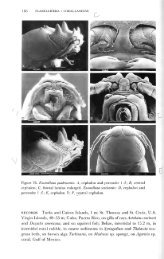
- Page 1: World catalog of terrestrial isopod
- Page 5 and 6: DISTR. - New Zealand: North and Sou
- Page 7 and 8: SYN. - Illyrionethes c. BIBL. - VER
- Page 9 and 10: Agnara hispida (Collinge, 1915) SYN
- Page 11 and 12: BIBL. - COLLINGE 1922b (figs.); ARC
- Page 13 and 14: Alpioniscus absoloni (Strouhal, 193
- Page 15 and 16: Amazoniscus arlei Lemos de Castro,
- Page 17 and 18: Anchiphiloscia longisetosa (Ferrara
- Page 19 and 20: DISTR. - Guatemala. A n d r o n i s
- Page 21 and 22: BIBL. - BARNARD 1924a, 1932; BRIAN
- Page 23 and 24: DISTR. - SW-Cameroon: Mount Cameroo
- Page 25 and 26: BIBL. - VERHOEFF 1907a; STROUHAL 19
- Page 27 and 28: REMARKS. - The species is not a syn
- Page 29 and 30: DISTR. - NW-Spain. Armadillidium ga
- Page 31 and 32: DISTR. - Corsica. The record of thi
- Page 33 and 34: Orig. descr.: KOCH, C. 1841 (Armadi
- Page 35 and 36: Syst.: BUDDE-LUND 1885; VANDEL 1962
- Page 37 and 38: BIBL. - MILNE-EDWARDS 1840; LUCAS 1
- Page 39 and 40: Ontog.: HATCHETT 1947; LAWLOR 1976a
- Page 41 and 42: Armadillo caeruleus Collinge, 1914
- Page 43 and 44: Armadillo longipes Budde-Lund, 1909
- Page 45 and 46: Armadillo rectifrons Dollfus, 1898
- Page 47 and 48: Armadilloniscus coronocapitalis Men
- Page 49 and 50: Atlantoscia alceui Ferrara & Taiti,
- Page 51 and 52: REMARKS. - The ascription to the ge
- Page 53 and 54:
BIBL. - STROUHAL 1968a (figs.); CAR
- Page 55 and 56:
Beroniscus capreolus Vandel, 1967 B
- Page 57 and 58:
Synocheta: family Trichoniscidae Bo
- Page 59 and 60:
Buddelundia frontosa (Budde-Lund, 1
- Page 61 and 62:
BIBL. - VERHOEFF 1930b (figs.), 193
- Page 63 and 64:
Burmoniscus gracilis Nunomura & Xie
- Page 65 and 66:
SYN. - Setaphora s. BIBL. - NUNOMUR
- Page 67 and 68:
BIBL. - BARNARD 1960c (figs.); FERR
- Page 69 and 70:
C h a e t o p h i l o s c i a Verho
- Page 71 and 72:
BIBL. - SCHMÖLZER 1965a (figs.), 1
- Page 73 and 74:
BIBL. - VANDEL 1968c (figs.); SCHUL
- Page 75 and 76:
BIBL. - CHILTON 1915a (figs.); JACK
- Page 77 and 78:
C u b a r i s Brandt, 1833 Crinoche
- Page 79 and 80:
DISTR. - Lord Howe Island 800 km NE
- Page 81 and 82:
Cubaris multipunctata (Budde-Lund,
- Page 83 and 84:
C u z c o d i n e l l a Armas & Jua
- Page 85 and 86:
DISTR. - NW-Turkey: Ereğli 200 km
- Page 87 and 88:
DISTR. - Corsica. Cylisticus zangez
- Page 89 and 90:
DISTR. - Algeria: region of Biskra.
- Page 91 and 92:
Diploexochus flavescens (Brandt, 18
- Page 93 and 94:
Echinarmadillidium absoloni Strouha
- Page 95 and 96:
Genus Ethelomorus = Genus Ethelumor
- Page 97 and 98:
Eubelum rusingaense Morris, 1979 BI
- Page 99 and 100:
BIBL. - NUNOMURA & XIE 2000 (figs.)
