776-00301 TYRIN IM bro - The Dow Chemical Company
776-00301 TYRIN IM bro - The Dow Chemical Company
776-00301 TYRIN IM bro - The Dow Chemical Company
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
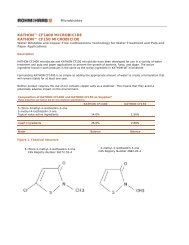
Window Profile,<br />
Pipe, and Rigid Sheet<br />
Applications for<br />
<strong>TYRIN</strong> 6000 CPE and<br />
<strong>TYRIN</strong> 7000 CPE<br />
Impact Modifiers<br />
<strong>TYRIN</strong> 6000 CPE and <strong>TYRIN</strong> 7000 CPE<br />
Impact Modifiers<br />
Performance Plastics – Europe, Middle East and Africa<br />
1 of 9
2 of 9<br />
<strong>TYRIN</strong> 6000 CPE and <strong>TYRIN</strong> 7000 CPE Impact Modifiers<br />
<strong>TYRIN</strong> Chlorinated Polyethylene (CPE) thermoplastic resins are widely used as impact modifiers in PVC extrusion<br />
and injection molding applications. Especially effective in products such as window profiles, pipe, and siding,<br />
<strong>TYRIN</strong> 6000 CPE and <strong>TYRIN</strong> 7000 CPE provide excellent corner weld strength and high surface gloss. <strong>The</strong>se resins<br />
offer high impact efficiency and perform well at low temperatures, giving very good weather resistance for all<br />
climate conditions. <strong>The</strong> resins can be blended with acrylics resulting in an optimum cost/performance solution.<br />
<strong>TYRIN</strong> 7000 is available in bulk, supplied by truck and can be stored in silos. <strong>TYRIN</strong> CPE offers the possibility to<br />
reduce the overall color pigment costs on colored window profile applications. Furthermore, <strong>TYRIN</strong> CPE resins<br />
work particularly well with calcium-zink stabilization to control gelation levels and melt temperature.<br />
All in, <strong>TYRIN</strong> resins help fabricators and compounders meet increasingly critical performance requirements and<br />
cost-control needs.<br />
Real Solutions<br />
<strong>Dow</strong> provides solutions that help meet the<br />
unique processing and performance requirements<br />
of current and next generation impact<br />
modification products, along with technical<br />
support that extends from formulation<br />
through processing and end-use requirements.<br />
<strong>The</strong> Global R&D Center in the USA, along<br />
with <strong>Dow</strong>’s local Technical Service &<br />
Development facilities, have the scientists,<br />
equipment, and technologies to provide a<br />
very high level of customer-focused services.<br />
® Trademark of <strong>The</strong> <strong>Dow</strong> <strong>Chemical</strong> <strong>Company</strong> (“<strong>Dow</strong>”) or an affiliated company of <strong>Dow</strong><br />
Product Properties<br />
<strong>The</strong> typical product properties of <strong>TYRIN</strong> 6000<br />
and <strong>TYRIN</strong> 7000 are summarized in Table 1.<br />
<strong>The</strong>y are both free flowing white powders,<br />
produced by the chlorination of low pressure<br />
polyethylene in a water slurry.<br />
Table 1: Typical properties of <strong>TYRIN</strong> CPE grades for impact modification<br />
Typical Properties Units Test Method <strong>TYRIN</strong> 6000 <strong>TYRIN</strong> 7000<br />
Chlorine content<br />
Melt Viscosity<br />
wt % ISO 1158 35 35<br />
(145 s-1 , 190°C) Pa.s ISO 11443 2400 2900<br />
Heat of Fusion J/g EH-TYR-QP-AV 2011
PVC Modification<br />
Polyvinyl-chloride (PVC) is an outstanding<br />
material for the production of rigid extruded<br />
goods, such as pipes or profiles. However<br />
due to its high glass transition temperature,<br />
