SRPS PS - Plastic Surgery Internal
SRPS PS - Plastic Surgery Internal
SRPS PS - Plastic Surgery Internal
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Critical sensibility of the fingertip can be restored by<br />
free neurosensory flaps 510–516 or microvascular toe-pulp<br />
transfer. 517–519 Toe-to-hand transfers in cases of thumb<br />
reconstruction are discussed in the “Microsurgery: Free<br />
Tissue Transfer and Replantation” issue of Selected<br />
Readings in <strong>Plastic</strong> <strong>Surgery</strong>. Protective sensibility of the<br />
palm and dorsum of the hand usually is achieved by<br />
thin muscle, fascial, or fasciocutaneous flaps. 520<br />
The first web space flap of the foot is the “gold<br />
standard” of neurosensory flaps. 513 It consists of the<br />
lateral aspect of the great toe and the medial aspect of<br />
the second toe. The flap is supplied by the first dorsal<br />
metatarsal artery, a branch of the dorsalis pedis artery,<br />
or the first plantar metatarsal artery. Its innervation is<br />
through both the deep peroneal nerve and the medial<br />
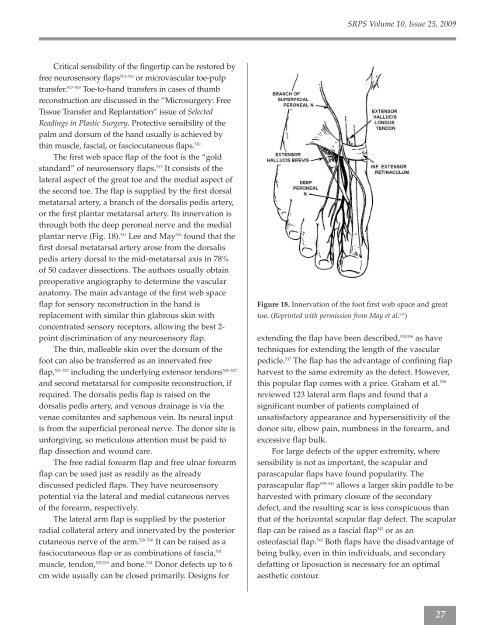
plantar nerve (Fig. 18). 511 Lee and May 516 found that the<br />
first dorsal metatarsal artery arose from the dorsalis<br />
pedis artery dorsal to the mid-metatarsal axis in 78%<br />
of 50 cadaver dissections. The authors usually obtain<br />
preoperative angiography to determine the vascular<br />
anatomy. The main advantage of the first web space<br />
flap for sensory reconstruction in the hand is<br />
replacement with similar thin glabrous skin with<br />
concentrated sensory receptors, allowing the best 2point<br />
discrimination of any neurosensory flap.<br />
The thin, malleable skin over the dorsum of the<br />
foot can also be transferred as an innervated free<br />
flap, 521–523 including the underlying extensor tendons 524–527<br />
and second metatarsal for composite reconstruction, if<br />
required. The dorsalis pedis flap is raised on the<br />
dorsalis pedis artery, and venous drainage is via the<br />
venae comitantes and saphenous vein. Its neural input<br />
is from the superficial peroneal nerve. The donor site is<br />
unforgiving, so meticulous attention must be paid to<br />
flap dissection and wound care.<br />
The free radial forearm flap and free ulnar forearm<br />
flap can be used just as readily as the already<br />
discussed pedicled flaps. They have neurosensory<br />
potential via the lateral and medial cutaneous nerves<br />
of the forearm, respectively.<br />
The lateral arm flap is supplied by the posterior<br />
radial collateral artery and innervated by the posterior<br />
cutaneous nerve of the arm. 528–530 It can be raised as a<br />
fasciocutaneous flap or as combinations of fascia, 531<br />
muscle, tendon, 532,533 and bone. 534 Donor defects up to 6<br />
cm wide usually can be closed primarily. Designs for<br />
<strong>SR<strong>PS</strong></strong> Volume 10, Issue 25, 2009<br />
Figure 18. Innervation of the foot first web space and great<br />
toe. (Reprinted with permission from May et al. 511 )<br />
extending the flap have been described, 535,536 as have<br />
techniques for extending the length of the vascular<br />
pedicle. 537 The flap has the advantage of confining flap<br />
harvest to the same extremity as the defect. However,<br />
this popular flap comes with a price. Graham et al. 538<br />
reviewed 123 lateral arm flaps and found that a<br />
significant number of patients complained of<br />
unsatisfactory appearance and hypersensitivity of the<br />
donor site, elbow pain, numbness in the forearm, and<br />
excessive flap bulk.<br />
For large defects of the upper extremity, where<br />
sensibility is not as important, the scapular and<br />
parascapular flaps have found popularity. The<br />
parascapular flap 539–541 allows a larger skin paddle to be<br />
harvested with primary closure of the secondary<br />
defect, and the resulting scar is less conspicuous than<br />
that of the horizontal scapular flap defect. The scapular<br />
flap can be raised as a fascial flap 542 or as an<br />
osteofascial flap. 543 Both flaps have the disadvantage of<br />
being bulky, even in thin individuals, and secondary<br />
defatting or liposuction is necessary for an optimal<br />
aesthetic contour.<br />
27