Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
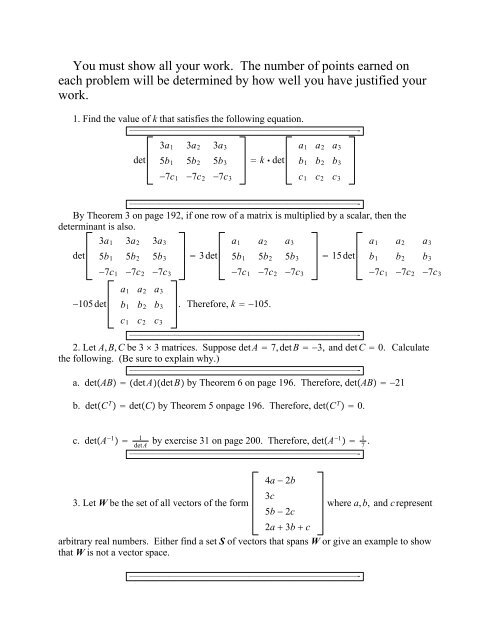
You must show all your work. The number of points earned on<br />
each problem will be determined by how well you have justified your<br />
work.<br />
1. Find the value of k that satisfies the following equation.<br />
———————————————————————-<br />
det<br />
3a1 3a2 3a3<br />
5b1 5b2 5b3<br />
7c1 7c2 7c3<br />
k det<br />
a1 a2 a3<br />
b1 b2 b3<br />
c1 c2 c3<br />
———————————————————————-<br />
By Theorem 3 on page 192, if one row of a matrix is multiplied by a scalar, then the<br />
determinant is also.<br />
3a1 3a2 3a3<br />
a1 a2 a3<br />
det 5b1 5b2 5b3 3det 5b1 5b2 5b3 15det<br />
105det<br />
7c1 7c2 7c3<br />
a1 a2 a3<br />
b1 b2 b3<br />
c1 c2 c3<br />
7c1 7c2 7c3<br />
. Therefore, k 105.<br />
a1 a2 a3<br />
b1 b2 b3<br />
7c1 7c2 7c3<br />
———————————————————————-<br />
2. Let A,B,C be 3 3 matrices. Suppose detA 7,detB 3, and detC 0. Calculate<br />
the following. (Be sure to explain why.)<br />
———————————————————————a.<br />
detAB detAdetB by Theorem 6 on page 196. Therefore, detAB 21<br />
b. detC T detC by Theorem 5 onpage 196. Therefore, detC T 0.<br />
c. detA 1 1<br />
det A by exercise 31 on page 200. Therefore, detA1 1<br />
7 .<br />
———————————————————————-<br />
3. Let W be the set of all vectors of the form<br />
4a 2b<br />
3c<br />
5b 2c<br />
2a 3b c<br />
where a,b, andcrepresent<br />
arbitrary real numbers. Either find a set S of vectors that spans W or give an example to show<br />
that W is not a vector space.<br />
———————————————————————-
The set W can be written as<br />
4a 2b<br />
3c<br />
5b 2c<br />
2a 3b c<br />
4 2 0<br />
Let S <br />
0<br />
0<br />
,<br />
0<br />
5<br />
,<br />
3<br />
2<br />
. Since a,b, andcrepresent arbitrary real<br />
2 3 1<br />
numbers, W is a set of all linear combinations the vectors in S or the span of the vectors in S.<br />
a<br />
4<br />
0<br />
0<br />
2<br />
b<br />
2<br />
0<br />
5<br />
3<br />
———————————————————————-<br />
4. Prove that the set of all vectors of the form a<br />
1<br />
1<br />
0<br />
b<br />
subspace of 3 . Use the definition of subspace on page 220.<br />
i) 0 0<br />
1<br />
1<br />
0<br />
ii) Let u a1<br />
0<br />
1<br />
0<br />
———————————————————————-<br />
0<br />
1<br />
1<br />
0<br />
0<br />
1<br />
0<br />
b1<br />
so the zero vector is in the given set.<br />
0<br />
1<br />
0<br />
and v a2<br />
1 0<br />
1 0<br />
a1 1 b1 1 a2 1 b2 1<br />
0 0<br />
0 0<br />
which has the required form. So, u v is in the required set.<br />
1 0<br />
iii) u a 1 b 1 . Then<br />
0 0<br />
2<br />
1<br />
1<br />
0<br />
b2<br />
0<br />
1<br />
0<br />
c<br />
0<br />
3<br />
2<br />
1<br />
,a,b , forms a<br />
a1 a2<br />
. Then u v <br />
1<br />
1<br />
0<br />
.<br />
b1
1 0<br />
1 0<br />
ku k a 1 b 1 ak 1 bk 1<br />
0 0<br />
0 0<br />
which again has the required form. So, ku is in the required set.<br />
By the definition on page 220 the set is a subset of 3 .<br />
———————————————————————-<br />
2 4<br />
0<br />
5. Let A <br />
and w .<br />