it has shortcomings in impact strength. It has<br />
therefore to be modified to provide impact<br />
strength at ambient and low temperature.<br />
Impact modifiers provide PVC compounds a<br />
consistently ductile behaviour over a <strong>bro</strong>ad<br />
temperature range. <strong>The</strong>y are flexible materials<br />
which are partially compatible with PVC.<br />
<strong>The</strong>y form a discrete phase in the PVC matrix,<br />
which absorbs and dissipates shock energy.<br />
During suspension polymerization of PVC grain<br />
particles with a typical diameter of 65-150<br />
microns are formed. (Figure 1). <strong>The</strong>se consist<br />
of smaller particles ranging from 0.2 to 1.5<br />
microns in size: the primary particles. When<br />
the PVC powder is being processed into a<br />
fabricated product (e.g. by extrusion, calendering)<br />
the grain structure is <strong>bro</strong>ken down<br />
mainly by shear and the primary particles are<br />
molten together at their surfaces.<br />
<strong>The</strong> dominant factor in controlling the<br />
degree of fusion is the melt temperature<br />
and the additive package, consisting of<br />
stablizers, lubricants, fillers, and impact<br />
modifiers can affect the range of processing<br />
conditions required for optimum impact<br />
strength. This process is called fusion or<br />
gelation. <strong>The</strong> achieved impact strength is<br />
controlled by the degree of fusion of the<br />
PVC matrix. An under fused or over fused<br />
melt lowers the impact strength of the<br />
final product.<br />
Trademark of <strong>The</strong> <strong>Dow</strong> <strong>Chemical</strong> <strong>Company</strong> (“<strong>Dow</strong>”) or an affiliated company of <strong>Dow</strong><br />
Essentially two classes of impact modifiers<br />
exist, which are physically blended with s-PVC<br />
during extrusion on twin screw extruders.<br />
Acrylic based modifiers are often used,<br />
which are core-shell particles of typically a<br />
butyl-acrylate flexible core with a rigid shell<br />
of poly-methyl-methacrylate. <strong>The</strong> shell<br />
enables a good flowability of the product<br />
and a good compatibility to PVC to enable a<br />
good dispersion.<br />
<strong>TYRIN</strong> Chlorinated Polyethylene (CPE) is a<br />
thermoplastic material and its morphology<br />
will develop during the melt processing of<br />
the PVC dry-blend. <strong>TYRIN</strong> CPE and other low<br />
melting ingredients will coat the PVC particles.<br />
Figure 1: Primary particles structure of s-PVC<br />
65-150 Micron<br />
During subsequent extrusion a phase inversion<br />
occurs and creates discrete CPE particles in a<br />
continuous matrix of PVC.<br />
<strong>TYRIN</strong> CPE offers an excellent combination of<br />
compatibility, processibility, weatherability,<br />
and impact efficiency in many rigid PVC formulations,<br />
like window profiles, pipes, rigid<br />
and foamed sheet, etc. <strong>The</strong> use of <strong>TYRIN</strong> CPE<br />
makes it possible to use higher filler levels<br />
because being thermoplastic in nature, it<br />
flows and encapsulates inorganic filler particles.<br />
This coating provides a mechanism to<br />
control the particle adhesion to the PVC<br />
matrix and thus improves the contribution to<br />
impact resistance, whereas the filler aids<br />
<strong>TYRIN</strong> dispersion.<br />
Primary<br />
Particles<br />
Skin<br />
Grain<br />
3 of 9
4 of 9<br />
<strong>TYRIN</strong> CPE in Window Profiles<br />
