Premier spherical roller bearings our vast experience
Premier spherical roller bearings: our vast experience - NTN Bearing
Premier spherical roller bearings: our vast experience - NTN Bearing
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
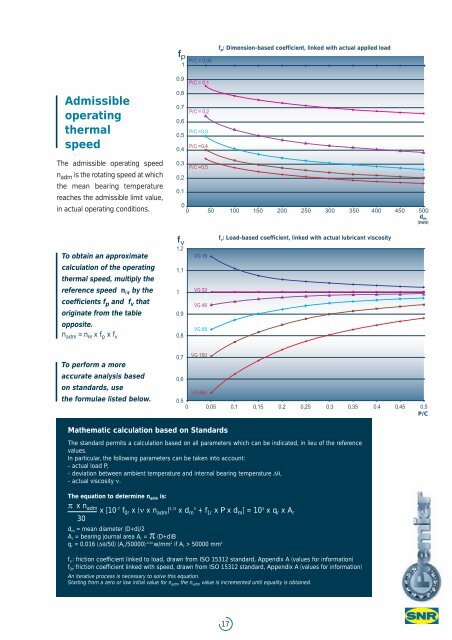
f p : Dimension-based coefficient, linked with actual applied load<br />
Admissible<br />
operating<br />
thermal<br />
speed<br />
1<br />
0,9<br />
0,8<br />
0,7<br />
0,6<br />
0,5<br />
0,4<br />
P/C = 0,05<br />
P/C = 0,1<br />
P/C = 0,2<br />
P/C =0,3<br />
P/C =0,4<br />
The admissible operating speed<br />
n adm is the rotating speed at which<br />
the mean bearing temperature<br />
reaches the admissible limit value,<br />
0,3<br />
0,2<br />
0,1<br />
P/C =0,5<br />
in actual operating conditions.<br />
0<br />
250 350 400 450 500<br />
opposite.<br />
VG 68<br />
n adm =n θr x f p x f v 0,8<br />
f v : Load-based coefficient, linked with actual lubricant viscosity<br />
1,2<br />
To obtain an approximate<br />
VG 15<br />
calculation of the operating 1,1<br />
thermal speed, multiply the<br />
reference speed n θr by the 1 VG 32<br />
coefficients f p and f v that<br />
VG 46<br />
originate from the table<br />
0,9<br />
d m<br />
(mm)<br />
To perform a more<br />
accurate analysis based<br />
on standards, use<br />
the formulae listed below.<br />
0,7 VG 150<br />
0,6<br />
VG 460<br />
0,5<br />
0 0,05 0,1 0,15 0,2 0,25 0,3 0,35 0,4 0,45 0,5<br />
P/C<br />
Mathematic calculation based on Standards<br />
The standard permits a calculation based on all parameters which can be indicated, in lieu of the reference<br />
values.<br />
In particular, the following parameters can be taken into account:<br />
- actual load P,<br />
- deviation between ambient temperature and internal bearing temperature Δθ,<br />
- actual viscosity ν.<br />
The equation to determine n adm is:<br />
π x n adm<br />
x [10 -7 f 0r x (ν x n adm ) 2 /3 x d m3<br />
+ f 1r x P x d m ] = 10 3 x q r x A r<br />
30<br />
d m = mean diameter (D+d)/2<br />
A r = bearing j<strong>our</strong>nal area A r = π (D+d)B<br />
q r = 0.016 (Δθ/50) (A r /50000) -0.34 w/mm 2 if A r > 50000 mm 2<br />
f 1r : friction coefficient linked to load, drawn from ISO 15312 standard, Appendix A (values for information)<br />
f 0r : friction coefficient linked with speed, drawn from ISO 15312 standard, Appendix A (values for information)<br />
An iterative process is necessary to solve this equation.<br />
Starting from a zero or low initial value for n adm the n adm value is incremented until equality is obtained.<br />
17