General Introduction to In Situ Hybridization
General Introduction to In Situ Hybridization
General Introduction to In Situ Hybridization
You also want an ePaper? Increase the reach of your titles
YUMPU automatically turns print PDFs into web optimized ePapers that Google loves.
Procedures for <strong>In</strong> <strong>Situ</strong> <strong>Hybridization</strong> <strong>to</strong> Chromosomes, Cells, and Tissue Sections<br />
ISH <strong>to</strong> whole chromosomes<br />
<br />
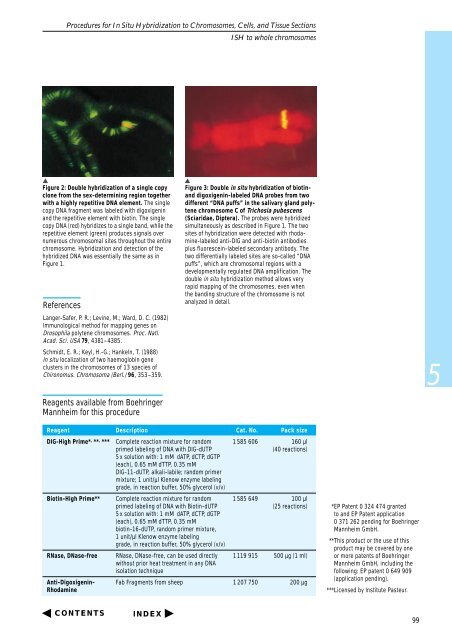
Figure 2: Double hybridization of a single copy<br />
clone from the sex-determining region <strong>to</strong>gether<br />
with a highly repetitive DNA element. The single<br />
copy DNA fragment was labeled with digoxigenin<br />
and the repetitive element with biotin. The single<br />
copy DNA (red) hybridizes <strong>to</strong> a single band, while the<br />
repetitive element (green) produces signals over<br />
numerous chromosomal sites throughout the entire<br />
chromosome. <strong>Hybridization</strong> and detection of the<br />
hybridized DNA was essentially the same as in<br />
Figure 1.<br />
References<br />
Langer-Safer, P. R.; Levine, M.; Ward, D. C. (1982)<br />
Immunological method for mapping genes on<br />
Drosophila polytene chromosomes. Proc. Natl.<br />
Acad. Sci. USA 79, 4381–4385.<br />
Schmidt, E. R.; Keyl, H.-G.; Hankeln, T. (1988)<br />
<strong>In</strong> situ localization of two haemoglobin gene<br />
clusters in the chromosomes of 13 species of<br />
Chironomus. Chromosoma (Berl.) 96, 353–359.<br />
Reagents available from Boehringer<br />
Mannheim for this procedure<br />
Reagent Description Cat. No. Pack size<br />
DIG-High Prime* , ** , *** Complete reaction mixture for random 1 585 606 160 µl<br />
primed labeling of DNA with DIG-dUTP<br />
5 x solution with: 1 mM dATP, dCTP, dGTP<br />
(each), 0.65 mM dTTP, 0.35 mM<br />
DIG-11-dUTP, alkali-labile; random primer<br />
mixture; 1 unit/µl Klenow enzyme labeling<br />
grade, in reaction buffer, 50% glycerol (v/v)<br />
(40 reactions)<br />
Biotin-High Prime** Complete reaction mixture for random 1 585 649 100 µl<br />
primed labeling of DNA with Biotin-dUTP (25 reactions)<br />
5 x solution with: 1 mM dATP, dCTP, dGTP<br />
(each), 0.65 mM dTTP, 0.35 mM<br />
biotin-16-dUTP, random primer mixture,<br />
1 unit/µl Klenow enzyme labeling<br />
grade, in reaction buffer, 50% glycerol (v/v)<br />
RNase, DNase-free RNase, DNase-free, can be used directly 1119 915 500 µg (1 ml)<br />
without prior heat treatment in any DNA<br />
isolation technique<br />
Anti-Digoxigenin- Fab Fragments from sheep 1 207 750 200 µg<br />
Rhodamine<br />
CONTENTS<br />
INDEX<br />
Figure 3: Double in situ hybridization of biotinand<br />
digoxigenin-labeled DNA probes from two<br />
different “DNA puffs” in the salivary gland polytene<br />
chromosome C of Trichosia pubescens<br />
(Sciaridae, Diptera). The probes were hybridized<br />
simultaneously as described in Figure 1. The two<br />
sites of hybridization were detected with rhodamine-labeled<br />
anti-DIG and anti-biotin antibodies<br />
plus fluorescein-labeled secondary antibody. The<br />
two differentially labeled sites are so-called “DNA<br />
puffs”, which are chromosomal regions with a<br />
developmentally regulated DNA amplification. The<br />
double in situ hybridization method allows very<br />
rapid mapping of the chromosomes, even when<br />
the banding structure of the chromosome is not<br />
analyzed in detail.<br />
***EP Patent 0 324 474 granted<br />
<strong>to</strong> and EP Patent application<br />
0 371 262 pending for Boehringer<br />
Mannheim GmbH.<br />
***This product or the use of this<br />
product may be covered by one<br />
or more patents of Boehringer<br />
Mannheim GmbH, including the<br />
following: EP patent 0 649 909<br />
(application pending).<br />
***Licensed by <strong>In</strong>stitute Pasteur.<br />
99<br />
5