Wheatstone Bridge
Wheatstone Bridge
Wheatstone Bridge
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
Dividing equation 5 by equation 1 gives<br />
Now and solving for R m we get<br />
R3 m R<br />
= (6)<br />
R R<br />
1 2<br />
R2<br />
Rm = R3<br />
(6)<br />
R<br />
Typically, 1 R and 2 R are fixed resistors and 3 R is a variable resistor. R m is the resistance that<br />
is being measured. R 3 is adjusted until the detector indicates that the bridge is balanced. Then<br />
the value of R m is determined using equation 6.<br />
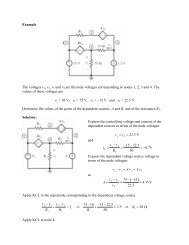
Example<br />
Consider using a <strong>Wheatstone</strong> bridge having R 1 = 200 Ω and R 2 = 2000 Ω to measure a<br />
resistance R m . The bridge is balanced by adjusting 3 R until R 3 = 250 Ω . What is the value of<br />
R m ?<br />
Solution<br />
From equation 6<br />
R2<br />
2000<br />
Rm= R3=<br />
250 = 2500 Ω<br />
R 200<br />
1<br />
Example<br />
Consider using a <strong>Wheatstone</strong> bridge having R 1 = 200 Ω and R 2 = 2000 Ω to measure a<br />
resistance, R m , of a temperature sensor. Suppose the resistance of the temperature sensor, R m ,<br />
in Ω, is related to the temperature T, in °C, by the equation<br />
R = 1500 + 25T<br />
m<br />
The bridge is balanced by adjusting 3 R until R 3 = 250 Ω . What is the value of the temperature?<br />
Solution<br />
From equation 6<br />
Next, the temperature in °C is given by<br />
R2<br />
2000<br />
Rm= R3=<br />
250 = 2500 Ω<br />
R 200<br />
1<br />
m 1500 R − 2500 −1500<br />
1000<br />
T = = = = 40 ° C<br />
25 25 25<br />
1<br />
2