- Page 1 and 2:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Rede
- Page 3 and 4:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 2. T
- Page 5 and 6:
II La capa de aplicación 81 Redes
- Page 7 and 8:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 8. E
- Page 9 and 10:
III La capa de transporte de datos
- Page 11 and 12:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 14.C
- Page 13 and 14:
IV La capa de red 324 Redes de Comp
- Page 15 and 16:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 21.2
- Page 17 and 18:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 25.4
- Page 19 and 20:
28.6. CSMA/CA (Carrier Sense Multip
- Page 21 and 22:
A.6. Señales binarias y bits . . .
- Page 23 and 24:
E. Códigos de corrección de error
- Page 25 and 26:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Cap
- Page 27 and 28:
1.2. ¿Qué es una internet? Redes
- Page 29 and 30:
1.4. ¿Qué es un router? En Intern
- Page 31 and 32:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 La s
- Page 33 and 34:
1.7. ¿Qué servicios proporciona l
- Page 35 and 36:
1.9. ¿Qué es un protocolo de red?
- Page 37 and 38:
Cliente Servidor Solicitud de conex
- Page 39 and 40:
4. Aunque garantiza la entrega corr
- Page 41 and 42:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Cap
- Page 43 and 44:
2.2. Conmutación de paquetes La re
- Page 45 and 46:
Frecuencia FDM Frecuencia TDM w Can
- Page 47 and 48:
Los slots de tiempo no quedan reser
- Page 49 and 50:
2.6. ¿Qué inconvenientes genera l
- Page 51 and 52:
2.8. Segmentación de los mensajes
- Page 53 and 54:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 2. L
- Page 55 and 56:
3.1. Teléfono de voz Redes de Comp
- Page 57 and 58:
3.2. ADSL (Asymetric Digital Subscr
- Page 59 and 60:
3.3. Cable coaxial de TV Se utiliza
- Page 61 and 62:
3.4. Ethernet conmutada Es la tecno
- Page 63 and 64:
3.5. Wireless LAN o Wi-Fi Está ree
- Page 65 and 66:
3.6. Telefonía móvil digital celu
- Page 67 and 68:
3.8. ATM (Asynchronous Transfer Mod
- Page 69 and 70:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 3.8
- Page 71 and 72:
4.1. Funcionamiento básico de un r
- Page 73 and 74:
4.2. Tiempo de procesamiento (t pro
- Page 75 and 76:
4.3. Tiempo de cola (t cola ) Tiemp
- Page 77 and 78:
4.4. Tiempo de transmisión (t tran
- Page 79 and 80:
La velocidad de propagación depend
- Page 81 and 82:
4.7. Pérdida de paquetes a causa d
- Page 83 and 84:
4.8. Ejemplos Redes de Computadoras
- Page 85 and 86:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 3. E
- Page 87 and 88:
Determine el tiempo de transmisión
- Page 89 and 90:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Supo
- Page 91 and 92:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Supo
- Page 93 and 94:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Cap
- Page 95 and 96:
5.2. Funciones de las capas en el m
- Page 97 and 98:
5.4. Capas y protocolos La funciona
- Page 99 and 100:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 5.5
- Page 101 and 102:
Solución: 7,5 × 10 6 b 1,5 × 10
- Page 103 and 104:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Come
- Page 105 and 106:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Cap
- Page 107 and 108:
6.2. La comunicación Web Redes de
- Page 109 and 110:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Un o
- Page 111 and 112:
6.3.1. Conexiones no persistentes C
- Page 113 and 114:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 6.4.
- Page 115 and 116:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 6.4.
- Page 117 and 118:
se pueden enviar páginas HTML dife
- Page 119 and 120:
un objeto comprimido). En la siguie
- Page 121 and 122:
6.5. Paso de parámetros en las URL
- Page 123 and 124:
6.6.1. Autorización “login/passw
- Page 125 and 126:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 En e
- Page 127 and 128:
6.7.1. GET (normal) Redes de Comput
- Page 129 and 130:
6.8. Las cachés Web (proxies Web)
- Page 131 and 132:
6.9. Arquitecturas Web Redes de Com
- Page 133 and 134:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 6.9.
- Page 135 and 136:
6.9.4. Sistemas proxy distribuidos
- Page 137 and 138:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Cap
- Page 139 and 140:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 7.2.
