WLS Charolais Catalogue April 2024 L2
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Bri 琀 sh <strong>Charolais</strong> MyOSTATIN Myosta 琀 n Guide<br />
What is Myosta 琀 n?<br />
Why<br />
Myosta<br />
Myostatin?<br />
琀 n is a gene that in 昀 uences the produc 琀 on of proteins which control muscle<br />
Knowing the myostatin status of your animals, will help you to select bulls with the most appropriate<br />
myostatin development. traits for When your breeding an animal program. is iden This 琀 昀 will ed lead as having to better one calving of the ease muta and help 琀 ons with it means the everpresent<br />
that they trend have to improve inac 琀 ve carcass genes which confirmation do not control and quality. muscle There growth are both as e 昀 advantages ec 琀 vely, this and<br />
disadvantages can result in of increased breeding with muscle animals mass. carrying Currently the myostatin ca 琀 le, gene, there which are is 19 why known it is imperative muta 琀 ons that<br />
you know the carrier status of your breeding animals.<br />
of the gene and a 昀 er extensive tes 琀 ng for the nine most common varients, we have<br />
What concluded is Myostatin? that the Bri 琀 sh <strong>Charolais</strong> ca 琀 le popula 琀 on only contains two - F94L &<br />
Myostatin Q204X. is a gene that influences the production of proteins which control muscle development. When<br />
an animal is identified as having one of the mutations it means that they have inactive genes which do<br />
Why are we tes 琀 ng for Myosta 琀 n?<br />
not control muscle growth as effectively, this can result in increased muscle mass, or “double muscling”.<br />
Knowing the myosta 琀 n status of your animals will help you to select bulls with<br />
Currently in cattle, there are 19 known mutations of the gene, some of these mutations are breed specific<br />
the most appropriate myosta 琀 n traits for your breeding programme. This will lead<br />
and within the British <strong>Charolais</strong> herd book, two prevalent variants are found – F94L & Q204X.<br />
to be 琀 er calving ease and help with the ever-present trend to improve carcase<br />
F94L conforma 琀 on and quality. However, it is just one tool which should be used in<br />
Research conjunc conducted 琀 with by the Adelaide wider University informa 琀 in on Australia available concluded such as that Es the 琀 mated effect of Breeding the F94L Values mutation<br />
on birth and growth traits was not significant but was associated with an increase in meat weight and<br />
(EBV’s) – which predict the performance of the animal based on its back pedigree,<br />
a reduction in fat depth. The results for the average effect of substituting a single copy of the variant<br />
F94L accurate variant indicated measurements an increase and in silverside the performance between 5.8 of and its 7.2% herd and mates meat weight – and of your between own 5.9<br />
and judgement 7.3%. There on was type also and a reduction pedigree. in P8 fat depth, intramuscular fat and carcass fat weight.<br />
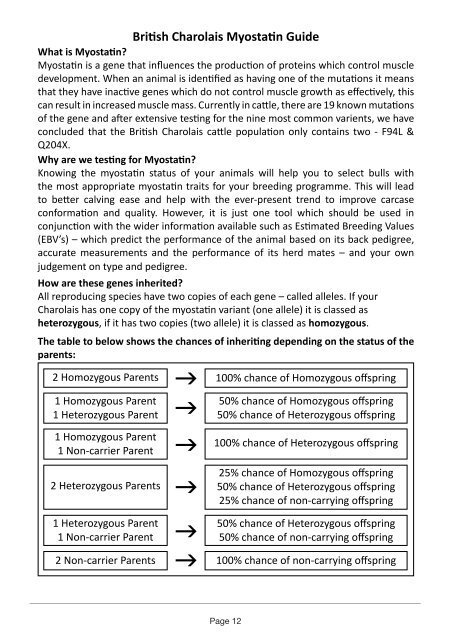
Calves How used are these for this genes study, inherited?<br />
carrying 2 copies of the variant F94L marker, produced carcasses with<br />
approximately 12 to 15% more meat and 16 to 33% less fat compared with calves with no copies of<br />
All reproducing species have two copies of each gene – called alleles. If your<br />
the variant F94L allele, while single carriers produced approximately 3% more meat weight, while fat<br />
depth <strong>Charolais</strong> measured has on one live copy calves of was the myosta 9.8% lower. 琀 n variant Therefore, (one the allele) F94L variant it is classed appears as to have many<br />
positive heterozygous, effects without if has correlated two copies negative (two effects allele) of some it is other classed myostatin as homozygous.<br />
variants.<br />
Q204X The table to below shows the chances of inheri 琀 ng depending on the status of the<br />
In parents: a study published in the Oxford University Press Journal of Science on the effects of the Q204X gene<br />
in <strong>Charolais</strong> cattle, it was shown that the Q204X mutation leads to an increase in muscle mass. This<br />
creates 2 Homozygous a dramatic increase Parents in saleable meat yield 100% because chance of of the Homozygous improved dressing o 昀 spring percentage,<br />
reduced carcass fatness, and fineness gof the limb bones. In this study, animals with a single copy of a<br />
mutated allele were slightly heavier at birth.<br />
1 Homozygous Parent<br />
50% chance of Homozygous o 昀 spring<br />
These 1 animals Heterozygous showed consistently Parent greater gcarcass 50% yields, chance the thighs of Heterozygous were thicker, and o the 昀 spring rib eye areas<br />
were larger. They were also markedly leaner, with less internal fat and less fat on the 6th rib. Therefore,<br />
the presence<br />
1 Homozygous<br />
of even one<br />
Parent<br />
copy of Q204X was shown to increase the beef value of these animals<br />
drastically. Regarding meat quality, trained taste 100% panellists chance of indicated Heterozygous that the o meat 昀 spring of young<br />
heterozygous 1 Non-carrier bulls was Parent more tender. gThis better tenderness can be a consequence of a reduced<br />
collagen content and a smaller mean area of the muscle fibre section because both characteristics have<br />
been shown to be related to muscle tenderness. 25% chance of Homozygous o 昀 spring<br />
2 Heterozygous Parents<br />
50% chance of Heterozygous o 昀 spring<br />
g<br />
Variant Double Increased Increased Increased Increased 25% chance Lower of non-carrying Breeding o 昀 spring<br />
Name muscling muscling birth calving Meat Fat Recommendation<br />
weight difficulty tenderness<br />
g<br />
g<br />
1 Heterozygous Parent<br />
50% chance of Heterozygous o 昀 spring<br />
1 Non-carrier Parent<br />
50% chance of non-carrying o 昀 spring<br />
Q204X ✔ ✔ ✔ ✔<br />
2 Non-carrier Parents 100% chance of non-carrying o 昀 spring<br />
F94L ✔ ✔ ✔<br />
Best for breeding terminal animals.<br />
Not recommended to use a<br />
homozygous bull on heterozygous<br />
heifers or cows with a smaller pelvis<br />
OK for all breeding animals<br />
to be homozygous<br />
Page 12