cistus laurifolius
The genus is one of the characteristic genera of the Mediterranean region, colonizing degraded areas (Attaguile et al., 2000). L. (cistaceae) is a common plant in Anatolia and is used against various ailments in traditional medicine. The plant leaves are used to treat rheumatic and related inflammatory diseases, externally as a bath or poultice to reduce pain in rheumatism, against fever in common cold or applied externally as a plaster on the dorsal part of the body in a line of the kidneys for urinary inflammations.
The genus is one of the characteristic genera of the Mediterranean region, colonizing degraded areas (Attaguile et al., 2000). L. (cistaceae) is a common plant in Anatolia and is used against various ailments in traditional medicine. The plant leaves are used to treat rheumatic and related inflammatory diseases, externally as a bath or poultice to reduce pain in rheumatism, against fever in common cold or applied externally as a plaster on the dorsal part of the body in a line of the kidneys for urinary inflammations.
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
456<br />
Male Swiss albino mice (20–25 g) were purchased from the<br />
animal breeding laboratories of Refik Saydam Central Institute<br />
of Health (Ankara, Turkey). The animals left for 2 days for<br />
acclimatization to animal room conditions were maintained on<br />
standard pellet diet and water ad libitum. The food was withdrawn<br />
on the day before the experiment, but allowed free access<br />
of water. A minimum of six animals was used in each group.<br />
Throughout the experiments, animals were processed according<br />
to the suggested international ethical guidelines for the care of<br />
laboratory animals.<br />
L. leaves were collected from Bolu,<br />
Dörtdivan in May 2002 and was identified by Prof. Dr. M. Vural<br />
from the Department of Botany, Faculty of Science, Gazi University.<br />
A voucher specimen is deposited in the Herbarium of<br />
Faculty of Pharmacy, Gazi University (GUE-2300).<br />
Some 2 kg of powdered material was extracted three times<br />
with EtOH (10 L) by stirring in a 60 C water bath for 8 days<br />
each. The combined ethanol extract was evaporated to dryness<br />
under reduced pressure to yield ‘EtOH extract’ (315 g).<br />
The EtOH extract was then resuspanded in 1500 ml of MeOH<br />
and extracted with -hexane (7 500 ml). Combined hexane<br />
extract was evaporated under reduced pressure to yield<br />
‘Hexane fraction’ (64.8 g). MeOH was removed from the<br />
remaining solution and diluted with distilled H 2 O to 2000 ml<br />
and further fractionated by successive extractions with chloroform<br />
(7 500 ml), ethyl acetate (5 250 ml) and watersaturated<br />
-butanol (3 200 ml). The extracts as well as the<br />
remaining aqueous phase were evaporated to dryness under<br />
reduced pressure to yield the “CHCl 3 Fr.” (98.4 g), “EtOAc<br />
Fr.” (28.3 g), “BuOH Fr.” (29.7 g) and “R–H 2 O Fr.” (84.5 g),<br />
respectively.<br />
Four grams of the CHCl 3 fraction was permeated on a<br />
Sephadex LH-20 column using MeOH as eluent. Some 43<br />
fractions of 15 ml each were collected. Fractions were compared<br />
by TLC on silica gel using CHCl 3 /MeOH (8:2) and<br />
toluene/ether (1:1) as mobile systems and combined as follows:<br />
Fr.1–13 (1.23 g), Fr.14–19 (0.72 g), Fr.20–30 (0.91 g), Fr.31–43<br />
(1.12 g). Some additional 5.36 g of the CHCl 3 fraction were<br />
worked-up under identical conditions to obtain more material for<br />
further purification. Vacuum-chromatography of the flavonoidenriched<br />
fractions (silica gel; petroleum ether/EtOAc (1:1), (1:2)<br />
and EtOAc/MeOH (8:2) as solvent system) and reverse-phase<br />
(RP-18) chromatography using MeOH/H 2 O yielded three pure<br />
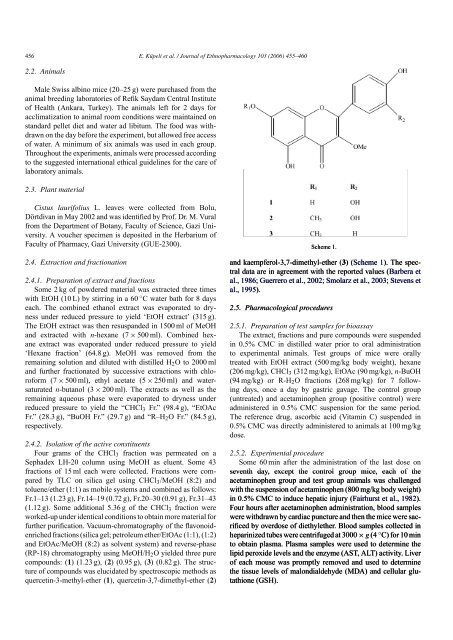
compounds: ( ) (1.23 g), ( ) (0.95 g), ( ) (0.82 g). The structure<br />
of compounds was elucidated by spectroscopic methods as<br />
quercetin-3-methyl-ether ( ), quercetin-3,7-dimethyl-ether ( )<br />
Scheme 1.<br />
and kaempferol-3,7-dimethyl-ether ( ) (Scheme 1). The spectral<br />
data are in agreement with the reported values (Barbera et<br />
al., 1986; Guerrero et al., 2002; Smolarz et al., 2003; Stevens et<br />
al., 1995).<br />
The extract, fractions and pure compounds were suspended<br />
in 0.5% CMC in distilled water prior to oral administration<br />
to experimental animals. Test groups of mice were orally<br />
treated with EtOH extract (500 mg/kg body weight), hexane<br />
(206 mg/kg), CHCl 3 (312 mg/kg), EtOAc (90 mg/kg), -BuOH<br />
(94 mg/kg) or R-H 2 O fractions (268 mg/kg) for 7 following<br />
days, once a day by gastric gavage. The control group<br />
(untreated) and acetaminophen group (positive control) were<br />
administered in 0.5% CMC suspension for the same period.<br />
The reference drug, ascorbic acid (Vitamin C) suspended in<br />
0.5% CMC was directly administered to animals at 100 mg/kg<br />
dose.<br />
Some 60 min after the administration of the last dose on<br />
seventh day, except the control group mice, each of the<br />
acetaminophen group and test group animals was challenged<br />
with the suspension of acetaminophen (800 mg/kg body weight)<br />
in 0.5% CMC to induce hepatic injury (Fairhurst et al., 1982).<br />
Four hours after acetaminophen administration, blood samples<br />
were withdrawn by cardiac puncture and then the mice were sacrificed<br />
by overdose of diethylether. Blood samples collected in<br />
heparinized tubes were centrifuged at 3000 (4 C) for 10 min<br />
to obtain plasma. Plasma samples were used to determine the<br />
lipid peroxide levels and the enzyme (AST, ALT) activity. Liver<br />
of each mouse was promptly removed and used to determine<br />
the tissue levels of malondialdehyde (MDA) and cellular glutathione<br />
(GSH).