- Page 141 and 142:
7.2.2. Correo local usando lectores
- Page 143 and 144:
se almacenan en una cola local 2 pa
- Page 145 and 146:
7.3. El SMTP RFC 2821. Redes de Com
- Page 147 and 148:
7.4. Formato de un e-mail Redes de
- Page 149 and 150:
7.5. Las extensiones MIME RFC’s 2
- Page 151 and 152:
Los tipos de mensajes MIME más usu
- Page 153 and 154:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 3. a
- Page 155 and 156:
7.6. Los lectores/escritores de cor
- Page 157 and 158:
Las ventajas más frecuentes por la
- Page 159 and 160:
7.8. Web-Based E-mail Redes de Comp
- Page 161 and 162:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Cap
- Page 163 and 164:
8.2. Descripción del DNS RFC’s 1
- Page 165 and 166:
Un mismo nombre (canónico o alias)
- Page 167 and 168:
3. Que seamos atendidos por el serv
- Page 169 and 170:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Los
- Page 171 and 172:
8.4.2. Servidores de nombres de alt
- Page 173 and 174:
8.5. Las consultas Redes de Computa
- Page 175 and 176:
gogh$ /usr/bin/host -v miro.ace.ual
- Page 177 and 178:
$ /usr/bin/host -v filabres.ual.es
- Page 179 and 180:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Ejem
- Page 181 and 182:
8.7. Los registros DNS Los registro
- Page 183 and 184:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 3. S
- Page 185 and 186:
8.8. Regional Internet Registries C
- Page 187 and 188:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Cap
- Page 189 and 190:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 La c
- Page 191 and 192:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 La t
- Page 193 and 194:
9.2.1. Búsqueda usando un director
- Page 195 and 196:
9.2.2. Búsqueda usando un director
- Page 197 and 198:
Ventajas de la búsqueda descentral
- Page 199 and 200:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 1. E
- Page 201 and 202:
9.3. Acerca de la tasa de descarga
- Page 203 and 204:
9.4. Network File System Redes de C
- Page 205 and 206:
9.4.2. El NFSP Redes de Computadora
- Page 207 and 208:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 retu
- Page 209 and 210:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Cap
- Page 211 and 212:
10.2. Ejemplos de aplicaciones Rede
- Page 213 and 214:
10.4. ¿Cómo debería evolucionar
- Page 215 and 216:
10.5. Problemas y soluciones en la
- Page 217 and 218:
¿Cómo solucionamos el problema? R
- Page 219 and 220:
2. Entrelazando la información (in
- Page 221 and 222:
10.6. Protocolos para la transmisi
- Page 223 and 224:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 10.6
- Page 225 and 226:
10.6.2. Real-Time Control Protocol
- Page 227 and 228:
10.6.3. Real-Time Streaming Protoco
- Page 229 and 230:
10.7. ReSerVation Protocol (RSVP) R
- Page 231 and 232:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Part
- Page 233 and 234:
11.1. ¿Dónde corre la capa de tra
- Page 235 and 236:
11.2. Servicios proporcionados por
- Page 237 and 238:
Permite aprovechar el servicio de e
- Page 239 and 240:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Cap
- Page 241 and 242:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 12.2
- Page 243 and 244:
12.3. La suma de comprobación (che
- Page 245 and 246:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 El r
- Page 247 and 248:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Cuan
- Page 249 and 250:
12.5. Sobre el control de la conges
- Page 251 and 252:
13.1. La transferencia fiable de da
- Page 253 and 254:
13.3. Protocolos ARQ Redes de Compu
- Page 255 and 256:
13.4.1. NAK vs sólo-ACK Redes de C
- Page 257 and 258:
13.4.3. Confirmación de los paquet
- Page 259 and 260:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 13.4
- Page 261 and 262:
Ejemplo 13.11: Supongamos que se es
- Page 263 and 264:
13.5.1. Longitud de la secuencia de
- Page 265 and 266:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Ejem
- Page 267 and 268:
13.6. ARQ con repetición selectiva
- Page 269 and 270:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 13.6
- Page 271 and 272:
Emisor Receptor A0 Redes de Computa
- Page 273 and 274:
13.7.2. Latencia media versus tasa
- Page 275 and 276:
13.8. Solución al desorden de los
- Page 277 and 278:
14.1. Control de flujo El control d
- Page 279 and 280:
14.3. Causas y costes de la congest
- Page 281 and 282:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Cap
- Page 283 and 284:
15.2. El contexto de trabajo Corre
- Page 285 and 286:
El tamaño de cada segmento depende
- Page 287 and 288:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 SrcP
- Page 289 and 290:
15.3.2. EL proceso de desmultiplexa
- Page 291 and 292:
x e y, los números de secuencia in
- Page 293 and 294:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 15.3
- Page 295 and 296:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 15.3
- Page 297 and 298:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 El c
