Chapter 1 Quantum kinetic equations: an introduction
Chapter 1 Quantum kinetic equations: an introduction
Chapter 1 Quantum kinetic equations: an introduction
Create successful ePaper yourself
Turn your PDF publications into a flip-book with our unique Google optimized e-Paper software.
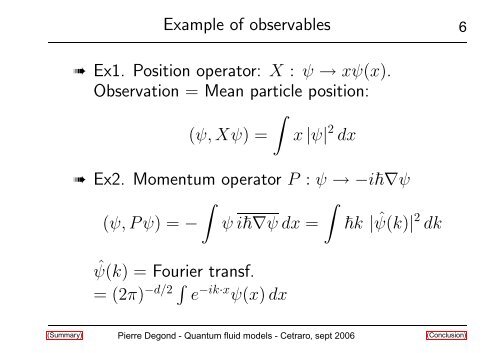
Example of observables<br />
➠ Ex1. Position operator: X : ψ → xψ(x).<br />
Observation = Me<strong>an</strong> particle position:<br />
<br />
(ψ, Xψ) = x |ψ| 2 dx<br />
➠ Ex2. Momentum operator P : ψ → −i∇ψ<br />
<br />
(ψ, Pψ) = − ψ i∇ψ dx = k | ˆ ψ(k)| 2 dk<br />
ˆψ(k) = Fourier tr<strong>an</strong>sf.<br />
= (2π) −d/2 e −ik·x ψ(x)dx<br />
(Summary) Pierre Degond - <strong>Qu<strong>an</strong>tum</strong> fluid models - Cetraro, sept 2006<br />
(Conclusion)<br />
6