Solenoid Worksheet - MAELabs UCSD
Solenoid Worksheet - MAELabs UCSD
Solenoid Worksheet - MAELabs UCSD
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
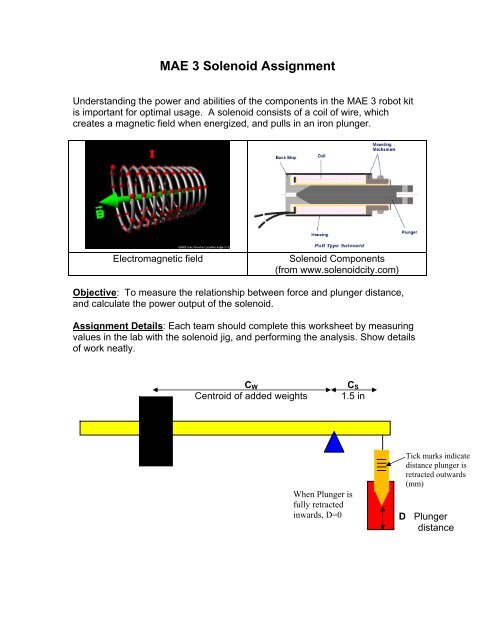
MAE 3 <strong>Solenoid</strong> Assignment<br />
Understanding the power and abilities of the components in the MAE 3 robot kit<br />
is important for optimal usage. A solenoid consists of a coil of wire, which<br />
creates a magnetic field when energized, and pulls in an iron plunger.<br />
Electromagnetic field <strong>Solenoid</strong> Components<br />
(from www.solenoidcity.com)<br />
Objective: To measure the relationship between force and plunger distance,<br />
and calculate the power output of the solenoid.<br />
Assignment Details: Each team should complete this worksheet by measuring<br />
values in the lab with the solenoid jig, and performing the analysis. Show details<br />
of work neatly.<br />
CW<br />
Centroid of added weights<br />
When Plunger is<br />
fully retracted<br />
inwards, D=0<br />
CS<br />
1.5 in<br />
Tick marks indicate<br />
distance plunger is<br />
retracted outwards<br />
(mm)<br />
D Plunger<br />
distance
Instructions:<br />
1. Plug the solenoid into the constant 5 VDC power source and turn the<br />
power source on.<br />
2. Set the gap adjustment screw and measure the plunger distance.<br />
3. Add weights onto the lever arm and slide them until the plunger is pulled<br />
out. Note, the lever itself is balanced, so only the added weight contributes<br />
to forces on the solenoid.<br />
4. Measure at least 4 gap distances, and record values in table below.<br />
5. Turn power source off.<br />
6. Calculate force on plunger using the moment balance equations below.<br />
Use the metric system so that the energy and power calculations provides<br />
Joules and Watts.<br />
Variable Description 1 2 3 4<br />
D Plunger Distance (m)<br />
Mw Total mass of added<br />
weights (g)<br />
Centroid of added<br />
Cw<br />
weights (m)<br />
CwMwag Moment of added<br />
weights (Nm)<br />
CwMwag/Cs Force on Plunger (N)<br />
**** cs = <strong>Solenoid</strong> moment arm = 1.5in = 38.1 mm<br />
ag = Acceleration due to gravity = 9.8 m/s 2<br />
7. Plot <strong>Solenoid</strong> Force vs. Plunger gap
8. Estimate energy output that occurs in a single activation of solenoid, which<br />
is the area under the curve. Use either a single triangle or the trapezoid<br />
method to estimate this area.<br />
9. To calculate power, estimate retraction time as due to an average force<br />
acting on the mass of the plunger. This is a rough estimate since the<br />
acceleration is not constant, but it will give you a ball park number.<br />
Variable Description Equation<br />
h Maximum Plunger Gap that can<br />
retract solenoid<br />
h<br />
a Average Acceleration a= average force*/mass<br />
of plunger<br />
t Retraction time t= sqrt(2h/a)<br />
*Estimate the average from the plot <strong>Solenoid</strong> Force vs. Plunger gap.