FiA_2015
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Ghana<br />
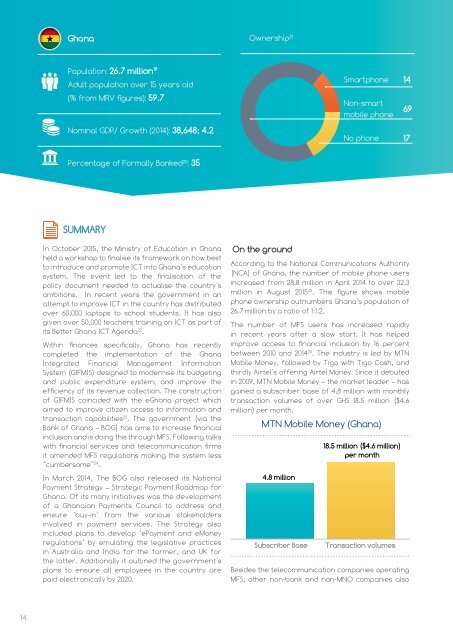
Ownership 21 Smartphone 14<br />
Population: 26.7 million 19<br />
Adult population over 15 years old<br />
(% from MRV figures): 59.7<br />
Non-smart<br />
mobile phone<br />
69<br />
Nominal GDP/ Growth (2014): 38,648; 4.2<br />
No phone 17<br />
Percentage of Formally Banked 20 : 35<br />
SUMMARY<br />
In October <strong>2015</strong>, the Ministry of Education in Ghana<br />
held a workshop to finalise its framework on how best<br />
to introduce and promote ICT into Ghana’s education<br />
system. The event led to the finalisation of the<br />
policy document needed to actualise the country’s<br />
ambitions. In recent years the government in an<br />
attempt to improve ICT in the country has distributed<br />
over 60,000 laptops to school students. It has also<br />
given over 50,000 teachers training on ICT as part of<br />
its Better Ghana ICT Agenda 22 .<br />
Within finances specifically, Ghana has recently<br />
completed the implementation of the Ghana<br />
Integrated Financial Management Information<br />
System (GIFMIS) designed to modernise its budgeting<br />
and public expenditure system; and improve the<br />
efficiency of its revenue collection. The construction<br />
of GIFMIS coincided with the eGhana project which<br />
aimed to improve citizen access to information and<br />
transaction capabilities 23 . The government (via the<br />
Bank of Ghana – BOG) has aims to increase financial<br />
inclusion and is doing this through MFS. Following talks<br />
with financial services and telecommunication firms<br />
it amended MFS regulations making the system less<br />
“cumbersome” 24 .<br />
In March 2014, The BOG also released its National<br />
Payment Strategy – Strategic Payment Roadmap for<br />
Ghana. Of its many initiatives was the development<br />
of a Ghanaian Payments Council to address and<br />
ensure ‘buy-in’ from the various stakeholders<br />
involved in payment services. The Strategy also<br />
included plans to develop ‘ePayment and eMoney<br />
regulations’ by emulating the legislative practices<br />
in Australia and India for the former, and UK for<br />
the latter. Additionally it outlined the government’s<br />
plans to ensure all employees in the country are<br />
paid electronically by 2020.<br />
On the ground<br />
According to the National Communications Authority<br />
(NCA) of Ghana, the number of mobile phone users<br />
increased from 28.8 million in April 2014 to over 32.3<br />
million in August <strong>2015</strong> 25 . This figure shows mobile<br />
phone ownership outnumbers Ghana’s population of<br />
26.7 million by a ratio of 1:1.2.<br />
The number of MFS users has increased rapidly<br />
in recent years after a slow start. It has helped<br />
improve access to financial inclusion by 16 percent<br />
between 2010 and 2014 26 . The industry is led by MTN<br />
Mobile Money, followed by Tigo with Tigo Cash, and<br />
thirdly Airtel’s offering Airtel Money. Since it debuted<br />
in 2009, MTN Mobile Money – the market leader – has<br />
gained a subscriber base of 4.8 million with monthly<br />
transaction volumes of over GHS 18.5 million ($4.6<br />
million) per month.<br />
MTN Mobile Money (Ghana)<br />
4.8 million<br />
Subscriber Base<br />
18.5 million ($4.6 million)<br />
per month<br />
Transaction volumes<br />
Besides the telecommunication companies operating<br />
MFS, other non-bank and non-MNO companies also<br />
14