<strong>The</strong> main advantages of <strong>TYRIN</strong> CPE in<br />
window profiles are:<br />
• Good low temperature impact strength<br />
• High surface gloss<br />
• Excellent corner weld strength<br />
• Good filler acceptance<br />
• Good lubrication properties with calciumzink<br />
stabilizers<br />
• Cost effective system<br />
• Compatible with acrylic modifiers<br />
Window profiles manufactured with <strong>TYRIN</strong><br />
impact modifiers can meet all requirements of<br />
the European standards. An overview of the<br />
common standards can be found in Table 2.<br />
Table 2: European Standards<br />
for window profiles<br />
Germany DIN 16830<br />
RAL GZ 716/1<br />
UK BS 7413<br />
France P 24-500<br />
Italy UNI 8648<br />
Trademark of <strong>The</strong> <strong>Dow</strong> <strong>Chemical</strong> <strong>Company</strong> (“<strong>Dow</strong>”) or an affiliated company of <strong>Dow</strong><br />
Window profiles are very demanding in terms<br />
of properties. <strong>TYRIN</strong> CPE helps to achieve the<br />
best corner weld strength and can provide<br />
very good gloss.<br />
During the welding process, <strong>TYRIN</strong> CPE act<br />
efficiently as a flow enhancer and can significantly<br />
improve the corner weld strength of<br />
existing formulations. (Figure 2).<br />
<strong>TYRIN</strong> CPE will give excellent impact properties<br />
in order to meet the requirements under<br />
a wide processing range and it also reduces<br />
waste generated during finishing operations,<br />
such as sawing, drilling, and cutting, due to<br />
its excellent resistance against shattering<br />
and brittle breaks.<br />
<strong>The</strong> U-notched Charpy impact strength has<br />
been shown to be most sensitive to melt<br />
temperature variations and has been chosen<br />
to give an indication of the impact efficiency<br />
and the processing window. <strong>TYRIN</strong> 7000 is<br />
more efficient at lower addition levels<br />
(Shown in Figure 3). <strong>The</strong> Double-V notched<br />
impact strength shows the same trend, but is<br />
not so sensitive at lower addition levels.<br />
Data have shown that a ductile V-notched<br />
Charpy impact is achievable with 6 phr.<br />
<strong>TYRIN</strong> 7000.<br />
<strong>The</strong> processing window indicates the temperature<br />
range which allows the production of<br />
window profiles with the required properties.<br />
Figure 4 gives a comparison between profiles<br />
with different impact modification, extruded<br />
at different temperature settings. <strong>The</strong> difference<br />
in their respective viscosity results in a<br />
more robust behavior of <strong>TYRIN</strong> 7000 at higher<br />
temperatures and <strong>TYRIN</strong> 6000 at lower<br />
temperatures, which makes <strong>TYRIN</strong> 7000<br />
more suitable for high speed extrusion and<br />
calcium-zink stabilization, where higher melt<br />
temperatures are experienced. Typical formulations<br />
can be found in Tables 3 and 4. Due<br />
to the voluntary vinyl agreement, many new<br />
developments will be based on calcium-zink<br />
stabilization, but lead stabilization is still<br />
widely used as an efficient stabilizer system<br />
for PVC window profiles with a good longterm<br />
track record.<br />
Due to their slight lubrication effect, both<br />
<strong>TYRIN</strong> CPE grades are in general very suitable<br />
for calcium-zink stabilization to control<br />
the gelation levels and melt temperature.
