while the two industries c<strong>on</strong>tributed substantially to the total export receipts, they are also themajor users of such receipts through imports of their raw material requirements. In net terms,their c<strong>on</strong>tributi<strong>on</strong> to the total export value has been minimal.Although total exports grew by about 17 percent in 1997-98, the traditi<strong>on</strong>al exportproducts (e.g., coc<strong>on</strong>ut, sugar, fru<str<strong>on</strong>g>its</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> vegetable, etc.), have generally been in a dismal stagewith <strong>on</strong>ly sugar <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> sugar products showing a positive growth rate of 1.01 percent in 1997-98(Table 5).In the last two years, machinery <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> transport equipment replaced the garment industry asthe sec<strong>on</strong>d largest c<strong>on</strong>tributor to the total export value. In 1998, it c<strong>on</strong>tributed 11 percent of thetotal export receipts. The electr<strong>on</strong>ics industry, however, c<strong>on</strong>tinues to c<strong>on</strong>tribute substantially tothe growth of the export sector. In fact, it c<strong>on</strong>tributed about 58 percent of the total export valuein 1998.Although the <strong>Philippine</strong>s showed the highest export growth in 1998 compared to otherAsian countries, it is <strong>on</strong>e of the few (including India <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> Sri-Lanka) countries still experiencing anegative balance of trade. This c<strong>on</strong>tinuous negative balance of trade despite a significant increasein export is due to the import dependence of the export sector for their inputs.POLICY REFORMS TO STABILIZE PRICES AND SUSTAINECONOMIC GROWTHUnder a free market system, <str<strong>on</strong>g>price</str<strong>on</strong>g>s of basic commodities are determined by dem<str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g>supply c<strong>on</strong>diti<strong>on</strong>s. Domestic supply, is, in turn, determined by domestic producti<strong>on</strong> <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g>foreign trade. Measures that promote, therefore, domestic producti<strong>on</strong> <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> improve access toforeign supplies of commodities can help stabilize <str<strong>on</strong>g>price</str<strong>on</strong>g>s. This implies that a more liberalizedtrade regime is beneficial towards <str<strong>on</strong>g>price</str<strong>on</strong>g> stability.The government, through <str<strong>on</strong>g>its</str<strong>on</strong>g> various agencies, is pursuing producti<strong>on</strong>-related programs<str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> has instituted policies to enhance productivity, efficiency, <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> competitiveness. Theseinclude producti<strong>on</strong> programs, training, provisi<strong>on</strong> of basic infrastructure like irrigati<strong>on</strong> <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> farmto-market roads, shipping ports, storage <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> post harvest facilities, credit, etc. There are alsol<strong>on</strong>g- term programs such as increased agricultural research expenditures. For agriculture, theproductivity <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> efficiency enhancing <str<strong>on</strong>g>measures</str<strong>on</strong>g> are c<strong>on</strong>tained in the Agricultural <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> FisheriesModernizati<strong>on</strong> Act (AFMA).Measures to improve competitiveness such as improved productivity <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> efficiency ofthe country's products in the world market are also beneficial in terms of <str<strong>on</strong>g>price</str<strong>on</strong>g> stability. Therecent commitment of the country to the World Trade Organizati<strong>on</strong> (WTO) has, thereforeimproved the country's chances of achieving <str<strong>on</strong>g>price</str<strong>on</strong>g> stability through trade liberalizati<strong>on</strong>particularly of basic commodities. When the country is in short supply of a certain commodity, amore liberalized trade regime would prevent a large hike in domestic <str<strong>on</strong>g>price</str<strong>on</strong>g>s.14
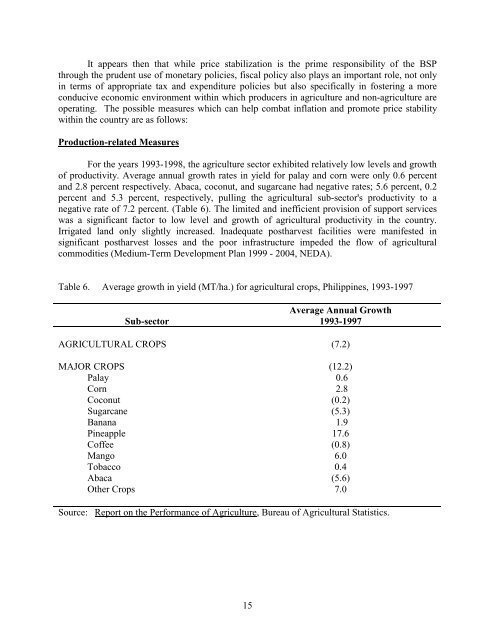
It appears then that while <str<strong>on</strong>g>price</str<strong>on</strong>g> <str<strong>on</strong>g>stabilizati<strong>on</strong></str<strong>on</strong>g> is the prime resp<strong>on</strong>sibility of the BSPthrough the prudent use of m<strong>on</strong>etary policies, fiscal policy also plays an important role, not <strong>on</strong>lyin terms of appropriate tax <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> expenditure policies but also specifically in fostering a morec<strong>on</strong>ducive ec<strong>on</strong>omic envir<strong>on</strong>ment within which producers in agriculture <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> n<strong>on</strong>-agriculture areoperating. The possible <str<strong>on</strong>g>measures</str<strong>on</strong>g> which can help combat inflati<strong>on</strong> <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> promote <str<strong>on</strong>g>price</str<strong>on</strong>g> stabilitywithin the country are as follows:Producti<strong>on</strong>-related MeasuresFor the years 1993-1998, the agriculture sector exhibited relatively low levels <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> growthof productivity. Average annual growth rates in yield for palay <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> corn were <strong>on</strong>ly 0.6 percent<str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> 2.8 percent respectively. Abaca, coc<strong>on</strong>ut, <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> sugarcane had negative rates; 5.6 percent, 0.2percent <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> 5.3 percent, respectively, pulling the agricultural sub-sector's productivity to anegative rate of 7.2 percent. (Table 6). The limited <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> inefficient provisi<strong>on</strong> of support serviceswas a significant factor to low level <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> growth of agricultural productivity in the country.Irrigated l<str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> <strong>on</strong>ly slightly increased. Inadequate postharvest facilities were manifested insignificant postharvest losses <str<strong>on</strong>g>and</str<strong>on</strong>g> the poor infrastructure impeded the flow of agriculturalcommodities (Medium-Term Development Plan 1999 - 2004, NEDA).Table 6. Average growth in yield (MT/ha.) for agricultural crops, <strong>Philippine</strong>s, 1993-1997Sub-sectorAverage Annual Growth1993-1997AGRICULTURAL CROPS (7.2)MAJOR CROPSPalayCornCoc<strong>on</strong>utSugarcaneBananaPineappleCoffeeMangoTobaccoAbacaOther Crops(12.2)0.62.8(0.2)(5.3)1.917.6(0.8)6.00.4(5.6)7.0Source: Report <strong>on</strong> the Performance of Agriculture, Bureau of Agricultural Statistics.15