RPD Manual 11 - Removable Prosthodontics - Dalhousie University
RPD Manual 11 - Removable Prosthodontics - Dalhousie University
RPD Manual 11 - Removable Prosthodontics - Dalhousie University
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Surveying, Path of Insertion, Guiding Planes - 23<br />
2. Place composite resin above the position of the retentive tip, using rubber dam isolation.<br />
Place a Mylar matrix to separate the tooth from adjacent teeth. Clean the tooth with flour<br />
of pumice, etch, apply bonding agent and place the composite with plastic instrument.<br />
Place and contour the material as indicated below. Ensure there is adequate undercut<br />
only in the area needed, even after polishing.<br />
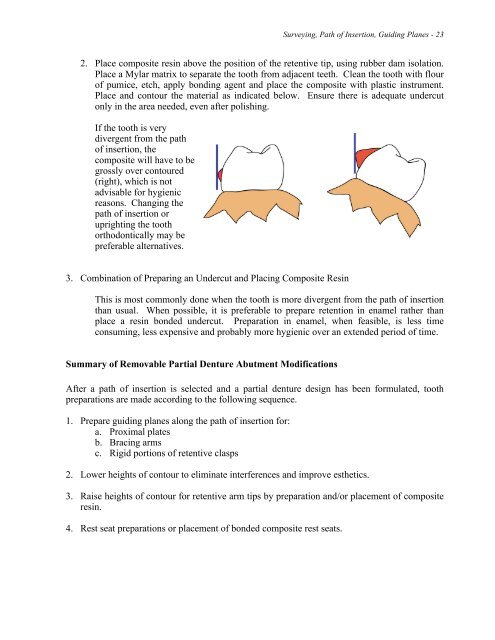
If the tooth is very<br />
divergent from the path<br />
of insertion, the<br />
composite will have to be<br />
grossly over contoured<br />
(right), which is not<br />
advisable for hygienic<br />
reasons. Changing the<br />
path of insertion or<br />
uprighting the tooth<br />
orthodontically may be<br />
preferable alternatives.<br />
3. Combination of Preparing an Undercut and Placing Composite Resin<br />
This is most commonly done when the tooth is more divergent from the path of insertion<br />
than usual. When possible, it is preferable to prepare retention in enamel rather than<br />
place a resin bonded undercut. Preparation in enamel, when feasible, is less time<br />
consuming, less expensive and probably more hygienic over an extended period of time.<br />
Summary of <strong>Removable</strong> Partial Denture Abutment Modifications<br />
After a path of insertion is selected and a partial denture design has been formulated, tooth<br />
preparations are made according to the following sequence.<br />
1. Prepare guiding planes along the path of insertion for:<br />
a. Proximal plates<br />
b. Bracing arms<br />
c. Rigid portions of retentive clasps<br />
2. Lower heights of contour to eliminate interferences and improve esthetics.<br />
3. Raise heights of contour for retentive arm tips by preparation and/or placement of composite<br />
resin.<br />
4. Rest seat preparations or placement of bonded composite rest seats.