6. INFLAMACION AGUDA.pdf - VeoApuntes.com
6. INFLAMACION AGUDA.pdf - VeoApuntes.com
6. INFLAMACION AGUDA.pdf - VeoApuntes.com
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Laura del Olmo<br />
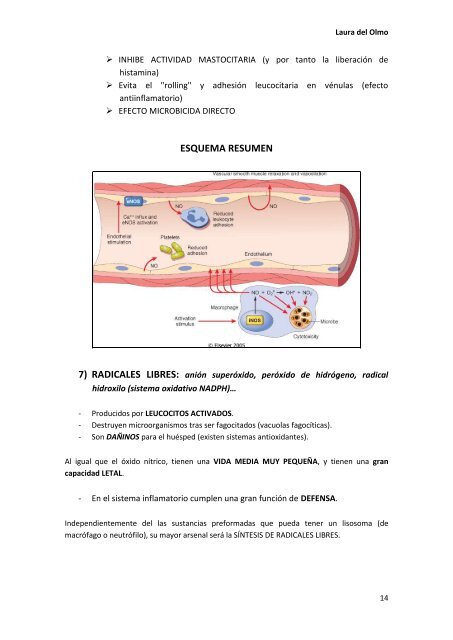
‣ INHIBE ACTIVIDAD MASTOCITARIA (y por tanto la liberación de<br />
histamina)<br />
‣ Evita el "rolling" y adhesión leucocitaria en vénulas (efecto<br />
antiinflamatorio)<br />
‣ EFECTO MICROBICIDA DIRECTO<br />
ESQUEMA RESUMEN<br />
7) RADICALES LIBRES: anión superóxido, peróxido de hidrógeno, radical<br />
hidroxilo (sistema oxidativo NADPH)…<br />
- Producidos por LEUCOCITOS ACTIVADOS.<br />
- Destruyen microorganismos tras ser fagocitados (vacuolas fagocíticas).<br />
- Son DAÑINOS para el huésped (existen sistemas antioxidantes).<br />
Al igual que el óxido nítrico, tienen una VIDA MEDIA MUY PEQUEÑA, y tienen una gran<br />
capacidad LETAL.<br />
- En el sistema inflamatorio cumplen una gran función de DEFENSA.<br />
Independientemente del las sustancias preformadas que pueda tener un lisosoma (de<br />
macrófago o neutrófilo), su mayor arsenal será la SÍNTESIS DE RADICALES LIBRES.<br />
14