pathology services handbook - St George's Healthcare NHS Trust
pathology services handbook - St George's Healthcare NHS Trust
pathology services handbook - St George's Healthcare NHS Trust
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
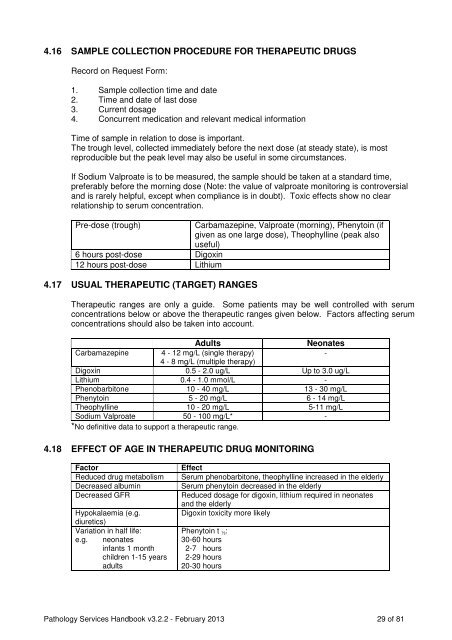
4.16 SAMPLE COLLECTION PROCEDURE FOR THERAPEUTIC DRUGS<br />
Record on Request Form:<br />
1. Sample collection time and date<br />
2. Time and date of last dose<br />
3. Current dosage<br />
4. Concurrent medication and relevant medical information<br />
Time of sample in relation to dose is important.<br />
The trough level, collected immediately before the next dose (at steady state), is most<br />
reproducible but the peak level may also be useful in some circumstances.<br />
If Sodium Valproate is to be measured, the sample should be taken at a standard time,<br />
preferably before the morning dose (Note: the value of valproate monitoring is controversial<br />
and is rarely helpful, except when compliance is in doubt). Toxic effects show no clear<br />
relationship to serum concentration.<br />
Pre-dose (trough) Carbamazepine, Valproate (morning), Phenytoin (if<br />
given as one large dose), Theophylline (peak also<br />
useful)<br />
6 hours post-dose Digoxin<br />
12 hours post-dose Lithium<br />
4.17 USUAL THERAPEUTIC (TARGET) RANGES<br />
Therapeutic ranges are only a guide. Some patients may be well controlled with serum<br />
concentrations below or above the therapeutic ranges given below. Factors affecting serum<br />
concentrations should also be taken into account.<br />
Adults Neonates<br />
Carbamazepine 4 - 12 mg/L (single therapy)<br />
4 - 8 mg/L (multiple therapy)<br />
-<br />
Digoxin 0.5 - 2.0 ug/L Up to 3.0 ug/L<br />
Lithium 0.4 - 1.0 mmol/L -<br />
Phenobarbitone 10 - 40 mg/L 13 - 30 mg/L<br />
Phenytoin 5 - 20 mg/L 6 - 14 mg/L<br />
Theophylline 10 - 20 mg/L 5-11 mg/L<br />
Sodium Valproate 50 - 100 mg/L* -<br />
*No definitive data to support a therapeutic range.<br />
4.18 EFFECT OF AGE IN THERAPEUTIC DRUG MONITORING<br />
Factor Effect<br />
Reduced drug metabolism Serum phenobarbitone, theophylline increased in the elderly<br />
Decreased albumin Serum phenytoin decreased in the elderly<br />
Decreased GFR Reduced dosage for digoxin, lithium required in neonates<br />
and the elderly<br />
Hypokalaemia (e.g. Digoxin toxicity more likely<br />
diuretics)<br />
Variation in half life:<br />
e.g. neonates<br />
infants 1 month<br />
children 1-15 years<br />
adults<br />
Phenytoin t ½:<br />
30-60 hours<br />
2-7 hours<br />
2-29 hours<br />
20-30 hours<br />
Pathology Services Handbook v3.2.2 - February 2013 29 of 81