TUBERCULOSIS
2dnCECj
2dnCECj
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
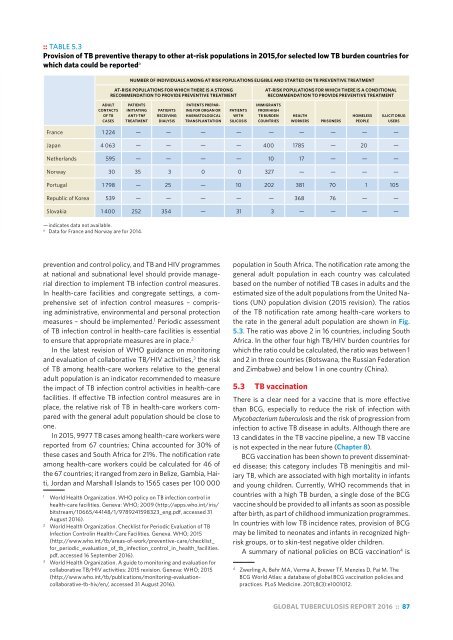
:: TABLE 5.3<br />
Provision of TB preventive therapy to other at-risk populations in 2015,for selected low TB burden countries for<br />
which data could be reported a<br />
NUMBER OF INDIVIDUALS AMONG AT RISK POPULATIONS ELIGIBLE AND STARTED ON TB PREVENTIVE TREATMENT<br />
AT-RISK POPULATIONS FOR WHICH THERE IS A STRONG<br />
RECOMMENDATION TO PROVIDE PREVENTIVE TREATMENT<br />
AT-RISK POPULATIONS FOR WHICH THERE IS A CONDITIONAL<br />
RECOMMENDATION TO PROVIDE PREVENTIVE TREATMENT<br />
ADULT<br />
CONTACTS<br />
OF TB<br />
CASES<br />
PATIENTS<br />
INITIATING<br />
ANTI-TNF<br />
TREATMENT<br />
PATIENTS<br />
RECEIVING<br />
DIALYSIS<br />
PATIENTS PREPAR-<br />
ING FOR ORGAN OR<br />
HAEMATOLOGICAL<br />
TRANSPLANTATION<br />
PATIENTS<br />
WITH<br />
SILICOSIS<br />
IMMIGRANTS<br />
FROM HIGH<br />
TB BURDEN<br />
COUNTRIES<br />
HEALTH<br />
WORKERS<br />
PRISONERS<br />
HOMELESS<br />
PEOPLE<br />
ILLICIT DRUG<br />
USERS<br />
France 1 224 — — — — — — — — —<br />
Japan 4 063 — — — — 400 1785 — 20 —<br />
Netherlands 595 — — — — 10 17 — — —<br />
Norway 30 35 3 0 0 327 — — — —<br />
Portugal 1 798 — 25 — 10 202 381 70 1 105<br />
Republic of Korea 539 — — — — — 368 76 — —<br />
Slovakia 1 400 252 354 — 31 3 — — — —<br />
— indicates data not available.<br />
a<br />
Data for France and Norway are for 2014.<br />
prevention and control policy, and TB and HIV programmes<br />
at national and subnational level should provide managerial<br />
direction to implement TB infection control measures.<br />
In health-care facilities and congregate settings, a comprehensive<br />
set of infection control measures – comprising<br />
administrative, environmental and personal protection<br />
measures – should be implemented. 1 Periodic assessment<br />
of TB infection control in health-care facilities is essential<br />
to ensure that appropriate measures are in place. 2<br />
In the latest revision of WHO guidance on monitoring<br />
and evaluation of collaborative TB/HIV activities, 3 the risk<br />
of TB among health-care workers relative to the general<br />
adult population is an indicator recommended to measure<br />
the impact of TB infection control activities in health-care<br />
facilities. If effective TB infection control measures are in<br />
place, the relative risk of TB in health-care workers compared<br />
with the general adult population should be close to<br />
one.<br />
In 2015, 9977 TB cases among health-care workers were<br />
reported from 67 countries; China accounted for 30% of<br />
these cases and South Africa for 21%. The notification rate<br />
among health-care workers could be calculated for 46 of<br />
the 67 countries; it ranged from zero in Belize, Gambia, Haiti,<br />
Jordan and Marshall Islands to 1565 cases per 100 000<br />
1<br />
World Health Organization. WHO policy on TB infection control in<br />
health-care facilities. Geneva: WHO; 2009 (http://apps.who.int/iris/<br />
bitstream/10665/44148/1/9789241598323_eng.pdf, accessed 31<br />
August 2016).<br />
2<br />
World Health Organization. Checklist for Periodic Evaluation of TB<br />
Infection Controlin Health-Care Facilities. Geneva. WHO; 2015<br />
(http://www.who.int/tb/areas-of-work/preventive-care/checklist_<br />
for_periodic_evaluation_of_tb_infection_control_in_health_facilities.<br />
pdf, accessed 16 September 2016).<br />
3<br />
World Health Organization. A guide to monitoring and evaluation for<br />
collaborative TB/HIV activities: 2015 revision. Geneva: WHO; 2015<br />
(http://www.who.int/tb/publications/monitoring-evaluationcollaborative-tb-hiv/en/,<br />
accessed 31 August 2016).<br />
population in South Africa. The notification rate among the<br />
general adult population in each country was calculated<br />
based on the number of notified TB cases in adults and the<br />
estimated size of the adult populations from the United Nations<br />
(UN) population division (2015 revision). The ratios<br />
of the TB notification rate among health-care workers to<br />
the rate in the general adult population are shown in Fig.<br />
5.3. The ratio was above 2 in 16 countries, including South<br />
Africa. In the other four high TB/HIV burden countries for<br />
which the ratio could be calculated, the ratio was between 1<br />
and 2 in three countries (Botswana, the Russian Federation<br />
and Zimbabwe) and below 1 in one country (China).<br />
5.3 TB vaccination<br />
There is a clear need for a vaccine that is more effective<br />
than BCG, especially to reduce the risk of infection with<br />
Mycobacterium tuberculosis and the risk of progression from<br />
infection to active TB disease in adults. Although there are<br />
13 candidates in the TB vaccine pipeline, a new TB vaccine<br />
is not expected in the near future (Chapter 8).<br />
BCG vaccination has been shown to prevent disseminated<br />
disease; this category includes TB meningitis and miliary<br />
TB, which are associated with high mortality in infants<br />
and young children. Currently, WHO recommends that in<br />
countries with a high TB burden, a single dose of the BCG<br />
vaccine should be provided to all infants as soon as possible<br />
after birth, as part of childhood immunization programmes.<br />
In countries with low TB incidence rates, provision of BCG<br />
may be limited to neonates and infants in recognized highrisk<br />
groups, or to skin-test negative older children.<br />
A summary of national policies on BCG vaccination 4 is<br />
4<br />
Zwerling A, Behr MA, Verma A, Brewer TF, Menzies D, Pai M. The<br />
BCG World Atlas: a database of global BCG vaccination policies and<br />
practices. PLoS Medicine. 2011;8(3):e1001012.<br />
GLOBAL <strong>TUBERCULOSIS</strong> REPORT 2016 :: 87