Glucagon Diabetes mellitus Islet microcirculation
Glucagon Diabetes mellitus Islet microcirculation
Glucagon Diabetes mellitus Islet microcirculation
- No tags were found...
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
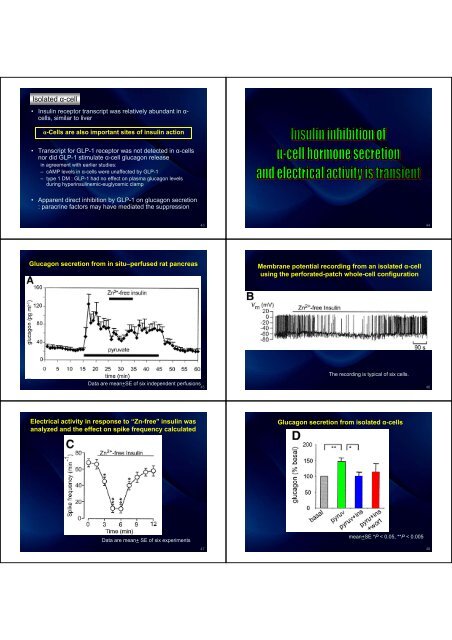
Isolated α-cell<br />
• Insulin receptor transcript was relatively abundant in α-<br />
cells, similar to liver<br />
α-Cells are also important sites of insulin action<br />
• Transcript for GLP-1 receptor was not detected in α-cells<br />
nor did GLP-1 stimulate α-cell glucagon release<br />
in agreement with earlier studies:<br />
– cAMP levels in α-cells were unaffected by GLP-1<br />
– type 1 DM : GLP-1 had no effect on plasma glucagon levels<br />
during hyperinsulinemic-euglycemic clamp<br />
• Apparent direct inhibition by GLP-1 on glucagon secretion<br />
: paracrine factors may have mediated the suppression<br />
43<br />
44<br />
<strong>Glucagon</strong> secretion from in situ–perfused rat pancreas<br />
Membrane potential recording from an isolated α-cell<br />
using the perforated-patch whole-cell configuration<br />
Data are mean+SE of six independent perfusions<br />
45<br />
The recording is typical of six cells.<br />
46<br />
Electrical activity in response to “Zn-free" insulin was<br />
analyzed and the effect on spike frequency calculated<br />
<strong>Glucagon</strong> secretion from isolated α-cells<br />
Data are mean+ SE of six experiments<br />
47<br />
mean+SE *P < 0.05, **P < 0.005<br />
48







![Integ50 MedII_KSA3 [Compatibility Mode].pdf](https://img.yumpu.com/53541610/1/190x146/integ50-medii-ksa3-compatibility-modepdf.jpg?quality=85)