EFM Evaporators - FOCUS GmbH
EFM Evaporators - FOCUS GmbH
EFM Evaporators - FOCUS GmbH
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
2<br />
Precise Real-Time<br />
Flux Control<br />
The <strong>EFM</strong> evaporators with integrated<br />
flux monitor are ideal for high-purity<br />
evaporation of a wide range of materials<br />
in UHV, ranging from refractory metal<br />
wires and rods to delicate, reactive substances<br />
evaporated from crucibles.<br />
Materials such as Fe, Co, Ni, Pt, Ag, Au, Al,<br />
Mo, Ta, W, and also non-conducting materials<br />
or semiconductors, e.g. silicon, can be evaporated.<br />
Delicate or reactive materials can be<br />
precisely and cleanly deposited.<br />
Using a stainless steel crucible with a nozzle, a<br />
gentle Knudsen evaporation of C 60 and many<br />
other aromatic compounds is achieved with<br />
minimum loss of material. An integral flux<br />
monitor enables reproducible real-time control<br />
of the deposition rate and, once calibrated,<br />
removes the need for a quartz thickness monitor.<br />
The degassing state of the evaporant and<br />
the start of the real flux are also shown more<br />
accurately than by temperature measurement.<br />
The flux is displayed on the control unit and is<br />
also available for computer-controlled evaporation<br />
processes.<br />
A built-in shutter with manual or optional computer<br />
controlled motor activation governs the<br />
deposition time. The desired flux can be monitored<br />
and adjusted with the shutter closed.<br />
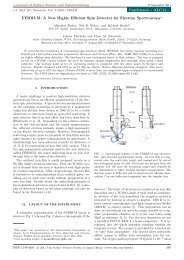
The <strong>EFM</strong> evaporators are designed to effectively<br />
focus the heating power onto the evaporant<br />
with minimum heat dissipation.<br />
To absorb the heat radiation<br />
and maintain an ultra high<br />
vacuum (to below 10 -10 mbar),<br />
the evaporant is completely<br />
surrounded by a water-cooled<br />
shroud.<br />
The rear-loading feature of<br />
the <strong>EFM</strong> evaporators enables<br />
crucibles to be exchanged<br />
without detaching the <strong>EFM</strong><br />
from the vacuum chamber<br />
for deposition of different<br />
materials with identical source<br />
alignment.<br />
Low stray magnetic fields at<br />
the sample enable the evaporator<br />
to be used during RHEED<br />
or LEED analysis.<br />
Example of Ag-induced structural transformation<br />
at 850 K starting at steps of<br />
Si(111)7x7, observed by STM during continuous<br />
in-situ evaporation. (210 x 210 nm 2 ;<br />
the moiré pattern results from interference<br />
of 7x7 structure and data point density)