OWLS: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Solutions - UCLA
OWLS: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Solutions - UCLA
OWLS: Electrophilic Aromatic Substitution Solutions - UCLA
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
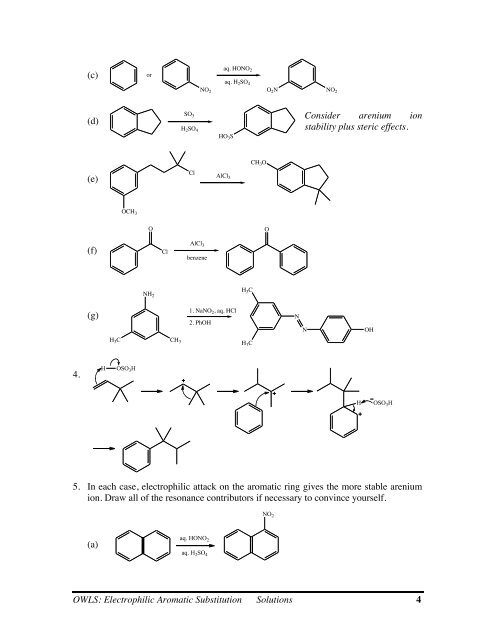
4.<br />
(c)<br />
(d)<br />
(e)<br />
(f)<br />
(g)<br />
H 3C<br />
OCH 3<br />
H OSO 3H<br />
or<br />
O<br />
NH 2<br />
Cl<br />
CH 3<br />
SO 3<br />
H 2SO 4<br />
Cl<br />
AlCl 3<br />
NO 2<br />
benzene<br />
aq. HONO 2<br />
aq. H 2SO 4<br />
HO 3S<br />
AlCl 3<br />
1. NaNO 2, aq. HCl<br />
2. PhOH<br />
H 3C<br />
H 3C<br />
<strong>OWLS</strong>: <strong>Electrophilic</strong> <strong>Aromatic</strong> <strong>Substitution</strong> <strong>Solutions</strong> 4<br />
CH 3O<br />
O 2N<br />
O<br />
N<br />
NO 2<br />
Consider arenium ion<br />
stability plus steric effects.<br />
N<br />
OH<br />
H OSO 3H<br />
5. In each case, electrophilic attack on the aromatic ring gives the more stable arenium<br />
ion. Draw all of the resonance contributors if necessary to convince yourself.<br />
(a)<br />
aq. HONO 2<br />
aq. H 2SO 4<br />
NO 2