I R 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 T 14 15 A
I R 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 T 14 15 A
I R 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 T 14 15 A
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
I<br />
R<br />
T<br />
1<br />
2<br />
3<br />
4<br />
5<br />
6<br />
7<br />
8<br />
9<br />
<strong>10</strong><br />
<strong>11</strong><br />
<strong>12</strong><br />
<strong>13</strong><br />
<strong>14</strong><br />
<strong>15</strong><br />
A<br />
ELEMENTS OF METRIC GEAR TECHNOLOGY<br />
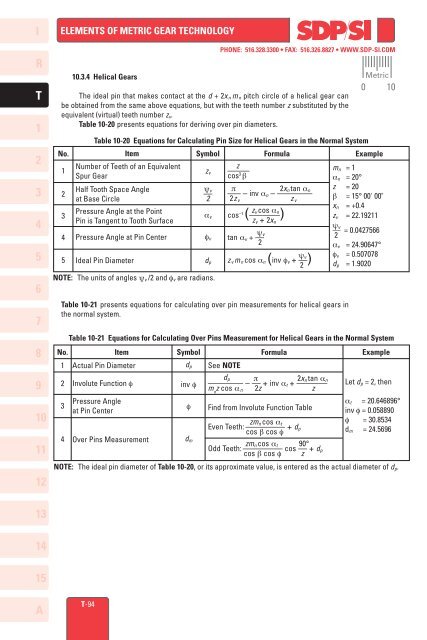
<strong>10</strong>.3.4 Helical Gears<br />
T-94<br />
PHONE: 516.328.3300 • FAX: 516.326.8827 • WWW.SDP-SI.COM<br />
The ideal pin that makes contact at the d + 2x n m n pitch circle of a helical gear can<br />
be obtained from the same above equations, but with the teeth number z substituted by the<br />
equivalent (virtual) teeth number zv.<br />
Table <strong>10</strong>-20 presents equations for deriving over pin diameters.<br />
Table <strong>10</strong>-20 Equations for Calculating Pin Size for Helical Gears in the Normal System<br />
No. Item Symbol<br />
Formula<br />
Example<br />
1<br />
2<br />
3<br />
4<br />
5<br />
Number of Teeth of an Equivalent<br />
Spur Gear<br />
Half Tooth Space Angle<br />
at Base Circle<br />
Pressure Angle at the Point<br />
Pin is Tangent to Tooth Surface<br />
Pressure Angle at Pin Center<br />
Ideal Pin Diameter<br />
NOTE: The units of angles ψv /2 and fv are radians.<br />
zv<br />
ψv<br />
–– 2<br />
av<br />
fv<br />
dp<br />
z<br />
–––––<br />
cos 3 b<br />
p 2xn tan an<br />
––– – inv an – ––––––––<br />
2zv z v<br />
zv cos an<br />
cos –1 (–––––––)<br />
zv + 2xn<br />
ψv<br />
tan av + ––<br />
2<br />
ψv<br />
z v m n cos an (inv fv + ––)<br />
2<br />
Table <strong>10</strong>-21 presents equations for calculating over pin measurements for helical gears in<br />
the normal system.<br />
mn = 1<br />
an = 20°<br />
z = 20<br />
b = <strong>15</strong>° 00' 00"<br />
xn = +0.4<br />
zv = 22.192<strong>11</strong><br />
ψv<br />
–– = 0.0427566<br />
2<br />
av = 24.90647°<br />
fv = 0.507078<br />
dp = 1.9020<br />
Table <strong>10</strong>-21 Equations for Calculating Over Pins Measurement for Helical Gears in the Normal System<br />
No. Item Symbol<br />
Formula<br />
Example<br />
1<br />
2<br />
3<br />
4<br />
Actual Pin Diameter<br />
Involute Function f<br />
Pressure Angle<br />
at Pin Center<br />
Over Pins Measurement<br />
dp<br />
inv f<br />
f<br />
dm<br />
See NOTE<br />
dp p 2xn tan an<br />
–––––––– – –– + inv at + –––––––<br />
m n z cos an 2z z<br />
Find from Involute Function Table<br />
zmn cos at<br />
Even Teeth: ––––––––– + dp<br />
cos b cos f<br />
zmn cos at 90°<br />
Odd Teeth: ––––––––– cos –– + dp<br />
cos b cos f z<br />
Metric<br />
0 <strong>10</strong><br />
Let dp = 2, then<br />
at = 20.646896°<br />
inv f = 0.058890<br />
f = 30.8534<br />
dm = 24.5696<br />
NOTE: The ideal pin diameter of Table <strong>10</strong>-20, or its approximate value, is entered as the actual diameter of dp.