Science Facing Aliens - Invasive Alien Species in Belgium - Belgian ...
Science Facing Aliens - Invasive Alien Species in Belgium - Belgian ...
Science Facing Aliens - Invasive Alien Species in Belgium - Belgian ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
28<br />
Laboratory results<br />
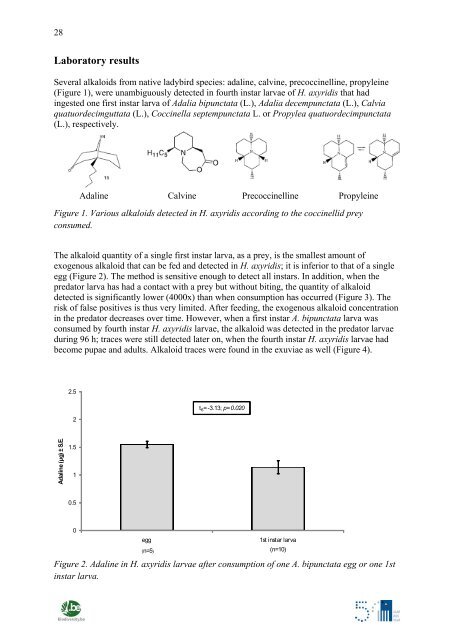
Several alkaloids from native ladybird species: adal<strong>in</strong>e, calv<strong>in</strong>e, precocc<strong>in</strong>ell<strong>in</strong>e, propyle<strong>in</strong>e<br />
(Figure 1), were unambiguously detected <strong>in</strong> fourth <strong>in</strong>star larvae of H. axyridis that had<br />
<strong>in</strong>gested one first <strong>in</strong>star larva of Adalia bipunctata (L.), Adalia decempunctata (L.), Calvia<br />
quatuordecimguttata (L.), Cocc<strong>in</strong>ella septempunctata L. or Propylea quatuordecimpunctata<br />
(L.), respectively.<br />
Adal<strong>in</strong>e Calv<strong>in</strong>e Precocc<strong>in</strong>ell<strong>in</strong>e Propyle<strong>in</strong>e<br />
Figure 1. Various alkaloids detected <strong>in</strong> H. axyridis accord<strong>in</strong>g to the cocc<strong>in</strong>ellid prey<br />
consumed.<br />
The alkaloid quantity of a s<strong>in</strong>gle first <strong>in</strong>star larva, as a prey, is the smallest amount of<br />
exogenous alkaloid that can be fed and detected <strong>in</strong> H. axyridis; it is <strong>in</strong>ferior to that of a s<strong>in</strong>gle<br />
egg (Figure 2). The method is sensitive enough to detect all <strong>in</strong>stars. In addition, when the<br />
predator larva has had a contact with a prey but without bit<strong>in</strong>g, the quantity of alkaloid<br />
detected is significantly lower (4000x) than when consumption has occurred (Figure 3). The<br />
risk of false positives is thus very limited. After feed<strong>in</strong>g, the exogenous alkaloid concentration<br />
<strong>in</strong> the predator decreases over time. However, when a first <strong>in</strong>star A. bipunctata larva was<br />
consumed by fourth <strong>in</strong>star H. axyridis larvae, the alkaloid was detected <strong>in</strong> the predator larvae<br />
dur<strong>in</strong>g 96 h; traces were still detected later on, when the fourth <strong>in</strong>star H. axyridis larvae had<br />
become pupae and adults. Alkaloid traces were found <strong>in</strong> the exuviae as well (Figure 4).<br />
Adal<strong>in</strong>e (µg) ± S.E.<br />
2.5<br />
2<br />
1.5<br />
1<br />
0.5<br />
0<br />
egg 1st <strong>in</strong>star larva<br />
(n=5)<br />
t 6= -3.13; p= 0.020<br />
Figure 2. Adal<strong>in</strong>e <strong>in</strong> H. axyridis larvae after consumption of one A. bipunctata egg or one 1st<br />
<strong>in</strong>star larva.<br />
(n=10)