Figure 2: Corner weld strength of window profiles.<br />
Corner Weld Strength (N)<br />
Figure 3: U-Notched Charpy Impact Strength [kJ/m 2 ] as a function of<br />
modifier addition level.<br />
Notched Impact (kJ/m 2)<br />
Figure 4: U-Notched Charpy Impact Strength [kJ/m 2 ] as a function of<br />
processing temperature.<br />
Notched Impact (kJ/m 2)<br />
1,400<br />
1,200<br />
1,000<br />
800<br />
600<br />
400<br />
200<br />
0<br />
60<br />
50<br />
40<br />
30<br />
20<br />
Incumbent Modifier With 6 phr <strong>TYRIN</strong> 6000<br />
10<br />
0<br />
<strong>TYRIN</strong> 7000<br />
<strong>TYRIN</strong> 6000<br />
3 4 5 6 7 8<br />
60<br />
50<br />
40<br />
30<br />
Modifier Level (phr)<br />
20<br />
<strong>TYRIN</strong> 6000 /Pb<br />
10<br />
0<br />
<strong>TYRIN</strong> 7000 /CaZn<br />
<strong>TYRIN</strong> 7000 /Pb<br />
Cold Normal Hot<br />
Processing Temperature Settings<br />
Trademark of <strong>The</strong> <strong>Dow</strong> <strong>Chemical</strong> <strong>Company</strong> (“<strong>Dow</strong>”) or an affiliated company of <strong>Dow</strong><br />
Table 3: Typical window profile<br />
formulation, lead stabilized, white<br />
S-PVC K-68 100 phr<br />
<strong>TYRIN</strong> CPE 5-7<br />
Di-basic lead phosphite 3.5<br />
Lead stearate 0.4<br />
Wax ester 0.2<br />
Calcium stearate 0.3<br />
Paraffin wax 0.1<br />
Processing aid 1<br />
Titanium dioxide 4<br />
Calcium carbonate 5<br />
Table 4: Typical window profile formulation,<br />
calcium-zink stabilized, white<br />
S-PVC K-68 100 phr<br />
<strong>TYRIN</strong> CPE 5-7<br />
Calcium-Zink One-Pack 4.5<br />
Titanium dioxide 4<br />
Calcium carbonate 5<br />
5 of 9
6 of 9<br />
Weatherability<br />
In rigid PVC window profiles the use of lead<br />
stabilizers is common practice. In the last<br />
decennium the use of calcium-zink stabilizers<br />
has increased substantially, as their cost/performance<br />
has become very attractive as well.<br />
Natural weatherability tests with <strong>TYRIN</strong> CPE<br />
have been conducted in Bandol (France), an<br />
area with high levels of sun exposure, combined<br />
with a wide range of humidity levels<br />
with an annual solar energy of around 6<br />
GJ/m2 . Relevant profile characteristics like<br />
brightness, yellowness, and impact strength<br />
were compared before and after exposure,<br />
as shown in Figures 5, 6, and 7.<br />
<strong>The</strong> stabilizer systems were provided by<br />
major European suppliers and the data are<br />
average numbers of the good systems, which<br />
were all within a narrow bandwidth. After<br />
2 years of exposure, the color stability and<br />
the impact properties remain very good and<br />
the requirements, as set by the different<br />
standards and authorities can be met with<br />
profiles modified with <strong>TYRIN</strong> CPE, when<br />
properly formulated and processed, both with<br />
lead and with calcium-zink stabilization.<br />
Trademark of <strong>The</strong> <strong>Dow</strong> <strong>Chemical</strong> <strong>Company</strong> (“<strong>Dow</strong>”) or an affiliated company of <strong>Dow</strong><br />
Figure 5: Color change of profiles modified with <strong>TYRIN</strong> CPE.<br />
b (yellow-blue)<br />
5<br />
4<br />
3<br />
2<br />
1<br />
0<br />
Figure 6: Tensile Impact after natural weathering of profiles modified<br />
with <strong>TYRIN</strong> CPE.<br />
Tensile Impact (kJm 2 )<br />
700<br />
650<br />
600<br />
550<br />
500<br />
0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0<br />
