Apuntes de rectas
Apuntes de rectas
Apuntes de rectas
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Geometría Plana 16<br />
y<br />
6<br />
4<br />
2<br />
6 4 2 2 4 6<br />
2<br />
4<br />
6<br />
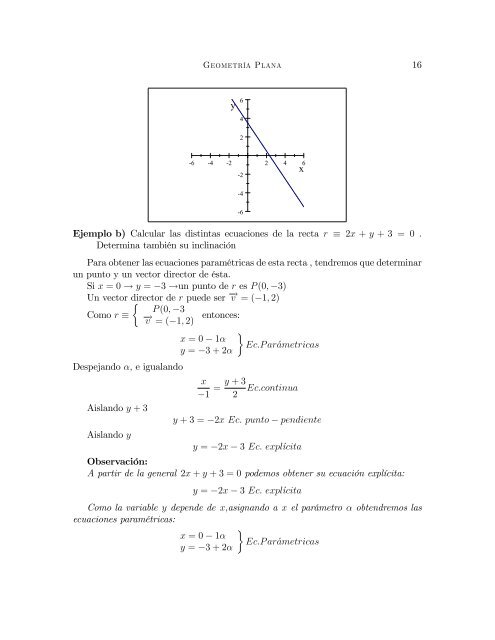
Ejemplo b) Calcular las distintas ecuaciones <strong>de</strong> la recta r 2x + y + 3 = 0 .<br />
Determina también su inclinación<br />
Para obtener las ecuaciones paramétricas <strong>de</strong> esta recta , tendremos que <strong>de</strong>terminar<br />
un punto y un vector director <strong>de</strong> ésta.<br />
Si x = 0 ! y = 3 !un punto <strong>de</strong> r es P (0; 3)<br />
Un vector director <strong>de</strong> r pue<strong>de</strong> ser ! v = ( 1; 2)<br />
Como r<br />
Despejando ; e igualando<br />
Aislando y + 3<br />
Aislando y<br />
P (0; 3<br />
! v = ( 1; 2) entonces:<br />
x = 0 1<br />
y = 3 + 2<br />
x<br />
1<br />
x<br />
Ec:P arametricas<br />
= y + 3<br />
2 Ec:continua<br />
y + 3 = 2x Ec: punto pendiente<br />
y = 2x 3 Ec: expl{cita<br />
Observación:<br />
A partir <strong>de</strong> la general 2x + y + 3 = 0 po<strong>de</strong>mos obtener su ecuación explícita:<br />
y = 2x 3 Ec: expl{cita<br />
Como la variable y <strong>de</strong>pen<strong>de</strong> <strong>de</strong> x;asignando a x el parámetro obtendremos las<br />
ecuaciones paramétricas:<br />
x = 0 1<br />
y = 3 + 2<br />
Ec:P arametricas