IJTCS Vol.-1 Issue-1 March-May, 2017
The Indian Journal of Textile and Clothing Science (IJTCS) is a peer reviewed (refereed) national journal (India). Which is aimed at providing platform to exchange information pertaining to all sectors of textile and the clothing industry among researchers, textile technocrats, fashion designers and industrial experts. The journal focuses on scientific, technical, economical, managerial and all other aspects of textile activity at theoretical and experimental level. IJTCS is aimed at publishing original research articles, review papers, short communications, and letters to the editor and book reviews catering the needs of both industry and academia.
The Indian Journal of Textile and Clothing Science (IJTCS) is a peer reviewed (refereed) national journal (India). Which is aimed at providing platform to exchange information pertaining to all sectors of textile and the clothing industry among researchers, textile technocrats, fashion designers and industrial experts.
The journal focuses on scientific, technical, economical, managerial and all other aspects of textile activity at theoretical and experimental level. IJTCS is aimed at publishing original research articles, review papers, short communications, and letters to the editor and book reviews catering the needs of both industry and academia.
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Indian Journal of Textile and Clothing Science<br />
3.1.1 Strip Strength<br />
Tensile strength has been acknowledged as a<br />
standout amongst the most vital qualities of woven<br />
textiles. Tensile strength is characterized as a most<br />
extreme load that a test example will continue<br />
when subjected to uniaxial tensile stacking. The<br />
strength of a fabric depends on the strength of<br />
constituent yarns, as well as on the yarn and fabric<br />
structure and numerous different components. The<br />
elements, which have impact on the tensile<br />
strength of fabric other than yarn strength, are yarn<br />
material, yarn fineness, number of finishes and<br />
picks per unit length and weave plan. Impact of<br />
weave, weft sort, and compound process on warp<br />
and weft way strip strength of fabric was shown in<br />
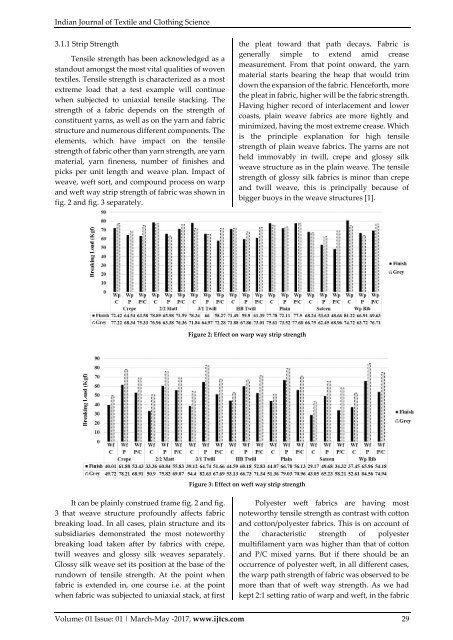
fig. 2 and fig. 3 separately.<br />
the pleat toward that path decays. Fabric is<br />
generally simple to extend amid crease<br />
measurement. From that point onward, the yarn<br />
material starts bearing the heap that would trim<br />
down the expansion of the fabric. Henceforth, more<br />
the pleat in fabric, higher will be the fabric strength.<br />
Having higher record of interlacement and lower<br />
coasts, plain weave fabrics are more tightly and<br />
minimized, having the most extreme crease. Which<br />
is the principle explanation for high tensile<br />
strength of plain weave fabrics. The yarns are not<br />
held immovably in twill, crepe and glossy silk<br />
weave structure as in the plain weave. The tensile<br />
strength of glossy silk fabrics is minor than crepe<br />
and twill weave, this is principally because of<br />
bigger buoys in the weave structures [1].<br />
Figure 2: Effect on warp way strip strength<br />
Figure 3: Effect on weft way strip strength<br />
It can be plainly construed frame fig. 2 and fig.<br />
3 that weave structure profoundly affects fabric<br />
breaking load. In all cases, plain structure and its<br />
subsidiaries demonstrated the most noteworthy<br />
breaking load taken after by fabrics with crepe,<br />
twill weaves and glossy silk weaves separately.<br />
Glossy silk weave set its position at the base of the<br />
rundown of tensile strength. At the point when<br />
fabric is extended in, one course i.e. at the point<br />
when fabric was subjected to uniaxial stack, at first<br />
Polyester weft fabrics are having most<br />
noteworthy tensile strength as contrast with cotton<br />
and cotton/polyester fabrics. This is on account of<br />
the characteristic strength of polyester<br />
multifilament yarn was higher than that of cotton<br />
and P/C mixed yarns. But if there should be an<br />
occurrence of polyester weft, in all different cases,<br />
the warp path strength of fabric was observed to be<br />
more than that of weft way strength. As we had<br />
kept 2:1 setting ratio of warp and weft, in the fabric<br />
<strong>Vol</strong>ume: 01 <strong>Issue</strong>: 01 | <strong>March</strong>-<strong>May</strong> -<strong>2017</strong>, www.ijtcs.com 29