AIRY STRESS FUNCTION FOR TWO DIMENSIONAL INCLUSION ...
AIRY STRESS FUNCTION FOR TWO DIMENSIONAL INCLUSION ...
AIRY STRESS FUNCTION FOR TWO DIMENSIONAL INCLUSION ...
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
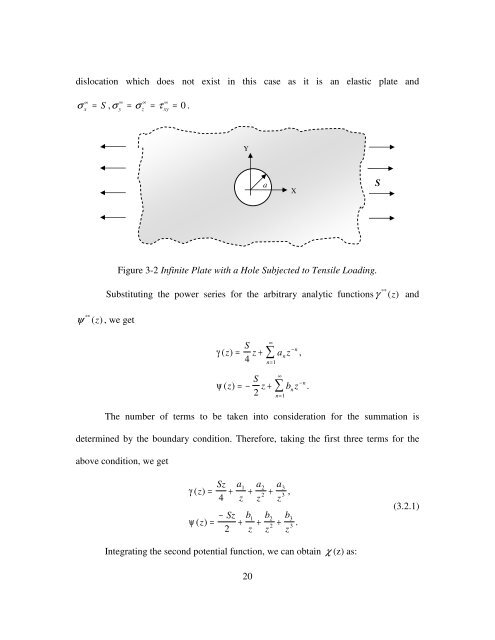
dislocation which does not exist in this case as it is an elastic plate and<br />
σ x<br />
∞ ∞ ∞ ∞<br />
= S ,σ = σ = τ = 0 .<br />
ψ ** ( z ) , we get<br />
y z xy<br />
Figure 3-2 Infinite Plate with a Hole Subjected to Tensile Loading.<br />
Substituting the power series for the arbitrary analytic functionsγ ** ( z) and<br />
∞<br />
S −n<br />
γ ( z)<br />
= z + ∑ an z ,<br />
4<br />
∞<br />
S −n<br />
ψ ( z)<br />
= − z + ∑ bnz .<br />
2<br />
The number of terms to be taken into consideration for the summation is<br />
determined by the boundary condition. Therefore, taking the first three terms for the<br />
above condition, we get<br />
20<br />
n=<br />
1<br />
n=<br />
1<br />
Sz a1<br />
a2<br />
a3<br />
γ ( z)<br />
= + + 2 + 3 ,<br />
4 z z z<br />
Sz b b b<br />
ψ ( z)<br />
= .<br />
z z z<br />
− 1 2 3<br />
+ + 2 + 3<br />
2<br />
Integrating the second potential function, we can obtain χ (z) as:<br />
Y<br />
a<br />
X<br />
S<br />
(3.2.1)