- Page 101 and 102:
Genus Gerutha = Genus Synarmadilloi
- Page 103 and 104:
BIBL. - VERHOEFF 1933c (figs.); VAN
- Page 105 and 106:
105 Distr.: SARS 1898 (N); PALMÉN
- Page 107 and 108:
Haplophthalmus teissieri Legrand, 1
- Page 109 and 110:
109 SYN. - Porcellio f. BIBL. - ULJ
- Page 111 and 112:
Hiallum rothschildi Richardson, 190
- Page 113 and 114:
Hyloniscus pilifer Verhoeff, 1933 B
- Page 115 and 116:
BIBL. - VANDEL 1973b (figs.). DISTR
- Page 117 and 118:
SYN. - Haplophthalmus paradoxus, s.
- Page 119 and 120:
Kuscheloniscus vandeli Strouhal, 19
- Page 121 and 122:
L e o n o s c i a Ferrara & Schmalf
- Page 123 and 124:
DISTR. - Northern Greece: Aegean is
- Page 125 and 126:
Physiol.: NUMANOI 1933, 1934c; CHAN
- Page 127 and 128:
Sense organs: EDWARDS 1969; ALEXAND
- Page 129 and 130:
DISTR. - Bosnia. REMARKS. - Probabl
- Page 131 and 132:
131 BIBL. - NUNOMURA 1983 (figs.),
- Page 133 and 134:
DISTR. - Thailand. Littorophiloscia
- Page 135 and 136:
Lucasioides nebulosus Nunomura, 200
- Page 137 and 138:
DISTR. - Malaysia: “Penisola di M
- Page 139 and 140:
Mesarmadillo alluaudi Dollfus, 1892
- Page 141 and 142:
Metastenoniscus osellai Taiti & Fer
- Page 143 and 144:
Mexiconiscus tlamayensis Schultz, 1
- Page 145 and 146:
DISTR. - Brazil: São Paulo region.
- Page 147 and 148:
Mongoloniscus masahitoi (Nunomura,
- Page 149 and 150:
N a g u r u s Holthuis, 1949 Crinoc
- Page 151 and 152:
SYN. - Nagara r. BIBL. - ARCANGELI
- Page 153 and 154:
Crinocheta: family Armadillidae Neo
- Page 155 and 156:
DISTR. - Micronesia: Gilbert Island
- Page 157 and 158:
Niambia griseoflavus Barnard, 1924
- Page 159 and 160:
BIBL. - VANDEL 1952d (figs.); LEMOS
- Page 161 and 162:
Oniscus angustus Dana, 1853 = nomen
- Page 163 and 164:
Oritoniscus beroni Ferrara & Taiti,
- Page 165 and 166:
DISTR. - Croatia: Dalmatia. Oronisc
- Page 167 and 168:
Crinocheta: family Armadillidae Pac
- Page 169 and 170:
BIBL. - DALENS 1988 (figs.). DISTR.
