- Page 1 and 2:
Oracle® Spatial User’s Guide and
- Page 3 and 4: List of of Tables Examples Figures
- Page 5 and 6: 1.9 Spatial Operators, Procedures,
- Page 7 and 8: 5.1.1 Address Representation ......
- Page 9 and 10: 8 Spatial Analysis and Mining 8.1 S
- Page 11 and 12: SDO_GEOM.SDO_XOR ..................
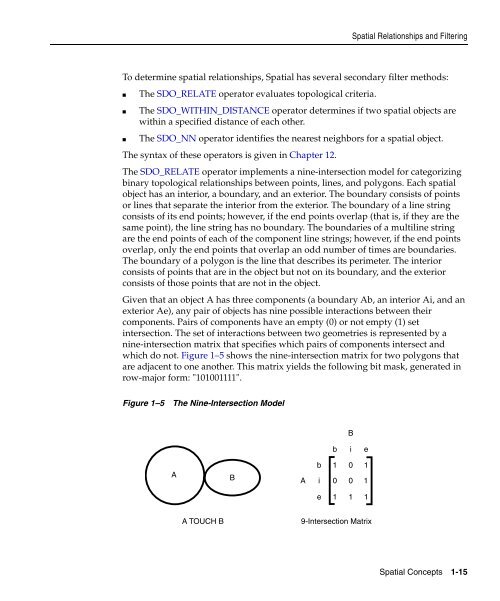
- Page 13 and 14: SDO_LRS.SPLIT_GEOM_SEGMENT.........
- Page 15 and 16: C.2 SDO_WITHIN_DISTANCE Examples...
- Page 17 and 18: List of Figures 1-1 Geometric Types
- Page 19: List of Tables 2-1 Valid SDO_GTYPE
- Page 22 and 23: xxii
- Page 24 and 25: Audience xxiv ■ Audience ■ Docu
- Page 26 and 27: xxvi Chapter 8, "Spatial Analysis a
- Page 28 and 29: Related Documentation Conventions x
- Page 30 and 31: xxx
- Page 32 and 33: Spatial Analysis and Mining Geocodi
- Page 34 and 35: SDO_NN Operator Behavior Changes xx
- Page 36 and 37: xxxvi Information about these subpr
- Page 38 and 39: New Schema: MDDATA xxxviii The new
- Page 41 and 42: 1 Spatial Concepts Oracle Spatial i
- Page 43 and 44: The benefits provided by the object
- Page 45 and 46: 1.5 Data Model Data Model Self-cros
- Page 47 and 48: Data Model Any spatial data has a c
- Page 49 and 50: Data Model If a function accepts an
- Page 51 and 52: Query Model the primary filter comp
- Page 53: Figure 1-3 MBR Enclosing a Geometry
- Page 57 and 58: Figure 1-6 Topological Relationship
- Page 59 and 60: Spatial Aggregate Functions ■ Wit
- Page 61 and 62: 1.12 Geocoding ■ Topology data mo
- Page 63 and 64: 1.16 Spatial Application Hardware R
- Page 65 and 66: 2 Spatial Data Types and Metadata O
- Page 67 and 68: Simple Example: Inserting, Indexing
- Page 69 and 70: 'cola_markets', 'shape', SDO_DIM_AR
- Page 71 and 72: 2.2.1 SDO_GTYPE SDO_GEOMETRY Object
- Page 73 and 74: 2.2.3 SDO_POINT 2.2.4 SDO_ELEM_INFO
- Page 75 and 76: SDO_GEOMETRY Object Type The elemen
- Page 77 and 78: 1003 or 2003 1003 or 2003 2.2.5 SDO
- Page 79 and 80: Figure 2-2 Rectangle Geometry Examp
- Page 81 and 82: Geometry Examples 19 indicates that
- Page 83 and 84: Geometry Examples ■ SDO_GTYPE = 2
- Page 85 and 86: 2.3.5 Point Geometry Examples The s
- Page 87 and 88: 2.3.6 Type 0 (Zero) Element 'point_
- Page 89 and 90: Geometry Metadata Views ■ The non
- Page 91 and 92: 2.4.3 DIMINFO Geometry Metadata Vie
- Page 93 and 94: Table 2-3 Columns in the xxx_SDO_IN
- Page 95 and 96: Table 2-4 (Cont.) Columns in the xx
- Page 97 and 98: Unit of Measurement Support geometr
- Page 99 and 100: 3.1 Bulk Loading 3 Loading Spatial
- Page 101 and 102: Bulk Loading Assume that the ASCII
- Page 103 and 104: Transactional Insert Operations Usi
- Page 105 and 106:
4 Indexing and Querying Spatial Dat
- Page 107 and 108:
Creating a Spatial Index ■ The tr