- Page 299 and 300:
Conexión Lo que sea/RESET Apertura
- Page 301 and 302:
La estructura de la cola de recepci
- Page 303 and 304:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 15.4
- Page 305 and 306:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Enla
- Page 307 and 308:
15.4.4. El síndrome de la ventana
- Page 309 and 310:
15.5. Control de la congestión Si
- Page 311 and 312:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 3. C
- Page 313 and 314:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 15.5
- Page 315 and 316:
15.5.1.2. El Algoritmo de Karn/Part
- Page 317 and 318:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Esti
- Page 319 and 320:
del RTT y 0 ≤ ρ ≤ 1 es otro fa
- Page 321 and 322:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Seq
- Page 323 and 324:
Enunciado: Estamos transmitiendo fi
- Page 325 and 326:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 la v
- Page 327 and 328:
16.1. Características Basado en el
- Page 329 and 330:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Para
- Page 331 and 332:
Con todo esto, la pila de protocolo
- Page 333 and 334:
Emisor Receptor Redes de Computador
- Page 335 and 336:
Cabecera de un paquete BLAST: Redes
- Page 337 and 338:
16.2.2. CHAN(nel) Implementa el mec
- Page 339 and 340:
Se crea un canal por cada interacci
- Page 341 and 342:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 aliv
- Page 343 and 344:
16.3. El caso particular de SunRPC
- Page 345 and 346:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 •
- Page 347 and 348:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Part
- Page 349 and 350:
17.1. El modelo de servicio Comunic
- Page 351 and 352:
17.2. El IP (Internet Protocol) Se
- Page 353 and 354:
Version: Versión del protocolo IP
- Page 355 and 356:
Destination Address: Dir IP del hos
- Page 357 and 358:
Version: Versión del protocolo (6)
- Page 359 and 360:
Ejemplo Comienzo de la Cabecera Ide
- Page 361 and 362:
Mensajes ICMP: Redes de Computadora
- Page 363 and 364:
El campo TTL figura en todas las ca
- Page 365 and 366:
17.4. El DHCP (Dynamic Host Configu
- Page 367 and 368:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Cap
- Page 369 and 370:
Por definición, todos los interfac
- Page 371 and 372:
18.2. Clases de dirs IP Las redes I
- Page 373 and 374:
18.3. Sub-netting y dirs CIDR en IP
- Page 375 and 376:
Usando sub-netting, cualquier rango
- Page 377 and 378:
18.4. Redes privadas RFC 1918. Rede
- Page 379 and 380:
La tabla NAT tiene 3 columnas: Puer
- Page 381 and 382:
18.6. La transición de IPv4 a IPv6
- Page 383 and 384:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Cap
- Page 385 and 386:
19.1.1. Búsqueda en las tablas de
- Page 387 and 388:
1 R 2 Redes de Computadoras, 2007/0
- Page 389 and 390:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Fina
- Page 391 and 392:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 podr
- Page 393 and 394:
Internet .1 .2 149.76.2.0/24 Redes
- Page 395 and 396:
19.2. Agregación de direcciones Cu
- Page 397 and 398:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 19.2
- Page 399 and 400:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Red
- Page 401 and 402:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Cap
- Page 403 and 404:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 La s
- Page 405 and 406:
20.2. La red como un grafo Redes de
- Page 407 and 408:
20.4. Routing jerárquico y sistema
- Page 409 and 410:
Por tanto, el routing jerárquico p
- Page 411 and 412:
Si un router tras el cálculo detec
- Page 413 and 414:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Ejem
- Page 415 and 416:
Entonces la tabla de routing del ro
- Page 417 and 418:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 El c
- Page 419 and 420:
20.7. El BGP (Border Gateway Protoc
- Page 421 and 422:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 20.7
- Page 423 and 424:
Flooding de los estados de los enla
- Page 425 and 426:
Ejemplo Dada la red de la figura Re
- Page 427 and 428:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 3 A
- Page 429 and 430:
Ejemplo Dada la red de la figura Re
- Page 431 and 432:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 3 A
- Page 433 and 434:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Cap
- Page 435 and 436:
21.2. El multicasting a nivel de ap
- Page 437 and 438:
21.3. Algoritmos de broadcasting Re
- Page 439 and 440:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 21.3
- Page 441 and 442:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Para
- Page 443 and 444:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 21.3
- Page 445 and 446:
Nadie controla quién pertenece a u
- Page 447 and 448:
21.5. El IGMP (Internet Group Manag
- Page 449 and 450:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 1. E
- Page 451 and 452:
21.6.2. PIM (Protocol Independent M