- Page 171 and 172:
P a r a s c h i z i d i u m Verhoef
- Page 173 and 174:
Parelumoides marginatus Ferrara & S
- Page 175 and 176:
DISTR. - Saudi Arabia. Periscyphis
- Page 177 and 178:
P e r i s c y p h o p s Hilgendorf,
- Page 179 and 180:
179 DISTR. - New Zealand. Phallonis
- Page 181 and 182:
“Philoscia” colimensis Mulaik,
- Page 183 and 184:
Syst.: VANDEL 1962b; GRUNER 1966a;
- Page 185 and 186:
Philoscina incisa Ferrara & Taiti,
- Page 187 and 188:
BIBL. - VERHOEFF 1931b (figs.), 193
- Page 189 and 190:
Distr.: VERHOEFF 1936a (BG), 1949a
- Page 191 and 192:
Porcellio aegaeus Verhoeff, 1907 =
- Page 193 and 194:
DISTR. - SE-Spain. Porcellio boliva
- Page 195 and 196:
195 Reprod.: HEELEY 1941a; MEINERTZ
- Page 197 and 198:
DISTR. - NE-Spain; France; western
- Page 199 and 200:
199 Porcellio klugii Brandt, 1833 =
- Page 201 and 202:
Porcellio marginenotatus Budde-Lund
- Page 203 and 204:
DISTR. - Northern Algeria to southe
- Page 205 and 206:
correct, but in RADU 1950a there is
- Page 207 and 208:
Porcellio serialis C. Koch, 1841 =
- Page 209 and 210:
Porcellio truncatus Brandt, 1833 =
- Page 211 and 212:
Porcellionides davisi Mulaik & Mula
- Page 213 and 214:
Mol. biol.: GARTHWAITE & SASSAMAN 1
- Page 215 and 216:
BIBL. - VERHOEFF 1901f, 1907b, 1917
- Page 217 and 218:
BIBL. - VANDEL 1952d (figs.); LEIST
- Page 219 and 220:
Protracheoniscus hedini Verhoeff, 1
- Page 221 and 222:
BIBL. - ARCANGELI 1934f (figs.). DI
- Page 223 and 224:
P s e u d o a g n a r a Taiti & Fer
- Page 225 and 226:
DISTR. - Western Australia. P s e u
- Page 227 and 228:
BIBL. - BUDDE-LUND 1904, 1908 (figs
- Page 229 and 230:
R h y s c o t u s Budde-Lund, 1885
- Page 231 and 232:
Synocheta: family Trichoniscidae Sa
- Page 233 and 234:
BIBL. - BUDDE-LUND 1909a (figs.); B
- Page 235 and 236:
DISTR. - Seychelles. Sechelloscia m
- Page 237 and 238:
DISTR. - China: Yunnan. Sinodillo s
- Page 239 and 240:
DISTR. - Madeira. S p e l a e o n e
- Page 241 and 242:
BIBL. - VERHOEFF 1908e; VANDEL 1940
- Page 243 and 244:
243 BIBL. - HELLER 1865 (figs.); MI
- Page 245 and 246:
Spherillo perkinsi Dollfus, 1900 =
- Page 247 and 248:
DISTR. - Central Italy: island Isch
- Page 249 and 250:
BIBL. - BARNARD 1932; FERRARA & TAI
- Page 251 and 252:
DISTR. - South Africa: Cape Provinc
- Page 253 and 254:
DISTR. - Tanzania. REMARKS. - Ascri
- Page 255 and 256:
Tendosphaera verrucosa Verhoeff, 19
- Page 257 and 258:
(figs.); SCHMALFUSS 1989f (figs.);
- Page 259 and 260:
Trachelipus brentanus Verhoeff, 192
- Page 261 and 262:
BIBL. - ARCANGELI 1932a (figs.); AR
- Page 263 and 264:
DISTR. - “Moldavia”. Trachelipu
- Page 265 and 266:
GRUNER 1966a (figs.); FLASAROVÁ 19
- Page 267 and 268:
Trichoniscus bassoti Vandel, 1960 B
- Page 269 and 270:
Trichoniscus georgiensis Barnard, 1
- Page 271 and 272:
271 Trichoniscus oedipus Sfenthoura
- Page 273 and 274:
Trichoniscus racovitzai Tabacaru, 1
- Page 275 and 276:
Trichorhina acuta Araujo & Buckup,
- Page 277 and 278:
DISTR. - NE-Brazil: Pará. Trichorh
- Page 279 and 280:
Crinocheta: family Cylisticidae Tro
- Page 281 and 282:
Turkonethes solifugus Verhoeff, 194
- Page 283 and 284:
(figs.); ARGANO & MANICASTRI 1991,
- Page 285 and 286:
Uropodias bermudensis Richardson, 1
- Page 287 and 288:
BIBL. - RIOJA 1955 (figs.); ARCANGE
- Page 289 and 290:
DISTR. - Jamaica. Venezillo kaokoen
- Page 291 and 292:
DISTR. - South Africa: Cape Provinc
- Page 293 and 294:
Venezillo soleiformis (Nunomura, 19
- Page 295 and 296:
DISTR. - Southern Somalia. Xeronisc