- Page 109 and 110:
4.1.5 Creating a Cross-Schema Index
- Page 111 and 112:
PARAMETERS (', ') [, PARTITION PAR
- Page 113 and 114:
4.2 Querying Spatial Data 4.2.1 Spa
- Page 115 and 116:
Querying Spatial Data In Figure 4-2
- Page 117 and 118:
Querying Spatial Data ■ geometry2
- Page 119 and 120:
Querying Spatial Data evaluated aga
- Page 121 and 122:
Querying Spatial Data The following
- Page 123 and 124:
5 Geocoding Address Data Geocoding
- Page 125 and 126:
5.1.2 Match Modes Concepts for Geoc
- Page 127 and 128:
Table 5-3 (Cont.) Match Codes for G
- Page 129 and 130:
Table 5-5 (Cont.) SDO_GEO_ADDR Type
- Page 131 and 132:
Using the Geocoding Capabilities SD
- Page 133 and 134:
6 Coordinate Systems (Spatial Refer
- Page 135 and 136:
6.1.8 Transformation Geodetic Coord
- Page 137 and 138:
2003, 8307, -- SRID for WGS 84 long
- Page 139 and 140:
Local Coordinate Support data. For
- Page 141 and 142:
The MDSYS.CS_SRS table contains the
- Page 143 and 144:
::= ::= UNIT [ "", ] ::= LOCAL_
- Page 145 and 146:
Table 6-3 MDSYS.SDO_DATUMS Table Co
- Page 147 and 148:
6.4.4 MDSYS.SDO_ELLIPSOIDS Table Co
- Page 149 and 150:
6.5 Creating a User-Defined Coordin
- Page 151 and 152:
Creating a User-Defined Coordinate
- Page 153 and 154:
6.7.2 Functions Not Supported with
- Page 155 and 156:
Example of Coordinate System Transf
- Page 157 and 158:
Example of Coordinate System Transf
- Page 159 and 160:
Example of Coordinate System Transf
- Page 161 and 162:
7 Linear Referencing System Linear
- Page 163 and 164:
Start Point (5, 10, 0) 7.1.2 Shape
- Page 165 and 166:
7.1.6 Measure Populating Terms and
- Page 167 and 168:
7.1.7 Measure Range of a Geometric
- Page 169 and 170:
Figure 7-7 Creating a Geometric Seg
- Page 171 and 172:
7.5 LRS Operations LRS Operations T
- Page 173 and 174:
Figure 7-10 Clipping, Splitting, an
- Page 175 and 176:
Figure 7-12 Segment Direction with
- Page 177 and 178:
Figure 7-14 Offsetting a Geometric
- Page 179 and 180:
Figure 7-17 Multiple Projection Poi
- Page 181 and 182:
Example of LRS Functions tolerance
- Page 183 and 184:
Table 7-1 (Cont.) Highway Features
- Page 185 and 186:
-- in the geometry. SDO_LRS.DEFINE_
- Page 187 and 188:
BEGIN Example of LRS Functions SELE
- Page 189 and 190:
SQL> -- Are result_geom_1 and resul
- Page 191 and 192:
4 AND a.route_id = 1; Example of LR
- Page 193 and 194:
Example of LRS Functions SDO_LRS.VA
- Page 195 and 196:
8 Spatial Analysis and Mining This
- Page 197 and 198:
Figure 8-1 Spatial Mining and Oracl
- Page 199 and 200:
Colocation Mining The following fun
- Page 201 and 202:
9 Extending Spatial Indexing Capabi
- Page 203 and 204:
SDO_DIM_ELEMENT('X', 0, 20, 0.005),
- Page 205 and 206:
SDO_GEOMETRY Objects in Function-Ba
