Cloning Protocols and Applications Guide-A4 format - Promega
Cloning Protocols and Applications Guide-A4 format - Promega
Cloning Protocols and Applications Guide-A4 format - Promega
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
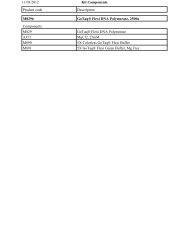
||||||||||||| 13<strong>Cloning</strong><br />
E. Transfer of Protein-Coding Region<br />
Transfer refers to moving your protein-coding region from<br />
one Flexi® Vector (donor) to another Flexi® Vector<br />
(acceptor). Choose an appropriate acceptor vector with the<br />
desired expression <strong>and</strong> tag options <strong>and</strong> a different antibiotic<br />
resistance marker than the donor because antibiotic<br />
selection is the basis for selecting the desired clone<br />
(Figures 13.5, 13.9 <strong>and</strong> 13.10).<br />
There are two basic categories of Flexi® Vectors: those<br />
containing SgfI <strong>and</strong> PmeI sites <strong>and</strong> expressing either a<br />
native (untagged) protein or an N-terminal-tagged protein,<br />
<strong>and</strong> those containing SgfI <strong>and</strong> EcoICRI sites <strong>and</strong> expressing<br />
a C-terminal-tagged protein. Flexi® Vectors for expressing<br />
C-terminal-tagged proteins act only as acceptors, never as<br />
donor vectors. To transfer protein-coding regions between<br />
Flexi® Vectors expressing native protein or an<br />
N-terminal-tagged protein, the donor <strong>and</strong> acceptor vectors<br />
are digested with SgfI <strong>and</strong> PmeI simultaneously, prior to<br />
ligation of the insert, trans<strong>format</strong>ion <strong>and</strong> selection of the<br />
cells (Figure 13.9).<br />
To create a C-terminal-tagged protein, the donor plasmid<br />
expressing native protein or an N-terminal-tagged protein<br />
is digested with SgfI <strong>and</strong> PmeI. Because EcoICRI cuts<br />
frequently in protein-coding regions, the acceptor plasmid<br />
containing the C-terminal tag is digested with SgfI <strong>and</strong><br />
EcoICRI in a separate reaction. The two separate digests<br />
are combined for ligation of the insert, trans<strong>format</strong>ion <strong>and</strong><br />
selection of the cells (Figure 13.10).<br />
<strong>Protocols</strong> & <strong>Applications</strong> <strong>Guide</strong><br />
www.promega.com<br />
rev. 1/12<br />
Figure 13.9. Transfer of a protein-coding region between<br />
N-terminal or native Flexi® Vectors. The donor Flexi® Vector<br />
containing the protein-coding region is mixed with an acceptor<br />
Flexi® Vector that has a different antibiotic resistance. The two<br />
plasmids are digested with SgfI <strong>and</strong> PmeI, <strong>and</strong> the mixture is<br />
ligated <strong>and</strong> transformed into E. coli. The cells are plated on the<br />
appropriate selective medium for the acceptor Flexi® Vector.<br />
Transfer of protein-coding regions into N-terminal fusion vectors<br />
allow translational readthrough of the SgfI site, which encodes the<br />
peptide sequence Ala-Ile-Ala.<br />
PROTOCOLS & APPLICATIONS GUIDE 13-16