11:00 - 11:15 h
- Page 68: Thursday 26th July, 11:30 - 11:45 h
- Page 71 and 72: Thursday 26th July, 14:15 - 14:30 h
- Page 73 and 74: Thursday 26th July, 14:45 - 15:00 h
- Page 75 and 76: Thursday 26th July, 15:15 - 15:30 h
- Page 77 and 78: Thursday 26th July, 15:45 - 16:00 h
- Page 79: Thursday 26th July, 16:45 - 17:00 h
- Page 83 and 84: Tuesday 24th July, 10:30 - 11:00 hK
- Page 85 and 86: Tuesday 24th July, 11:15 - 11:30 hC
- Page 87 and 88: Tuesday 24th July, 11:45 - 12:00 hA
- Page 89 and 90: Tuesday 24th July, 14:15 - 14:30 hG
- Page 91 and 92: Tuesday 24th July, 14:45- 15:00 hId
- Page 93 and 94: Tuesday 24th July, 15:15- 15:30 hTe
- Page 95 and 96: Tuesday 24th July, 16:30- 16:45 hMu
- Page 97 and 98: Tuesday 24th July, 17:00- 17:15 hEf
- Page 99 and 100: Symposium 4. Chemical Ecology ofMic
- Page 101 and 102: Tuesday 24th July, 14:30 - 14:45 hT
- Page 103 and 104: Tuesday 24th July, 15:00 - 15:15 hV
- Page 105 and 106: Tuesday 24th July, 15:30 - 15:45 hH
- Page 107 and 108: Tuesday 24th July, 16:30 - 17:00 hK
- Page 109 and 110: Tuesday 24th July, 17:15 - 17:30 hA
- Page 111 and 112: Wednesday 25th July, 10:30 - 10:45
- Page 113 and 114: Wednesday 25th July, 11:00 - 11:15
- Page 115 and 116: Wednesday 25th July, 11:30 - 11:45
- Page 117 and 118: Symposium 7. Climate Change, Invasi
- Page 119 and 120: Tuesday 24th July, 10:45 - 11:00 hU
- Page 121 and 122: Tuesday 24th July, 11:15 - 11:30 hT
- Page 123 and 124: Tuesday 24th July, 11:45 - 12:00 hC
- Page 125 and 126: Wednesday 25th July, 10:30 - 11:00
- Page 127 and 128: Wednesday 25th July, 11:15 - 11:30
- Page 129 and 130: Wednesday 25th July, 11:45 - 12:00
- Page 131 and 132:
Thursday 26th July, 11:00 - 11:15 h
- Page 133 and 134:
Thursday 26th July, 11:30 - 11:45 h
- Page 135 and 136:
Thursday 26th July, 14:00 - 14:30 h
- Page 137 and 138:
Thursday 26th July, 14:45 - 15:00 h
- Page 139 and 140:
Thursday 26th July, 15:15 - 15:30 h
- Page 141 and 142:
Thursday 26th July, 16:30 - 16:45 h
- Page 143 and 144:
Thursday 26th July, 17:00 - 17:15 h
- Page 145 and 146:
Poster Session145
- Page 147 and 148:
Poster P001Chemical constraint of s
- Page 149 and 150:
Poster P003Facultative social paras
- Page 151 and 152:
Poster P005Chemical signature overt
- Page 153 and 154:
Poster P007Phenotypic plasticity in
- Page 155 and 156:
Poster P009Growth responses in the
- Page 157 and 158:
Poster P011Interspecific hybridizat
- Page 159 and 160:
Poster P013Fall and beet armyworm d
- Page 161 and 162:
Poster P015Fertilization and defoli
- Page 163 and 164:
Poster P017Influence of naturally o
- Page 165 and 166:
Poster P019Semiochemicals from herb
- Page 167 and 168:
Poster P021Selenium contamination a
- Page 169 and 170:
Poster P023Host-plant volatiles att
- Page 171 and 172:
Poster P025Scots pine volatiles emi
- Page 173 and 174:
Poster P026Evolutionary patterns of
- Page 175 and 176:
Poster P28Cuckoo versus predatory M
- Page 177 and 178:
Poster P030Identification and synth
- Page 179 and 180:
Poster P032Fertility signals in the
- Page 181 and 182:
Symposium 3. Biosynthesis and Chemi
- Page 183 and 184:
Poster P035A new multi-dimensional
- Page 185 and 186:
Poster P037Sustainable green styren
- Page 187 and 188:
Poster P039Stereoselective synthesi
- Page 189 and 190:
Poster P041Thujopsene and its autox
- Page 191 and 192:
Poster P043Purification and cDNA cl
- Page 193 and 194:
Poster P045N-Linolenoyl-L-glutamic
- Page 195 and 196:
Poster P047Sex pheromone of Strepsi
- Page 197 and 198:
Poster P049Biosynthesis of terpenic
- Page 199 and 200:
Poster P051Timing of male sex phero
- Page 201 and 202:
Symposium 4. Chemical Ecology ofMic
- Page 203 and 204:
Poster P054Ammonia production by in
- Page 205 and 206:
Poster P056Identification of VOCs r
- Page 207 and 208:
Symposium 6. Aquatic Chemical Ecolo
- Page 209 and 210:
Poster P059When a repellent becomes
- Page 211 and 212:
Poster P061Antifungal activities of
- Page 213 and 214:
Poster P063Effects of allelopathica
- Page 215 and 216:
Poster P064Seed germination inhibit
- Page 217 and 218:
Poster P066Flexible aggregative beh
- Page 219 and 220:
Poster P068Differences in cuticular
- Page 221 and 222:
Symposium 8. Applied Chemical Ecolo
- Page 223 and 224:
Poster P071Ergography: A novel meth
- Page 225 and 226:
Poster P073From Justus Liebig Style
- Page 227 and 228:
Poster P075Organic nanofibers: a ne
- Page 229 and 230:
Poster P077Evidence of a female pro
- Page 231 and 232:
Poster P079Plant compounds modify b
- Page 233 and 234:
Poster P081The cost of vengeance: H
- Page 235 and 236:
Poster P083(E)--caryophyllene as ph
- Page 237 and 238:
Poster P085Electrical activity and
- Page 239 and 240:
Poster P087(8E,10Z)-8,10-Dodecadien
- Page 241 and 242:
Poster P089Identification and synth
- Page 243 and 244:
Poster P091Laser vibrometer for pre
- Page 245 and 246:
Poster P093Seasonal variation of ph
- Page 247 and 248:
ABAEV VD 240ABDULLAH F 15, 133ABE H
- Page 249 and 250:
GUERRERO A 12, 94, 169,244GURGUI C
- Page 251 and 252:
ONO T 189OPITZ SEW 67OPPEN S 158ORT
- Page 253 and 254:
WATHELET J-P 198WEE SL 39WEHRENFENN