Industrial ETHERNET
Industrial ETHERNET
Industrial ETHERNET
- No tags were found...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
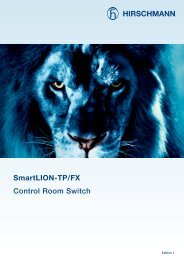
Network access<br />
Network member<br />
ready to transmit<br />
no<br />
Transmission medium<br />
available?<br />
yes<br />
Wait as determined<br />
by backoff strategy<br />
Start to<br />
transmit data<br />
Transmit<br />
jam signal<br />
CRC<br />
Cyclic Redundancy Check<br />
Term for algorithms that are used for<br />
error detection and correction of bitoriented<br />
protocols.<br />
no<br />
Collision?<br />
no<br />
End of<br />
transmission?<br />
yes<br />
Terminate<br />
network access<br />
yes<br />
CSA<br />
www.csa.ca<br />
Canadian Standard Association<br />
cUL 508<br />
US standard for the security of industrial<br />
control equipment.<br />
CSA-<br />
Canadian standard for the security of<br />
C22.2 No. 950 IT devices, including electrical office<br />
machines based on the IEC 950.<br />
CSA-<br />
Canadian standard for the safety of<br />
C22.2 No. 142 industrial control equipment, based on<br />
UL 508.<br />
CSA-<br />
Canadian standard for electrical<br />
C22.2 No. 213 operating equipment for explosionendangered<br />
rooms of the Class I<br />
and II, Department 2, and Class III;<br />
based on UL 1604.<br />
CSMA/CD Carrier Sense Multiple Access/<br />
Collision Detection<br />
Access process in <strong>ETHERNET</strong> as per<br />
IEEE 802.3. A station ready to transmit<br />
checks whether the transmission<br />
medium is free (carrier sense). It then<br />
starts transmitting while simultaneously<br />
checking whether other stations (multiple<br />
access) have also started to transmit<br />
data. If 2 or more stations transmit<br />
simultaneously, there is a collision. The<br />
stations stop transmission accordingly<br />
(collision detection) and attempt transmission<br />
later on. In the CSMA/CD<br />
process, the network expansion is<br />
determined by a maximum permissible<br />
runtime of data signals on the network<br />
that depend on the data rate.<br />
cUL 1604<br />
cUL 60950<br />
Cut Through<br />
DA<br />
DBPSK<br />
US standard for electrical operating<br />
equipment for explosion-endangered<br />
rooms of the Class I and II, Department 2,<br />
and Class III; based on UL 1604.<br />
US standard for the safety of IT<br />
equipments including electrical office<br />
machines; based on IEC 950.<br />
Method of working of switches in<br />
which a data packet is immediately<br />
relayed further after detecting the target<br />
address. The delay time (latency time)<br />
is thereby small, but wrong packets are<br />
also transmitted onward. In this process,<br />
it is not possible to adjust the speed<br />
between the individual segments. The<br />
phenomenon is also called “On-the-Fly-<br />
Switching”.<br />
Destination Address<br />
Target address within a data telegram.<br />
Differential Quaternary Phase Shift Keying<br />
DBPSK is a modulation procedure of<br />
which is used with the DSSS transmission<br />
method according to standard<br />
802.11 for systems with 1 Mps.<br />
263