Natural Weathering Time (years)<br />
Pb-Stablized<br />
CaZn-Stablized<br />
0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0<br />
Natural Weathering Time (years)<br />
Pb-Stablized<br />
CaZn-Stablized<br />
Figure 7: Double-V notched impact after natural weathering of profiles modified<br />
with <strong>TYRIN</strong> CPE.<br />
Notched Impact (kJm 2 )<br />
70<br />
60<br />
50<br />
40<br />
30<br />
20<br />
10<br />
0<br />
0.0 0.5 1.0 1.5 2.0<br />
Natural Weathering Time (years)<br />
Pb-Stablized<br />
CaZn-Stablized
<strong>TYRIN</strong> CPE in Pipes<br />
<strong>The</strong> vast majority of PVC pipes is unmodified<br />
and goes into applications where no particular<br />
impact strength is required, such as<br />
sewage pipes.<br />
<strong>The</strong>re are special applications which are<br />
more demanding where impact modifiers can<br />
be beneficial, such as:<br />
• Pressure pipes for mining<br />
• Gas pipes<br />
• Special drain pipes (corrugated pipes)<br />
• Pipes for wells or mining<br />
• Foam core pipes.<br />
Table 5: Starting point formulation<br />
for HI PVC pipe<br />
S-PVC K-68 100 phr<br />
<strong>TYRIN</strong> 6000 6-8<br />
3 basic lead sulphate 0.8<br />
2 basic lead stearate 0.8<br />
Ca-stearate 0.1-0.2<br />
Stearic acid 0.2-0.3<br />
CaCO3 5<br />
Trademark of <strong>The</strong> <strong>Dow</strong> <strong>Chemical</strong> <strong>Company</strong> (“<strong>Dow</strong>”) or an affiliated company of <strong>Dow</strong><br />
Typically, the impact strength requirements<br />
are less demanding than for profiles. <strong>TYRIN</strong><br />
is the ideal product for pipe applications,<br />
especially regarding the new or coming<br />
European standards for pressure and nonpressure<br />
pipes, where an impact test at 0°C<br />
or even at -10°C will be required. <strong>TYRIN</strong><br />
reduces the transition temperature, giving<br />
the end-users an extra margin of excellence<br />
through low temperature impact performance<br />
and ductility. <strong>TYRIN</strong> CPE modification also<br />
yields a better surface which is useful to avoid<br />
build-up on the inside of the pipe. This effect<br />
is visible at very low levels and already 3-4<br />
phr <strong>TYRIN</strong> 6000 are sufficient to give ductile<br />
failure below 0°C.<br />
<strong>TYRIN</strong> CPE offers excellent hot melt tear<br />
strength, ductility, and welding properties,<br />
essential in the extrusion of thin-wall<br />
corrugated pipes. For foam core pipes, <strong>TYRIN</strong><br />
CPE can be used in both the compact and the<br />
foam layer. In the compact layer, it improves<br />
the ductility and in the foam section, it can<br />
substitute to some extent the acrylic processing<br />
aids which are used to improve the cell<br />
structure. It will permit cost saving, improvements<br />
of flammability, and a higher ductility<br />
regarding impact tests at low temperature.<br />
<strong>TYRIN</strong> CPE provides a consistent improvement<br />
of the ductility of PVC pressure pipes and it<br />
is possible to reduce the design coefficient,<br />
where standardization and requirements<br />
allow it. In practice this will yield a substantial<br />
reduction of wall thickness which will<br />
more than compensate for the slightly higher<br />
cost of the impact modified compound. This<br />
concept is not included in the current European<br />
pipe standards.<br />
7 of 9
8 of 9<br />
<strong>TYRIN</strong> CPE in Extruded PVC Sheet<br />
PVCsheet is extensively used in advertising<br />