- Page 207 and 208:
(location long_lat, name varchar2(3
- Page 209:
This document has three parts: Part
- Page 212 and 213:
ALTER INDEX ALTER INDEX Purpose Syn
- Page 214 and 215:
ALTER INDEX Usage Notes Examples
- Page 216 and 217:
ALTER INDEX REBUILD ALTER INDEX REB
- Page 218 and 219:
ALTER INDEX REBUILD Usage Notes Exa
- Page 220 and 221:
CREATE INDEX CREATE INDEX Syntax Pu
- Page 222 and 223:
CREATE INDEX Prerequisites Usage No
- Page 224 and 225:
CREATE INDEX Examples Related Topic
- Page 226 and 227:
DROP INDEX 10-16 Oracle Spatial Use
- Page 228 and 229:
GET_DIMS GET_DIMS Format Descriptio
- Page 230 and 231:
GET_LRS_DIM GET_LRS_DIM Format Desc
- Page 232 and 233:
Table 12-2 Convenience Operators fo
- Page 234 and 235:
SDO_ANYINTERACT Examples The follow
- Page 236 and 237:
SDO_CONTAINS Examples The following
- Page 238 and 239:
SDO_COVEREDBY Examples The followin
- Page 240 and 241:
SDO_COVERS Examples The following e
- Page 242 and 243:
SDO_EQUAL Examples The following ex
- Page 244 and 245:
SDO_FILTER Examples geometry2 can c
- Page 246 and 247:
SDO_FILTER Related Topics ■ SDO_R
- Page 248 and 249:
SDO_INSIDE Examples The following e
- Page 250 and 251:
SDO_JOIN Returns Usage Notes SDO_JO
- Page 252 and 253:
SDO_JOIN Related Topics WHERE c.row
- Page 254 and 255:
SDO_NN Returns Usage Notes Table 12
- Page 256 and 257:
SDO_NN If this operator is used wit
- Page 258 and 259:
SDO_NN Related Topics ■ SDO_NN_DI
- Page 260 and 261:
SDO_NN_DISTANCE Examples Related To
- Page 262 and 263:
SDO_ON example uses the definitions
- Page 264 and 265:
SDO_OVERLAPBDYDISJOINT Examples The
- Page 266 and 267:
SDO_OVERLAPBDYINTERSECT Examples Th
- Page 268 and 269:
SDO_OVERLAPS Examples The following
- Page 270 and 271:
SDO_RELATE Returns Usage Notes The
- Page 272 and 273:
SDO_RELATE ---------- -------------
- Page 274 and 275:
SDO_TOUCH SDO_TOUCH Format Descript
- Page 276 and 277:
SDO_WITHIN_DISTANCE SDO_WITHIN_DIST
- Page 278 and 279:
SDO_WITHIN_DISTANCE Related Topics
- Page 280 and 281:
Table 13-1 (Cont.) Geometry Subprog
- Page 282 and 283:
SDO_GEOM.RELATE SDO_GEOM.RELATE For
- Page 284 and 285:
SDO_GEOM.RELATE Examples ■ EQUAL:
- Page 286 and 287:
SDO_GEOM.SDO_ARC_DENSIFY SDO_GEOM.S
- Page 288 and 289:
SDO_GEOM.SDO_ARC_DENSIFY Examples R
- Page 290 and 291:
SDO_GEOM.SDO_AREA Usage Notes Examp
- Page 292 and 293:
SDO_GEOM.SDO_BUFFER Usage Notes geo
- Page 294 and 295:
SDO_GEOM.SDO_BUFFER Related Topics
- Page 296 and 297:
SDO_GEOM.SDO_CENTROID Usage Notes E
- Page 298 and 299:
SDO_GEOM.SDO_CONVEXHULL Examples Re
- Page 300 and 301:
SDO_GEOM.SDO_DIFFERENCE Usage Notes
- Page 302 and 303:
SDO_GEOM.SDO_DISTANCE SDO_GEOM.SDO_
- Page 304 and 305:
SDO_GEOM.SDO_INTERSECTION SDO_GEOM.
