Trend in Optical Fibers and Cables for Fiber-To-The-Home
Trend in Optical Fibers and Cables for Fiber-To-The-Home
Trend in Optical Fibers and Cables for Fiber-To-The-Home
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
60<br />
Feature Articles: <strong>Optical</strong> <strong>Fiber</strong> Communications<br />
cost directly account <strong>for</strong> a cost per subscriber, <strong>and</strong><br />
should be able to be h<strong>and</strong>led easily <strong>for</strong> quick <strong>and</strong><br />
economical <strong>in</strong>stallation.<br />
A surplus optical fiber took out from the cables is<br />
wound <strong>and</strong> stored <strong>in</strong> a closure or a cab<strong>in</strong>et. In<br />
particular, the fiber <strong>in</strong> the drop cable is required to<br />
be able to be bent small to downsize the closure<br />
<strong>and</strong> the cab<strong>in</strong>et. Furthermore, a fiber <strong>in</strong> an <strong>in</strong>door<br />
cable may be bent with a small curvature <strong>for</strong> wir<strong>in</strong>g<br />
along a wall <strong>and</strong> <strong>for</strong> storage.<br />
Fig�� Fig�� Fig�� Fig�� Fig�� Configuration Configuration of of cables cables <strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong> <strong>in</strong> FTTH� FTTH� FTTH� FTTH� FTTH�<br />
3. OPTICAL FIBER USED IN FTTH<br />
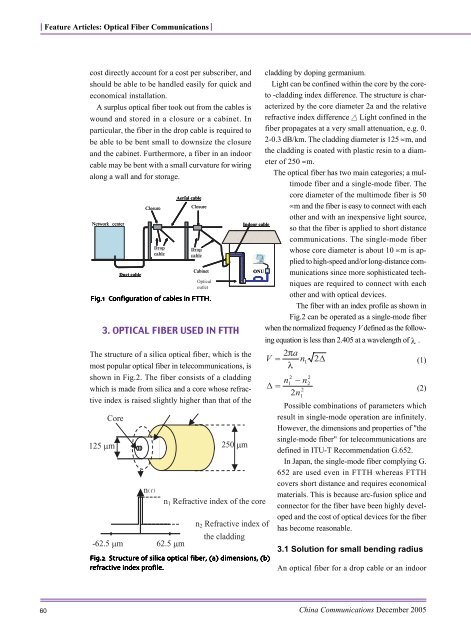
<strong>The</strong> structure of a silica optical fiber, which is the<br />
most popular optical fiber <strong>in</strong> telecommunications, is<br />
shown <strong>in</strong> Fig.2. <strong>The</strong> fiber consists of a cladd<strong>in</strong>g<br />
which is made from silica <strong>and</strong> a core whose refractive<br />
<strong>in</strong>dex is raised slightly higher than that of the<br />
Fig�� Fig�� Fig�� Fig�� Fig�� Structure Structure of of silica silica optical optical fiber� fiber� fiber� fiber� fiber� (a) (a) dimensions� dimensions� dimensions� dimensions� dimensions� (b)<br />
(b)<br />
refractive refractive <strong>in</strong>dex <strong>in</strong>dex profile� profile� profile�<br />
profile� profile�<br />
cladd<strong>in</strong>g by dop<strong>in</strong>g germanium.<br />
Light can be conf<strong>in</strong>ed with<strong>in</strong> the core by the coreto<br />
-cladd<strong>in</strong>g <strong>in</strong>dex difference. <strong>The</strong> structure is characterized<br />
by the core diameter 2a <strong>and</strong> the relative<br />
refractive <strong>in</strong>dex difference Light conf<strong>in</strong>ed <strong>in</strong> the<br />
fiber propagates at a very small attenuation, e.g. 0.<br />
2-0.3 dB/km. <strong>The</strong> cladd<strong>in</strong>g diameter is 125 µm, <strong>and</strong><br />
the cladd<strong>in</strong>g is coated with plastic res<strong>in</strong> to a diameter<br />
of 250 µm.<br />
<strong>The</strong> optical fiber has two ma<strong>in</strong> categories; a multimode<br />
fiber <strong>and</strong> a s<strong>in</strong>gle-mode fiber. <strong>The</strong><br />
core diameter of the multimode fiber is 50<br />
µm <strong>and</strong> the fiber is easy to connect with each<br />
other <strong>and</strong> with an <strong>in</strong>expensive light source,<br />
so that the fiber is applied to short distance<br />
communications. <strong>The</strong> s<strong>in</strong>gle-mode fiber<br />
whose core diameter is about 10 µm is applied<br />
to high-speed <strong>and</strong>/or long-distance communications<br />
s<strong>in</strong>ce more sophisticated techniques<br />
are required to connect with each<br />
other <strong>and</strong> with optical devices.<br />
<strong>The</strong> fiber with an <strong>in</strong>dex profile as shown <strong>in</strong><br />
Fig.2 can be operated as a s<strong>in</strong>gle-mode fiber<br />
when the normalized frequency V def<strong>in</strong>ed as the follow<strong>in</strong>g<br />
equation is less than 2.405 at a wavelength of .<br />
(1)<br />
(2)<br />
Possible comb<strong>in</strong>ations of parameters which<br />
result <strong>in</strong> s<strong>in</strong>gle-mode operation are <strong>in</strong>f<strong>in</strong>itely.<br />
However, the dimensions <strong>and</strong> properties of "the<br />
s<strong>in</strong>gle-mode fiber" <strong>for</strong> telecommunications are<br />
def<strong>in</strong>ed <strong>in</strong> ITU-T Recommendation G.652.<br />
In Japan, the s<strong>in</strong>gle-mode fiber comply<strong>in</strong>g G.<br />
652 are used even <strong>in</strong> FTTH whereas FTTH<br />
covers short distance <strong>and</strong> requires economical<br />
materials. This is because arc-fusion splice <strong>and</strong><br />
connector <strong>for</strong> the fiber have been highly developed<br />
<strong>and</strong> the cost of optical devices <strong>for</strong> the fiber<br />
has become reasonable.<br />
3.1 Solution <strong>for</strong> small bend<strong>in</strong>g radius<br />
An optical fiber <strong>for</strong> a drop cable or an <strong>in</strong>door<br />
Ch<strong>in</strong>a Communications December 2005