and decorative panels, as it can be easly<br />
printed and laminated with foils. Due to its<br />
resistance against humidity, weathering, and<br />
chemicals it is often used as wood replacement<br />
in construction applications.<br />
Both rigid and foamed PVC sheet can be<br />
modified with <strong>TYRIN</strong> CPE to improve its<br />
physical properties.<br />
Main properties of foamed sheets are:<br />
• Low density for ease of handling and cost<br />
• Smooth regular surface (esthetics and<br />
ease of cleaning)<br />
• Ductility (must not shatter during cutting<br />
of fixing with nails or screws).<br />
High melt strength is essential to allow the<br />
material to expand without the tearing of the<br />
cell membranes. If the cell membranes tear<br />
up, the foam structure collapses rapidly and<br />
the foam loses its mechanical strength. <strong>The</strong><br />
ideal is a very fine, regular cell structure with<br />
no or only little difference in cell size between<br />
the outer and inner layer of the part.<br />
<strong>The</strong>re are two basic processes: free foam and<br />
the Celluka process. In the free foam process,<br />
the melt can expand freely after leaving the<br />
die. After expansion, the extrudate is cooled<br />
at its surface, which limits the cell growth at<br />
the surface, giving foam with low density at<br />
the core and higher density at the surface.<br />
<strong>The</strong> surface is smoothened through contact<br />
with cool rolls, but keeps some structure.<br />
Trademark of <strong>The</strong> <strong>Dow</strong> <strong>Chemical</strong> <strong>Company</strong> (“<strong>Dow</strong>”) or an affiliated company of <strong>Dow</strong><br />
In the Celluka process, the extrudate goes<br />
straight into a cooled calibration and expands<br />
inward. <strong>The</strong> contact of the melt with the<br />
cooled calibration prevents expansion at the<br />
outside and gives a thick (0.1-1mm) compact<br />
skin with the surface quality of a compact<br />
part. <strong>The</strong> contact of the melt with rolls (for<br />
sheet) or a cooled calibration (for profiles)<br />
hinders the expansion and gives a compact<br />
skin at the part outside. (See table 6).<br />
Free foam allows only the production of very<br />
simple shapes, whereas the Celluka process<br />
Table 6: Starting point formulations for extruded PVC foams<br />
Ingredient Free, Celluka, Free, Celluka,<br />
Pb-stab Pb-stab Sn-stab Sn-stab<br />
S PVC K60 100 100<br />
S PVC K58 100 100<br />
Modifier 1 8 8 8 8<br />
Bas. Pb-Phosphite 2 2<br />
Butyl-Sn mercaptide 1.2 - 1.5 1.2 - 1.5<br />
Ca stearate 0.3 0.3 0.4 - 0.6 0.3 - 0.5<br />
Lubricants 2 0.8 - 1.2 0.8 - 1.2 0.8 - 1.2 0.8 - 1.2<br />
ADC 0.6 0.1 0.6 0.1<br />
Sodium bicarbonate 1.5- 2 1.7- 2<br />
TiO2 4 4 4 4<br />
1 blends with up to 50% <strong>TYRIN</strong> CPE<br />
2 blends of ester and hydrocarbon waxes<br />
allows also the production of fairly complex<br />
geometries. Lab studies have shown that up<br />
to 50% of the acrylic processing aid can be<br />
substituted with <strong>TYRIN</strong>, without negative<br />
impact on melt structure and density, but<br />
with improvements of flammability and<br />
impact strength. Formulations use pure or<br />
modified Azodicarbonamide (ADC) or sodium<br />
bicarbonate as blowing agents. ADC gives<br />
very fine, regular cell structures and expands<br />
quickly. Sodium bicarbonate expands more<br />
slowly and gives a coarser cell structure.<br />
Stabilizer systems are lead or tin based.