- Page 306 and 307:
SDO_GEOM.SDO_INTERSECTION Related T
- Page 308 and 309:
SDO_GEOM.SDO_LENGTH Usage Notes Exa
- Page 310 and 311:
SDO_GEOM.SDO_MAX_MBR_ORDINATE Usage
- Page 312 and 313:
SDO_GEOM.SDO_MBR Related Topics --
- Page 314 and 315:
SDO_GEOM.SDO_MIN_MBR_ORDINATE Usage
- Page 316 and 317:
SDO_GEOM.SDO_POINTONSURFACE Example
- Page 318 and 319:
SDO_GEOM.SDO_UNION Usage Notes Exam
- Page 320 and 321:
SDO_GEOM.SDO_XOR SDO_GEOM.SDO_XOR F
- Page 322 and 323:
SDO_GEOM.SDO_XOR Related Topics ---
- Page 324 and 325:
SDO_GEOM.VALIDATE_GEOMETRY Usage No
- Page 326 and 327:
SDO_GEOM.VALIDATE_GEOMETRY_WITH_CON
- Page 328 and 329:
SDO_GEOM.VALIDATE_LAYER SDO_GEOM.VA
- Page 330 and 331:
SDO_GEOM.VALIDATE_LAYER Examples Re
- Page 332 and 333:
SDO_GEOM.VALIDATE_LAYER_WITH_CONTEX
- Page 334 and 335:
SDO_GEOM.WITHIN_DISTANCE SDO_GEOM.W
- Page 336 and 337:
SDO_GEOM.WITHIN_DISTANCE Examples R
- Page 338 and 339:
SDO_AGGR_CENTROID SDO_AGGR_CENTROID
- Page 340 and 341:
SDO_AGGR_CONCAT_LINES SDO_AGGR_CONC
- Page 342 and 343:
SDO_AGGR_CONVEXHULL SDO_AGGR_CONVEX
- Page 344 and 345:
SDO_AGGR_LRS_CONCAT because the fir
- Page 346 and 347:
SDO_AGGR_MBR Examples The following
- Page 348 and 349:
SDO_AGGR_UNION See also the more co
- Page 350 and 351:
SDO_CS.TRANSFORM SDO_CS.TRANSFORM F
- Page 352 and 353:
SDO_CS.TRANSFORM SDO_CS.TRANSFORM(C
- Page 354 and 355:
SDO_CS.TRANSFORM_LAYER Examples ■
- Page 356 and 357:
SDO_CS.VALIDATE_WKT SDO_CS.VALIDATE
- Page 358 and 359:
SDO_CS.VIEWPORT_TRANSFORM Examples
- Page 360 and 361:
SDO_CS.VIEWPORT_TRANSFORM 15-12 Ora
- Page 362 and 363:
Table 16-1 (Cont.) Subprograms for
- Page 364 and 365:
Table 16-2 (Cont.) Subprograms for
- Page 366 and 367:
SDO_LRS.CLIP_GEOM_SEGMENT SDO_LRS.C
- Page 368 and 369:
SDO_LRS.CONCATENATE_GEOM_SEGMENTS S
- Page 370 and 371:
SDO_LRS.CONCATENATE_GEOM_SEGMENTS S
- Page 372 and 373:
SDO_LRS.CONNECTED_GEOM_SEGMENTS Usa
- Page 374 and 375:
SDO_LRS.CONVERT_TO_LRS_DIM_ARRAY De
- Page 376 and 377:
SDO_LRS.CONVERT_TO_LRS_GEOM SDO_LRS
- Page 378 and 379:
SDO_LRS.CONVERT_TO_LRS_GEOM WHERE m
- Page 380 and 381:
SDO_LRS.CONVERT_TO_LRS_LAYER Parame
- Page 382 and 383:
SDO_LRS.CONVERT_TO_STD_DIM_ARRAY SD
- Page 384 and 385:
SDO_LRS.CONVERT_TO_STD_GEOM SDO_LRS
- Page 386 and 387:
SDO_LRS.CONVERT_TO_STD_LAYER SDO_LR
- Page 388 and 389:
SDO_LRS.DEFINE_GEOM_SEGMENT SDO_LRS
- Page 390 and 391:
