Undirected graphs and networks
Undirected graphs and networks
Undirected graphs and networks
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
172 General Mathematics<br />
Hamiltonian paths <strong>and</strong> circuits<br />
Eulerian paths are used when we need to find a way to travel along each edge only<br />
once. This is useful in areas such as postal or delivery routes <strong>and</strong> garbage collections.<br />
However, there are occasions when we are interested in travelling to each vertex only<br />
once, but it is not important that we travel along each edge.<br />
For example, if the vertices are five tourist areas to be visited in<br />
a town, we may be interested in visiting each area (vertex) but not<br />
in travelling along each road. A path that passes through each<br />
vertex once is called a Hamiltonian path (named after Sir William<br />
Hamilton [1805–65], a Scottish mathematician). A Hamiltonian<br />
path must pass through each vertex once, but does not have to use each edge. Usually<br />
all of the edges are not required to draw a Hamiltonian path.<br />
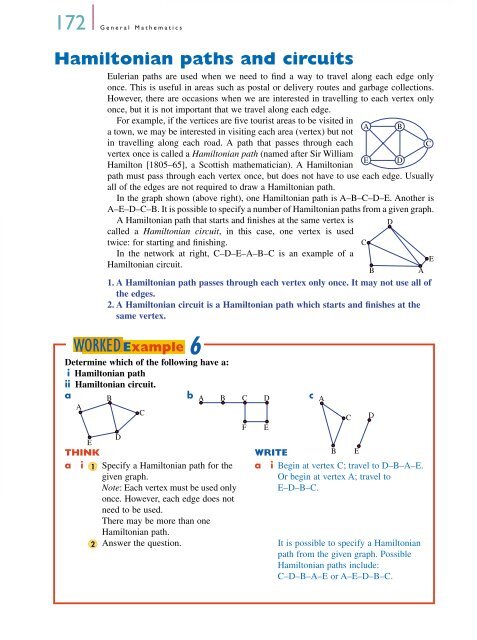
In the graph shown (above right), one Hamiltonian path is A–B–C–D–E. Another is<br />
A–E–D–C–B. It is possible to specify a number of Hamiltonian paths from a given graph.<br />
A Hamiltonian path that starts <strong>and</strong> finishes at the same vertex is<br />
called a Hamiltonian circuit, in this case, one vertex is used<br />
twice: for starting <strong>and</strong> finishing.<br />
In the network at right, C–D–E–A–B–C is an example of a<br />
Hamiltonian circuit.<br />
A B<br />
E D<br />
B A<br />
1. A Hamiltonian path passes through each vertex only once. It may not use all of<br />
the edges.<br />
2. A Hamiltonian circuit is a Hamiltonian path which starts <strong>and</strong> finishes at the<br />
same vertex.<br />
WORKED Example<br />
6<br />
Determine which of the following have a:<br />
i Hamiltonian path<br />
ii Hamiltonian circuit.<br />
a B b A B C D c A<br />
A<br />
C<br />
C D<br />
F E<br />
E<br />
D<br />
THINK WRITE<br />
B E<br />
a i 1 Specify a Hamiltonian path for the a i Begin at vertex C; travel to D–B–A–E.<br />
given graph.<br />
Or begin at vertex A; travel to<br />
Note: Each vertex must be used only<br />
once. However, each edge does not<br />
need to be used.<br />
There may be more than one<br />
Hamiltonian path.<br />
E–D–B–C.<br />
2 Answer the question. It is possible to specify a Hamiltonian<br />
path from the given graph. Possible<br />
Hamiltonian paths include:<br />
C–D–B–A–E or A–E–D–B–C.<br />
C<br />
D<br />
C<br />
E