Chapter 8. ORGANIC SOLAR CELLS - from and for SET students
Chapter 8. ORGANIC SOLAR CELLS - from and for SET students
Chapter 8. ORGANIC SOLAR CELLS - from and for SET students
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
<strong>Chapter</strong> 4<br />
III-V Technologies<br />
III-V Technologies are solar cells with high efficiencies due to high purities <strong>and</strong> multi junction technologies.<br />
These films are very expensive though. The main applications are space <strong>and</strong> concentrated PV.<br />
4.1 Theoretical limits of per<strong>for</strong>mances solar cells<br />
Photons incident on the surface of a semiconductor will be either reflected <strong>from</strong> the top surface, will be absorbed<br />
in the material or, failing either of the above two processes, will be transmitted through the material. For<br />
photovoltaic devices, reflection <strong>and</strong> transmission are typically considered loss mechanisms as photons which are<br />
not absorbed do not generate power. If the photon is absorbed it will raise an electron <strong>from</strong> the valence b<strong>and</strong><br />
to the conduction b<strong>and</strong>. A key factor in determining if a photon is absorbed or transmitted is the energy of the<br />
photon. Photons falling onto a semiconductor material can be divided into three groups based on their energy<br />
compared to that of the semiconductor b<strong>and</strong> gap.<br />
� Eph < EG: Photons with energy Eph less than the b<strong>and</strong> gap energy EG interact only weakly with the<br />
semiconductor, passing through it as if it were transparent.<br />
� Eph = EG: Just enough energy to create an electron hole pair, efficiently absorbed.<br />
� Eph > EG: Photons with energy much greater than the b<strong>and</strong> gap are strongly absorbed, subsequently<br />
thermal relaxation<br />
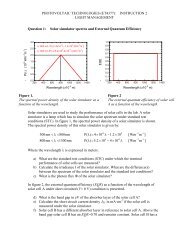
The b<strong>and</strong>gap is the point <strong>from</strong> which a solar cell starts to absorb, energy below it is lost. Another part of<br />
the photon energy is lost as heat (area above cell).<br />
Figure 4.1: Spectral Mismatch<br />
Photon utilization efficiency is the fraction of energy of photon which is used to create the electron<br />
whole pair.<br />
17