SDO_LRS.DEFINE_GEOM_SEGMENT dim_arr
- Page 392 and 393:
SDO_LRS.DYNAMIC_SEGMENT Usage Notes
- Page 394 and 395:
SDO_LRS.FIND_MEASURE SDO_LRS.FIND_M
- Page 396 and 397:
SDO_LRS.FIND_OFFSET SDO_LRS.FIND_OF
- Page 398 and 399:
SDO_LRS.GEOM_SEGMENT_END_MEASURE SD
- Page 400 and 401:
SDO_LRS.GEOM_SEGMENT_END_PT SDO_LRS
- Page 402 and 403:
SDO_LRS.GEOM_SEGMENT_LENGTH SDO_LRS
- Page 404 and 405:
SDO_LRS.GEOM_SEGMENT_START_MEASURE
- Page 406 and 407:
SDO_LRS.GEOM_SEGMENT_START_PT SDO_L
- Page 408 and 409:
SDO_LRS.GET_MEASURE SDO_LRS.GET_MEA
- Page 410 and 411:
SDO_LRS.GET_NEXT_SHAPE_PT SDO_LRS.G
- Page 412 and 413:
SDO_LRS.GET_NEXT_SHAPE_PT_MEASURE S
- Page 414 and 415:
SDO_LRS.GET_NEXT_SHAPE_PT_MEASURE -
- Page 416 and 417:
SDO_LRS.GET_PREV_SHAPE_PT Parameter
- Page 418 and 419:
SDO_LRS.GET_PREV_SHAPE_PT_MEASURE S
- Page 420 and 421:
SDO_LRS.GET_PREV_SHAPE_PT_MEASURE -
- Page 422 and 423:
SDO_LRS.IS_GEOM_SEGMENT_DEFINED FRO
- Page 424 and 425:
SDO_LRS.IS_MEASURE_DECREASING SELEC
- Page 426 and 427:
SDO_LRS.IS_MEASURE_INCREASING SELEC
- Page 428 and 429:
SDO_LRS.IS_SHAPE_PT_MEASURE Example
- Page 430 and 431:
SDO_LRS.LOCATE_PT Usage Notes Examp
- Page 432 and 433:
SDO_LRS.MEASURE_RANGE SDO_LRS.MEASU
- Page 434 and 435:
SDO_LRS.MEASURE_TO_PERCENTAGE SDO_L
- Page 436 and 437:
SDO_LRS.OFFSET_GEOM_SEGMENT SDO_LRS
- Page 438 and 439:
SDO_LRS.OFFSET_GEOM_SEGMENT Example
- Page 440 and 441:
SDO_LRS.PERCENTAGE_TO_MEASURE Usage
- Page 442 and 443:
SDO_LRS.PROJECT_PT Parameters Usage
- Page 444 and 445:
SDO_LRS.REDEFINE_GEOM_SEGMENT SDO_L
- Page 446 and 447:
SDO_LRS.REDEFINE_GEOM_SEGMENT dim_a
- Page 448 and 449:
SDO_LRS.RESET_MEASURE DECLARE geom_
- Page 450 and 451:
SDO_LRS.REVERSE_GEOMETRY Examples A
- Page 452 and 453:
SDO_LRS.REVERSE_MEASURE Examples Th
- Page 454 and 455:
SDO_LRS.SCALE_GEOM_SEGMENT Usage No
- Page 456 and 457:
SDO_LRS.SET_PT_MEASURE SDO_LRS.SET_
- Page 458 and 459:
SDO_LRS.SET_PT_MEASURE Examples The
- Page 460 and 461:
SDO_LRS.SPLIT_GEOM_SEGMENT Usage No
- Page 462 and 463:
SDO_LRS.TRANSLATE_MEASURE SDO_LRS.T
- Page 464 and 465:
SDO_LRS.VALID_GEOM_SEGMENT SDO_LRS.
- Page 466 and 467:
SDO_LRS.VALID_LRS_PT SDO_LRS.VALID_
- Page 468 and 469:
SDO_LRS.VALID_MEASURE SDO_LRS.VALID
- Page 470 and 471:
SDO_LRS.VALIDATE_LRS_GEOMETRY SDO_L
- Page 472 and 473:
SDO_LRS.VALIDATE_LRS_GEOMETRY 16-11
- Page 474 and 475:
SDO_MIGRATE.TO_CURRENT SDO_MIGRATE.
