Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
tertiary-aged Igneous occurrences<br />
Leucite Hills<br />
The Leucite Hills <strong>in</strong> the Green River Bas<strong>in</strong> make<br />
up one of the largest lamproite fields <strong>in</strong> the world<br />
(Hausel, 2006). Lamproites are ultrapotassic, mafic<br />
to ultramafic volcanic and subvolcanic rocks that<br />
can be extremely enriched <strong>in</strong> the LREE (Kuehner,<br />
1980; Ogden, 1979). Notable REE occurrences <strong>in</strong><br />
the Leucite Hills are located on Zirkel Mesa, Pilot<br />
Butte, and South Table Mounta<strong>in</strong> (table 13). Detailed<br />
descriptions of the geology and geochemistry<br />
of the Leucite Hills are available <strong>in</strong> WSGS Report<br />
of Investigations 56 (Hausel, 2006).<br />
Zirkel Mesa, NE¼NW¼ sec. 24, T. 22 N., R.<br />
102 W., Northwestern Sweetwater County<br />
Zirkel Mesa is the largest exposure of lamproite <strong>in</strong><br />
the Leucite Hills, and is dom<strong>in</strong>antly composed of<br />
orendite, a diopside-sanid<strong>in</strong>e-phlogopite lamproite<br />
(Hausel, 2006). Wyom<strong>in</strong>gite (diopside-leucitephlogopite<br />
lamproite) from Zirkel Mesa (Sample<br />
ZM1-WY) is enriched <strong>in</strong> the LREE, europium,<br />
gadol<strong>in</strong>ium, terbium, and dysprosium; lanthanum<br />
and cerium are enriched to greater than five times<br />
crustal abundance.<br />
Pilot Butte, SE¼NE¼ sec. 10, T. 19 N., R. 106<br />
W., Northwestern Sweetwater County<br />
The Pilot Butte lamproite consists of a volcanic<br />
neck, a s<strong>in</strong>gle lobate lava flow, and two associated<br />
small dikes exposed on the southwest flank of the<br />
butte. The volcanic and subvolcanic rocks on Pilot<br />
Butte are dom<strong>in</strong>antly madupite (diopside-phlogopite-leucite<br />
lamproite) with Green River Formation<br />
39<br />
xenoliths (Hausel, 2006). The Pilot Butte madupite<br />
(Sample PB1-95) is enriched <strong>in</strong> the LREE, europium,<br />
gadol<strong>in</strong>ium, terbium, and dysprosium; La,<br />
Ce, Pr, Nd, and Sm are enriched to greater than<br />
five times crustal abundance.<br />
South Table Mounta<strong>in</strong>, SE¼SW¼ sec. 6, T. 22<br />
N., R. 102 W., Northwestern Sweetwater County<br />
South Table Mounta<strong>in</strong> is composed of oliv<strong>in</strong>e orendite,<br />
and wyom<strong>in</strong>gite. The oliv<strong>in</strong>e orendite (Sample<br />
STM-1-2010) is enriched <strong>in</strong> LREE, europium,<br />
gadol<strong>in</strong>ium, and terbium; only cerium is enriched<br />
to greater than five times crustal abundance.<br />
sediment-hosted occurrences<br />
Important REE occurrences <strong>in</strong> Wyom<strong>in</strong>g are<br />
hosted <strong>in</strong> a number of sedimentary environments.<br />
These <strong>in</strong>clude fossil beach placers (paleoplacers)<br />
with<strong>in</strong> marg<strong>in</strong>al mar<strong>in</strong>e sandstones, uranium- and<br />
phosphate-rich horizons <strong>in</strong> Eocene lacustr<strong>in</strong>e<br />
deposits <strong>in</strong> southwestern Wyom<strong>in</strong>g, and phosphorite<br />
beds <strong>in</strong> western Wyom<strong>in</strong>g (K<strong>in</strong>g and Harris,<br />
2002). M<strong>in</strong>or REE occurrences are also present<br />
with<strong>in</strong> phosphate concretions <strong>in</strong> the Bighorn Bas<strong>in</strong><br />
and <strong>in</strong> alteration zones associated with reductionoxidation<br />
fronts <strong>in</strong> central Wyom<strong>in</strong>g.<br />
Paleoplacers may host REE-bear<strong>in</strong>g m<strong>in</strong>erals, such<br />
as monazite, zircon, and apatite. The Cambrian<br />
Flathead Sandstone and the Cretaceous Mesaverde<br />
Formation are the most notable REE-bear<strong>in</strong>g<br />
paleoplacers <strong>in</strong> Wyom<strong>in</strong>g; m<strong>in</strong>or paleoplacers are<br />
also found <strong>in</strong> the Cretaceous Frontier Formation<br />
(fig. 13). Quaternary alluvial deposits host placers<br />
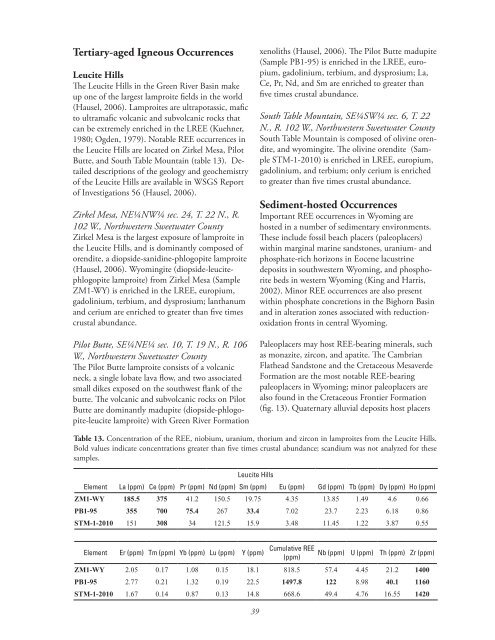
table 13. Concentration of the REE, niobium, uranium, thorium and zircon <strong>in</strong> lamproites from the Leucite Hills.<br />
Bold values <strong>in</strong>dicate concentrations greater than five times crustal abundance; scandium was not analyzed for these<br />
samples.<br />
Element La (ppm) Ce (ppm)<br />
Leucite Hills<br />
Pr (ppm) Nd (ppm) Sm (ppm) Eu (ppm) Gd (ppm) Tb (ppm) Dy (ppm) Ho (ppm)<br />
ZM1-WY 185.5 375 41.2 150.5 19.75 4.35 13.85 1.49 4.6 0.66<br />
PB1-95 355 700 75.4 267 33.4 7.02 23.7 2.23 6.18 0.86<br />
STM-1-2010 151 308 34 121.5 15.9 3.48 11.45 1.22 3.87 0.55<br />
Element Er (ppm) Tm (ppm) Yb (ppm) Lu (ppm) Y (ppm)<br />
Cumulative REE<br />
(ppm)<br />
Nb (ppm) U (ppm) Th (ppm) Zr (ppm)<br />
ZM1-WY 2.05 0.17 1.08 0.15 18.1 818.5 57.4 4.45 21.2 1400<br />
PB1-95 2.77 0.21 1.32 0.19 22.5 1497.8 122 8.98 40.1 1160<br />
STM-1-2010 1.67 0.14 0.87 0.13 14.8 668.6 49.4 4.76 16.55 1420