- Page 453 and 454:
21.8. Multicasting en Internet: el
- Page 455 and 456:
La distancia (en hops) que recorren
- Page 457 and 458:
22.1. Routing para hosts móviles R
- Page 459 and 460:
22.2. Nomenclatura Mobile host: el
- Page 461 and 462:
22.3. Routing indirecto Consiste en
- Page 463 and 464:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Tunn
- Page 465 and 466:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Ejem
- Page 467 and 468:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Cap
- Page 469 and 470:
La capa física está generalmente
- Page 471 and 472:
23.3. Servicios generalmente propor
- Page 473 and 474:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Tran
- Page 475 and 476:
24.1. Fundamentos Redes de Computad
- Page 477 and 478:
24.2. Paridad Redes de Computadoras
- Page 479 and 480:
24.3. Checksum Redes de Computadora
- Page 481 and 482:
24.4. CRC (Cyclic Redundancy Check)
- Page 483 and 484:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Erro
- Page 485 and 486:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Cap
- Page 487 and 488:
25.2. Las colisiones Cuando dos (o
- Page 489 and 490:
25.3.1. FDM y TDM Frecuencia FDM Fr
- Page 491 and 492:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 d i
- Page 493 and 494:
Ventajas: Redes de Computadoras, 20
- Page 495 and 496:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 25.4
- Page 497 and 498:
25.4.2. ALOHA (no ranurado) Igual q
- Page 499 and 500:
25.4.3. CSMA (Carrier Sense Multipl
- Page 501 and 502:
25.4.4. CSMA/CD (Collision Detect)
- Page 503 and 504:
25.5. Protocolos basados en turnos
- Page 505 and 506:
26.1. LAN: definición Una LAN (Loc
- Page 507 and 508:
En todos los frames transmitidos fi
- Page 509 and 510:
Cada nodo incorpora una tabla ARP:
- Page 511 and 512:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Cap
- Page 513 and 514:
27.2. Estructura del frame Todas la
- Page 515 and 516:
27.3. Tamaño máximo y mínimo de
- Page 517 and 518:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 27.5
- Page 519 and 520:
Todos los adaptadores que han produ
- Page 521 and 522:
27.7. Tecnologías Ethernet Estanda
- Page 523 and 524:
27.7.2. 10BaseT Ethernet y 100BaseT
- Page 525 and 526:
distancias se puede utilizar fibra
- Page 527 and 528:
No entienden los protocolos de la c
- Page 529 and 530:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 27.9
- Page 531 and 532:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Como
- Page 533 and 534:
La tabla de conmutación es dinámi
- Page 535 and 536:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Cap
- Page 537 and 538:
28.2. Capacidades Redes de Computad
- Page 539 and 540:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 28.3
- Page 541 and 542:
28.4. Canales Con la idea de acomod
- Page 543 and 544:
Cuando un nodo móvil se intenta as
- Page 545 and 546:
Este problema provoca las siguiente
- Page 547 and 548:
Las anteriores propuestas no evitan
- Page 549 and 550:
28.7. Estructura del frame IEEE 802
- Page 551 and 552:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 28.8
- Page 553 and 554:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Cap
- Page 555 and 556:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Cap
- Page 557 and 558:
30.2. Data framing Redes de Computa
- Page 559 and 560:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 30.3
- Page 561 and 562:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 El l
- Page 563 and 564:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 En e
- Page 565 and 566:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 La c
- Page 567 and 568:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Cap
- Page 569 and 570:
31.2. Principales características
- Page 571 and 572:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 mayo
- Page 573 and 574:
El formato de la cabecera es: Redes
- Page 575 and 576:
31.6. Canales virtuales y routing A
- Page 577 and 578:
31.7.1. La capa física Controla lo
- Page 579 and 580:
31.7.3. La capa AAL (ATM Adaptation
- Page 581 and 582:
En el caso de la AAL 5, la AAL no i
- Page 583 and 584:
31.8. Control de la congestión Red
- Page 585 and 586:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Apé
- Page 587 and 588:
A.1. Dato e información Estos dos
- Page 589 and 590:
A.3. Señales digitales y analógic
- Page 591 and 592:
A.5. Amplificadores y repetidores R
- Page 593 and 594:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 se m
- Page 595 and 596:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 supo
- Page 597 and 598:
|S(f)| 4 π Redes de Computadoras,
- Page 599 and 600:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Apé
- Page 601 and 602:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 señ
- Page 603 and 604:
|S(f)| 4 π Redes de Computadoras,
- Page 605 and 606:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 B.1.