For more information on the products, innovations, expertise, and other services<br />
available from <strong>Dow</strong>’s Plastics business group in your region, please visit our web site<br />
at www.dowplastics.com or contact us as indicated below.<br />
North America<br />
U.S. & Canada 1-800-441-4369<br />
1-989-832-1426<br />
Mexico +1-800-441-4369<br />
Latin America<br />
Argentina +54-11-4319-0100<br />
Brazil +55-11-5188-9222<br />
Colombia +57-1-319-2100<br />
Mexico +52-55-5201-4700<br />
Europe/Middle East +800-3694-6367<br />
+32-3-450-2240<br />
South Africa +800-99-5078<br />
Asia Pacific +800-7<strong>776</strong>-7<strong>776</strong><br />
+60-3-7958-3392<br />
Our belief in the principles of Responsible Care ® and Sustainable Development influenced the production of this literature.<br />
To help protect our environment, this document was printed in small quantities on paper containing recovered/postconsumer<br />
fiber and using 100 percent soy-based ink whenever possible.<br />
NOTE: <strong>The</strong> photographs of end-use applications in this document represent potential end-use applications but do not<br />
necessarily represent current commercial applications, nor do they represent an endorsement by <strong>The</strong> <strong>Dow</strong> <strong>Chemical</strong><br />
<strong>Company</strong> of the actual products. Further, these photographs are for illustration purposes only and do not reflect either<br />
an endorsement or sponsorship of any other manufacturer for a specific potential end-use product or application, or for<br />
<strong>The</strong> <strong>Dow</strong> <strong>Chemical</strong> <strong>Company</strong>, or specific products manufactured by <strong>The</strong> <strong>Dow</strong> <strong>Chemical</strong> <strong>Company</strong>.<br />
NOTICE: No freedom from infringement of any patent owned by <strong>Dow</strong> or others is to be inferred. Because use conditions<br />
and applicable laws may differ from one location to another and may change with time, the Customer is responsible<br />
for determining whether products and the information in this document are appropriate for the Customer’s use and for<br />
ensuring that the Customer’s workplace and disposal practices are in compliance with applicable laws and other governmental<br />
enactments. <strong>Dow</strong> assumes no obligation or liability for the information in this document. NO WARRANTIES<br />
ARE GIVEN; ALL <strong>IM</strong>PLIED WARRANTIES OF MERCHANTABILITY OR FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE<br />
ARE EXPRESSLY EXCLUDED.<br />
NOTICE: If products are described as “experimental” or “developmental”: (1) product specifications may not be fully<br />
determined; (2) analysis of hazards and caution in handling and use are required; and (3) there is greater potential for<br />
<strong>Dow</strong> to change specifications and/or discontinue production.<br />
DOW MEDICAL APPLICATION POLICY: <strong>Dow</strong> will not knowingly sell or sample any product or service (“Product”) into any<br />
commercial or developmental application that is intended for:<br />
a. permanent (Long term) contact with internal body fluids or internal body tissues. Long term is a use which exceeds<br />
72 continuous hours (except 30 days for PELLETHANE polyurethane elastomers);<br />
b. use in cardiac prosthetic devices regardless of the length of time involved; (Cardiac prosthetic devices include, but are<br />
not limited to, pacemaker leads and devices, artificial hearts, heart valves, intra-aortic balloons and control systems,<br />
and ventricular bypass assisted devices);<br />
c. use as a critical component in medical devices that support or sustain human life; or<br />
d. use specifically by pregnant women or in applications designed specifically to promote or interfere with<br />
human reproduction.<br />
Additionally, all Products intended for use in pharmaceutical applications, other than pharmaceutical packaging, must<br />
pass the current Pharmaceutical Liability Guidelines.<br />
• For the products sold by the Plastics Portfolio, new business opportunities require a business assessment prior to<br />
sale or sampling of <strong>Dow</strong> products.<br />
• Authorized distributors and resellers will adhere to this medical policy.<br />
• <strong>The</strong> <strong>Dow</strong> <strong>Chemical</strong> <strong>Company</strong> does not endorse or claim suitability of their products for specific medical applications.<br />
It is the responsibility of the medical device or pharmaceutical manufacturer to determine that the <strong>Dow</strong> product is<br />
safe, lawful, and technically suitable for the intended use. DOW MAKES NO WARRANTIES, EXPRESS OR <strong>IM</strong>PLIED,<br />
CONCERNING THE SUITABILITY OF ANY DOW PRODUCT FOR USE IN MEDICAL APPLICATIONS.<br />
Published June 2006<br />
®Trademark of <strong>The</strong> <strong>Dow</strong> <strong>Chemical</strong> <strong>Company</strong> (“<strong>Dow</strong>”) or an affiliated company of <strong>Dow</strong><br />
®Responsible Care is a service mark of the American Chemistry Council.<br />
<strong>Dow</strong> is a partner in the American Chemistry Council Responsible Care initiative.<br />
Form No. <strong>776</strong>-<strong>00301</strong>-0606 SMG<br />
SMG 11025<br />
9 of 9