1 7<br />
9<br />
———————————————————————-<br />
Is w in NulA?<br />
Aw <br />
NulA.<br />
2 4<br />
1 7<br />
Is w in ColA?<br />
0<br />
9<br />
36<br />
63<br />
. Since the product is not the zero vector, w is not in<br />
Solving the equation Ax b or x we write the augmented matrix:<br />
1 0 2<br />
0 1 1<br />
. Since the system is consistent w is in ColA.<br />
———————————————————————-<br />
2 4 0<br />
1 7 9<br />
6. Assume that A is row equivalent to B. Find bases for NulA and ColA.<br />
5 15 2 26 3<br />
1 3 0 4 1<br />
A 2 6 0 8 2 , B 0 0 1 3 4<br />
1 3 8 28 31<br />
0 0 0 0 0<br />
———————————————————————-<br />
AbasisforNulA :<br />
3
x2<br />
1 3 0 4 1<br />
0 0 1 3 4<br />
0 0 0 0 0<br />
3<br />
1<br />
0<br />
0<br />
0<br />
x4<br />
4<br />
0<br />
3<br />
1<br />
0<br />
<br />
x5<br />
Therefore the nullspace basis is<br />
x1<br />
x2<br />
x3<br />
x4<br />
x5<br />
1<br />
0<br />
4<br />
0<br />
1<br />
<br />
.<br />
3x2 4x4 x5<br />
x2<br />
3x4 4x5<br />
x4<br />
x5<br />
3 4<br />
1 0<br />
0 , 3 ,<br />
0 1<br />
0 0<br />
AbasisofColA :<br />
Since there are pivots in columns 1 and 3, we choose columns 1 and 3 from A to form the<br />
basis of ColA.<br />
5 2<br />
That is ColA 2 , 0<br />
1 8<br />
———————————————————————-<br />
7. The set B 1,1 t,t t2 ,t t3is a basis for P3 . Find the coordinate vector of<br />
pt 2t t2 8t3 .<br />
———————————————————————-<br />
The change of coordinate matrix, PB <br />
x B ,weusetheaugmentedmatrix<br />
4<br />
1<br />
0<br />
4<br />
0<br />
1<br />
1 1 0 0<br />
0 1 1 1<br />
0 0 1 0<br />
0 0 0 1<br />
1 1 0 0 0<br />
0 1 1 1 2<br />
0 0 1 0 1<br />
0 0 0 1 8<br />
<br />
<br />
. To find the coordinate vector<br />
1 0 0 0 5<br />
0 1 0 0 5<br />
0 0 1 0 1<br />
0 0 0 1 8<br />
.
Therefore, x B <br />
5<br />
5<br />
1<br />
8<br />
———————————————————————-<br />
8.<br />
———————————————————————a.<br />
Suppose a 5 8matrixAhas 5 pivot columns.<br />
What is dimNulA? There are 3 free variables and therefore dimNulA 3.<br />
What is rankA? Since there are 5 pivot columns rankA 5.<br />
b. The null space of a 20 18 matrix A is 10-dimensional.<br />
What is the dimension of ColA?<br />
Since there are 18 columns, i.e., n 18, rankA n dimNulA 18 10 8.<br />
c. If A is a 200 50 matrix, what is the largest possible dimension of the row space?<br />
By Theorem 14, the Rank Theorem, the dimension of the column space equals the<br />
dimension of the row space. There are at most 50 pivots, so the largest dimension of the<br />
column and row spaces is 50.<br />
What is the smallest possible dimension of NulA?<br />
Since the greatest dimension of the column space is 50, and<br />
rankA dimNulA n 50, the smallest possible dimension of NulA 0.<br />
d. A 38 50 matrix A has rank 30.<br />
Find dimNulA.<br />
By the Rank Theorem, rankA dimNulA n <br />
30 dimNulA 50 dimNulA 20.<br />
Find dimRowA.<br />
By the Rank Theorem, the dimension of the column space equals the dimension of the row<br />
space. This implies RowA 30.<br />
Find RankA T .<br />
RankA T dimColA T dimRowA 30.<br />
5<br />
Explain all.