- Page 607 and 608:
Shannon y Hartley estimaron que en
- Page 609 and 610:
Si los elementos de señalización
- Page 611 and 612:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Apé
- Page 613 and 614:
En la modulación intervienen tres
- Page 615 and 616:
C.3. Bits de datos, elementos de se
- Page 617 and 618:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Como
- Page 619 and 620:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 s(t)
- Page 621 and 622:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Si c
- Page 623 and 624: Teniendo en cuenta dicha representa
- Page 625 and 626: Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 C.4.
- Page 627 and 628: Bits 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0 1 s(t) t
- Page 629 and 630: |S FSK (f)| 1 Redes de Computadoras
- Page 631 and 632: Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 C.5.
- Page 633 and 634: Ejemplo: Bits 0 0 1 1 0 1 0 0 0 1 0
- Page 635 and 636: C.7. Modulación n-ária Redes de C
- Page 637 and 638: Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 port
- Page 639 and 640: Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Apé
- Page 641 and 642: Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 tram
- Page 643 and 644: Amplitud Bit de Inicio Bit de Datos
- Page 645 and 646: Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 los
- Page 647 and 648: D.2. Señalizaciones bipolares Rede
- Page 649 and 650: Amplitud Bit de Inicio Bit de Datos
- Page 651 and 652: Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Ampl
- Page 653 and 654: D.4. Señalizaciones más resistent
- Page 655 and 656: Amplitud Redes de Computadoras, 200
- Page 657 and 658: D.5. Delimitación de tramas Redes
- Page 659 and 660: D.7. Transmisiones síncronas Redes
- Page 661 and 662: Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 usar
- Page 663 and 664: Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Una
- Page 665 and 666: Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 0111
- Page 667 and 668: Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Apé
- Page 669 and 670: Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 erro
- Page 671 and 672: E.1. El código de Hamming Redes de
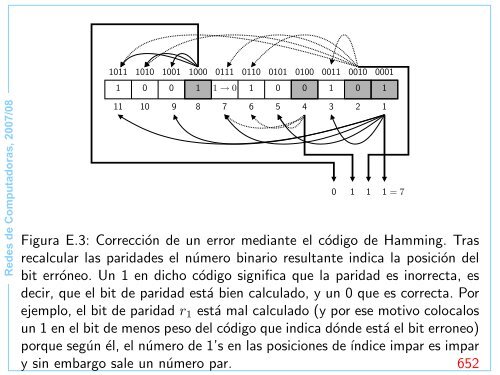
- Page 673: 11 10 9 8 7 6 5 4 3 1 0 0 1 1 0 1 1
- Page 677 and 678: Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 ASK
- Page 679 and 680: Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 de 2
- Page 681 and 682: Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Medi
- Page 683 and 684: Cubiertas Protectoras Fibra Óptica
- Page 685 and 686: Foco de Luz Revestimiento Núcleo R
- Page 687 and 688: Revestimiento Foco de Luz Núcleo R
- Page 689 and 690: Cuadro F.1: Capacidades típicas de
- Page 691 and 692: Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Apé
- Page 693 and 694: Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 prop
- Page 695 and 696: B Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 G
- Page 697 and 698: Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Apé
- Page 699 and 700: Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 La T
- Page 701 and 702: Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 señ
- Page 703 and 704: Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 pote
- Page 705 and 706: Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 se d
- Page 707 and 708: Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Apé
- Page 709 and 710: Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 E.1
- Page 711 and 712: Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 trav
- Page 713 and 714: Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 Tiem
- Page 715 and 716: a Hz Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08
- Page 717 and 718: L.2. Multiplexación en el dominio
- Page 719 and 720: Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 1 in
- Page 721 and 722: Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 desm
- Page 723 and 724: Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 fijo
- Page 725 and 726:
Redes de Computadoras, 2007/08 [5]
- Page 727 and 728:
[18] Network Working Group, AT&T Re
- Page 729:
[30] Sun Microsystems, Inc., http:/