ANTIMICROBIAL EFFECT OF FERROCENYL DIARYL BUTENES AGAINST OLIVE PLANTLET DISEASES
These compounds efficiently inhibited the growth of these microorganisms in culture media and in inoculated plantlets which did not contract the corresponding diseases, especially when treated with P8. These findings shed light on the potential utilisatio
These compounds efficiently inhibited the growth of these microorganisms in culture media and in inoculated plantlets which did not contract the corresponding diseases, especially when treated with P8. These findings shed light on the potential utilisatio
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
652 Ferrocenyl diaryl butenes against olive plantlets diseases Journal of Plant Pathology (2011), 93 (3), 651-657<br />
dida was enhanced by the addition of ferrocene (Biot et<br />
al., 2000). Finally, new pyrazole derivatives containing a<br />
ferrocene unit have shown a wide range of activities<br />
against bacterial and fungal/yeast strains (Damljanovic<br />
et al., 2009).<br />
Ferrocenyl-substituted derivatives of antifungal drugs<br />
used in plant protection have also been developed. A ferrocene<br />
triadimefon derivative showed lower antifungal<br />
activity than the parent triadimefon, but exhibited an unexpectedly<br />
promising plant growth regulatory activity<br />
(Zhong et al., 2006). Ferrocene-containing di- and<br />
tetrahydroxylic acetylenic alcohols showed bactericidal<br />
activity against the phytopathogenic bacteria Pectobacterium<br />
aroideae, Xanthomonas campestris, Agrobacterium<br />
tumefaciens, and the actinomycetes Streptomyces sp. and<br />
Nocardiophsis sp. (Asatiani et al., 1984). The use of ferrocene<br />
compounds as fertilizers and for the prevention<br />
and cure of iron deficiency-induced disorders in plants<br />
has long been patented (Mues et al., 1977). In spite of<br />
these multiple applications, the use of ferrocene derivatives<br />
in agriculture is still little investigated.<br />
We have previously shown that some ferrocene derivatives,<br />
analogue of hydroxytamoxifen, exhibit a high antiproliferative<br />
effect on both hormone-dependent and<br />
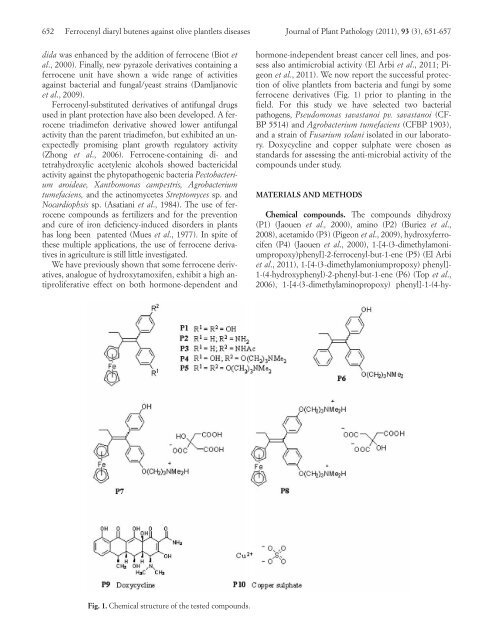
Fig. 1. Chemical structure of the tested compounds.<br />
hormone-independent breast cancer cell lines, and possess<br />
also antimicrobial activity (El Arbi et al., 2011; Pigeon<br />
et al., 2011). We now report the successful protection<br />
of olive plantlets from bacteria and fungi by some<br />
ferrocene derivatives (Fig. 1) prior to planting in the<br />
field. For this study we have selected two bacterial<br />
pathogens, Pseudomonas savastanoi pv. savastanoi (CF-<br />
BP 5514) and Agrobacterium tumefaciens (CFBP 1903),<br />
and a strain of Fusarium solani isolated in our laboratory.<br />
Doxycycline and copper sulphate were chosen as<br />
standards for assessing the anti-microbial activity of the<br />
compounds under study.<br />
MATERIALS AND METHODS<br />
Chemical compounds. The compounds dihydroxy<br />
(P1) (Jaouen et al., 2000), amino (P2) (Buriez et al.,<br />
2008), acetamido (P3) (Pigeon et al., 2009), hydroxyferrocifen<br />
(P4) (Jaouen et al., 2000), 1-[4-(3-dimethylamoniumpropoxy)phenyl]-2-ferrocenyl-but-1-ene<br />
(P5) (El Arbi<br />
et al., 2011), 1-[4-(3-dimethylamoniumpropoxy) phenyl]-<br />
1-(4-hydroxyphenyl)-2-phenyl-but-1-ene (P6) (Top et al.,<br />
2006), 1-[4-(3-dimethylaminopropoxy) phenyl]-1-(4-hy-