Foreword - CCS HAU, Hisar
Foreword - CCS HAU, Hisar
Foreword - CCS HAU, Hisar
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Number and size of samples<br />
Factors such as ease of sampling, accessibility, and time and money available for<br />
sampling should be considered. There are formulae for calculating sample size from the<br />
variance, cost, etc. The purpose of the sample is important. Is it descriptive and qualitative,<br />
or quantitative but only preliminary? Is it to give relative results or an exact economic<br />
assessment on a valuable crop?<br />
Type of sampling : Different types of sampling include randum, satisfied randum, vacuum<br />
sequential, etc.<br />
If the basic statistics of the pest or damage population are known, sequential sampling<br />
is useful in deciding whether or not to control. Sample size depends on the population<br />
found. Upper and lower limits are specified and sampling continued until the number of<br />
pests found goes above or below those limits. The method is described by Onsager (1976).<br />
Sampling techniques for some important crop pests<br />
Some commonly used sampling techniques employed for some of the important crop<br />
pests are summarized in Table 1. However, these may be suitably modified keeping in view<br />
the objectives and degree of precision required.<br />
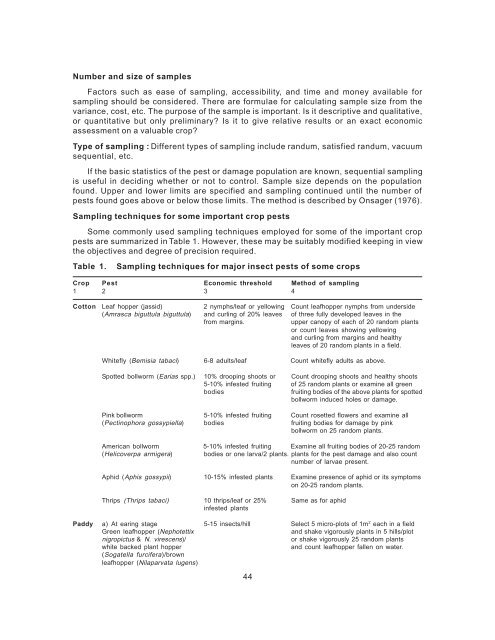
Table 1. Sampling techniques for major insect pests of some crops<br />
Crop Pest Economic threshold Method of sampling<br />
1 2 3 4<br />
Cotton Leaf hopper (jassid) 2 nymphs/leaf or yellowing Count leafhopper nymphs from underside<br />
(Amrasca biguttula biguttula) and curling of 20% leaves of three fully developed leaves in the<br />
from margins. upper canopy of each of 20 random plants<br />
or count leaves showing yellowing<br />
and curling from margins and healthy<br />
leaves of 20 random plants in a field.<br />
Whitefly (Bemisia tabaci) 6-8 adults/leaf Count whitefly adults as above.<br />
Spotted bollworm (Earias spp.) 10% drooping shoots or Count drooping shoots and healthy shoots<br />
5-10% infested fruiting of 25 random plants or examine all green<br />
bodies fruiting bodies of the above plants for spotted<br />
bollworm induced holes or damage.<br />
Pink bollworm 5-10% infested fruiting Count rosetted flowers and examine all<br />
(Pectinophora gossypiella) bodies fruiting bodies for damage by pink<br />
bollworm on 25 random plants.<br />
American bollworm 5-10% infested fruiting Examine all fruiting bodies of 20-25 random<br />
(Helicoverpa armigera) bodies or one larva/2 plants. plants for the pest damage and also count<br />
number of larvae present.<br />
Aphid (Aphis gossypii) 10-15% infested plants Examine presence of aphid or its symptoms<br />
on 20-25 random plants.<br />
Thrips (Thrips tabaci) 10 thrips/leaf or 25% Same as for aphid<br />
infested plants<br />
Paddy a) At earing stage 5-15 insects/hill Select 5 micro-plots of 1m 2 each in a field<br />
Green leafhopper (Nephotettix and shake vigorously plants in 5 hills/plot<br />
nigropictus & N. virescens)/ or shake vigorously 25 random plants<br />
white backed plant hopper and count leafhopper fallen on water.<br />
(Sogatella furcifera)/brown<br />
leafhopper (Nilaparvata lugens)<br />
44