- Page 476 and 477:
SDO_MIGRATE.TO_CURRENT Usage Notes
- Page 478 and 479:
SDO_TUNE.AVERAGE_MBR SDO_TUNE.AVERA
- Page 480 and 481:
SDO_TUNE.ESTIMATE_RTREE_INDEX_SIZE
- Page 482 and 483:
SDO_TUNE.ESTIMATE_RTREE_INDEX_SIZE
- Page 484 and 485:
SDO_TUNE.EXTENT_OF Related Topics S
- Page 486 and 487:
SDO_TUNE.MIX_INFO Usage Notes Examp
- Page 488 and 489:
SDO_TUNE.QUALITY_DEGRADATION Exampl
- Page 490 and 491:
Table 19-1 (Cont.) Spatial Utility
- Page 492 and 493:
SDO_UTIL.APPEND Examples Related To
- Page 494 and 495:
SDO_UTIL.CIRCLE_POLYGON Usage Notes
- Page 496 and 497:
SDO_UTIL.CONCAT_LINES Examples Rela
- Page 498 and 499:
SDO_UTIL.CONVERT_UNIT Examples Rela
- Page 500 and 501:
SDO_UTIL.ELLIPSE_POLYGON Usage Note
- Page 502 and 503:
SDO_UTIL.EXTRACT Usage Notes Exampl
- Page 504 and 505:
SDO_UTIL.GETNUMELEM SDO_UTIL.GETNUM
- Page 506 and 507:
SDO_UTIL.GETVERTICES SDO_UTIL.GETVE
- Page 508 and 509:
SDO_UTIL.INITIALIZE_INDEXES_FOR_TTS
- Page 510 and 511:
SDO_UTIL.POINT_AT_BEARING Examples
- Page 512 and 513:
SDO_UTIL.POLYGONTOLINE Related Topi
- Page 514 and 515:
SDO_UTIL.PREPARE_FOR_TTS Related To
- Page 516 and 517:
SDO_UTIL.REMOVE_DUPLICATE_VERTICES
- Page 518 and 519:
SDO_UTIL.REVERSE_LINESTRING Related
- Page 520 and 521:
SDO_UTIL.SIMPLIFY Examples For exam
- Page 522 and 523:
SDO_UTIL.SIMPLIFY Related Topics Fi
- Page 524 and 525:
SDO_UTIL.TO_GMLGEOMETRY Examples An
- Page 526 and 527:
SDO_UTIL.TO_GMLGEOMETRY SDO_UTIL.TO
- Page 528 and 529:
SDO_UTIL.TO_GMLGEOMETRY AS theXMLEl
- Page 530 and 531:
SDO_UTIL.TO_GMLGEOMETRY 19-42 Oracl
- Page 532 and 533:
SDO_GCDR.GEOCODE SDO_GCDR.GEOCODE F
- Page 534 and 535:
SDO_GCDR.GEOCODE_ALL SDO_GCDR.GEOCO
- Page 536 and 537:
SDO_GCDR.GEOCODE_AS_GEOMETRY SDO_GC
- Page 538 and 539:
SDO_GCDR.GEOCODE_AS_GEOMETRY 20-8 O
- Page 540 and 541:
Table 21-1 (Cont.) Subprograms for
- Page 542 and 543:
SDO_SAM.AGGREGATES_FOR_GEOMETRY Usa
- Page 544 and 545:
SDO_SAM.AGGREGATES_FOR_LAYER Usage
- Page 546 and 547:
SDO_SAM.BIN_GEOMETRY SDO_SAM.BIN_GE
- Page 548 and 549:
SDO_SAM.BIN_LAYER SDO_SAM.BIN_LAYER
- Page 550 and 551:
SDO_SAM.COLOCATED_REFERENCE_FEATURE
- Page 552 and 553:
SDO_SAM.COLOCATED_REFERENCE_FEATURE
- Page 554 and 555:
SDO_SAM.SIMPLIFY_GEOMETRY Usage Not
- Page 556 and 557:
SDO_SAM.SIMPLIFY_LAYER Usage Notes
- Page 558 and 559:
SDO_SAM.SPATIAL_CLUSTERS Usage Note
- Page 560 and 561:
SDO_SAM.TILED_AGGREGATES Usage Note
- Page 562 and 563:
SDO_SAM.TILED_BINS SDO_SAM.TILED_BI
- Page 564 and 565:
SDO_SAM.TILED_BINS 21-26 Oracle Spa
- Page 567 and 568:
A Installation, Compatibility, and
- Page 569 and 570:
B Oracle Locator Oracle Locator (al
- Page 571 and 572:
Table B-2 lists Spatial features th
- Page 573 and 574:
C Complex Spatial Queries: Examples
- Page 575 and 576:
C.3 SDO_NN Examples SDO_NN Examples
- Page 577 and 578:
SDO_NN Examples The statement in Ex
- Page 579 and 580:
area An extent or region of dimensi
- Page 581 and 582:
disjoint A geometric relationship w
- Page 583 and 584:
inside A geometric relationship whe
- Page 585 and 586:
proximity A measure of distance bet
- Page 587 and 588:
spatiotemporal data Data that conta
- Page 589 and 590:
Numerics 0 SRID value used with SDO
- Page 591 and 592:
CREATE INDEX statement, 10-10 creat
- Page 593 and 594:
eference information, 13-1 geometry
- Page 595 and 596:
SDO_NN_DISTANCE operator, 12-29 nei
- Page 597 and 598:
function, 14-7 SDO_AGGR_MBR aggrega
- Page 599 and 600:
GETNUMVERTICES, 19-17 GETVERTICES,
- Page 601 and 602:
W well-known text (WKT), 6-9 valida